J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2002 Jun;9(2):133-142.
The Relationship between Sagittal Spinal Alignment and Surgical Results in Degenerative Lumbar Scoliosis with Spinal Stenosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Eulji University, Taejon, Korea. ortho@hananet.net
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Cheongju St. Mary's Hospital, Korea.
- 3Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kon-Kuk University Hospital, Chungju, Korea.
Abstract
-
STUDY DESIGN: A retrospective study.
OBJECTIVES
To analyze the correlation between clinical results and sagittal vertical axis, clinical results and total lumbar lordosis in degenerative lumbar scoliosis with spinal stenosis. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: There has been no report about the relation between sagittal spinal alignment and surgical outcome of degenerative lumbar scoliosis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We reviewed 38 surgical cases of degenerative lumbar scoliosis from February 1997 to February 2001 with an average follow-up of 35 months. In whole spine standing AP and lateral radiographs, scoliotic angle(Cobb method), total lumbar lordosis(L1-S1) and the sagittal vertical axis(C7 plumb line) were measured. In lumbar flexion-extension and standing side bending views, the lateral translation was measured and instability was determined. Clinical results were evaluated based on the Kirkaldy-Willis criteria.
RESULTS
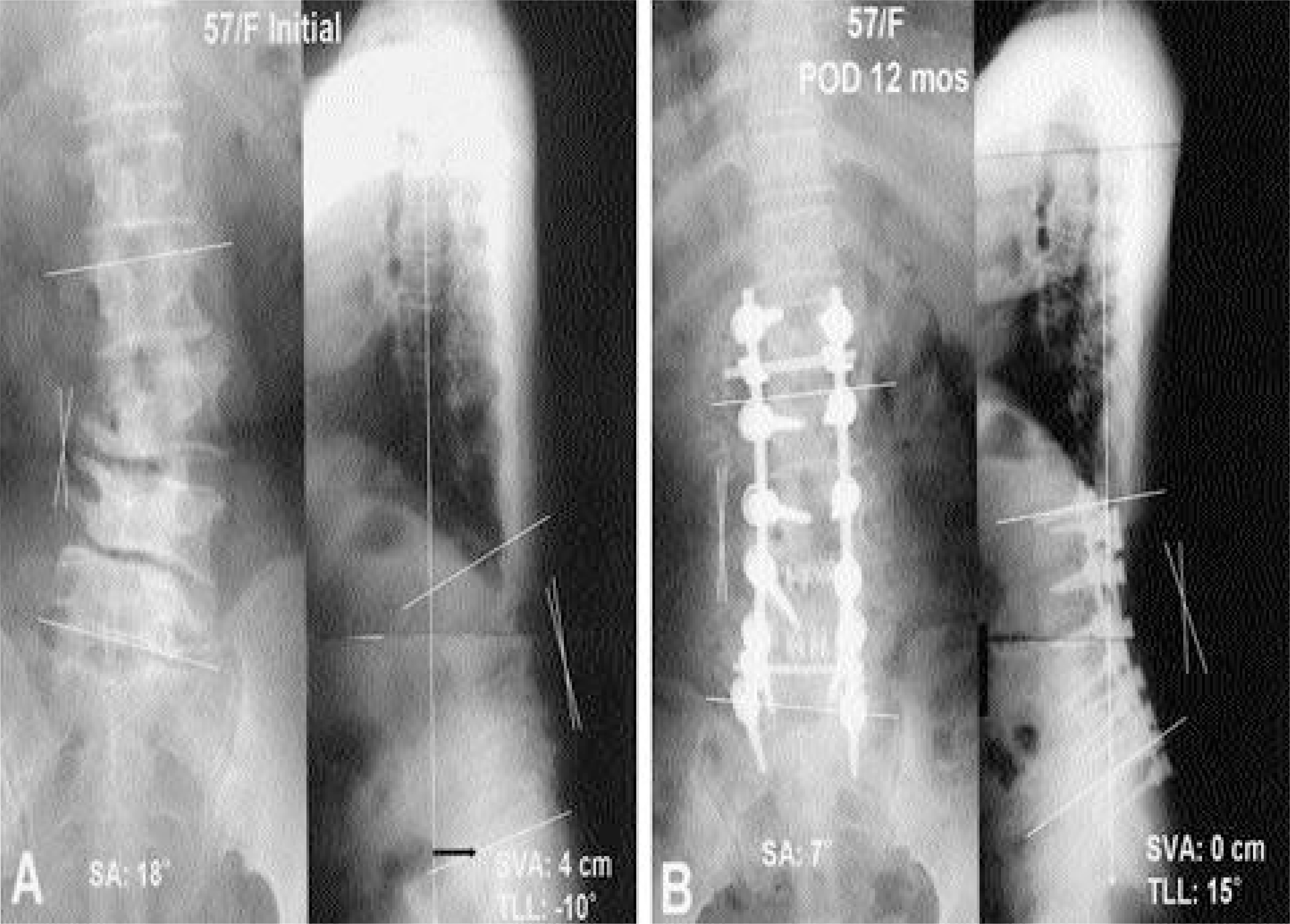
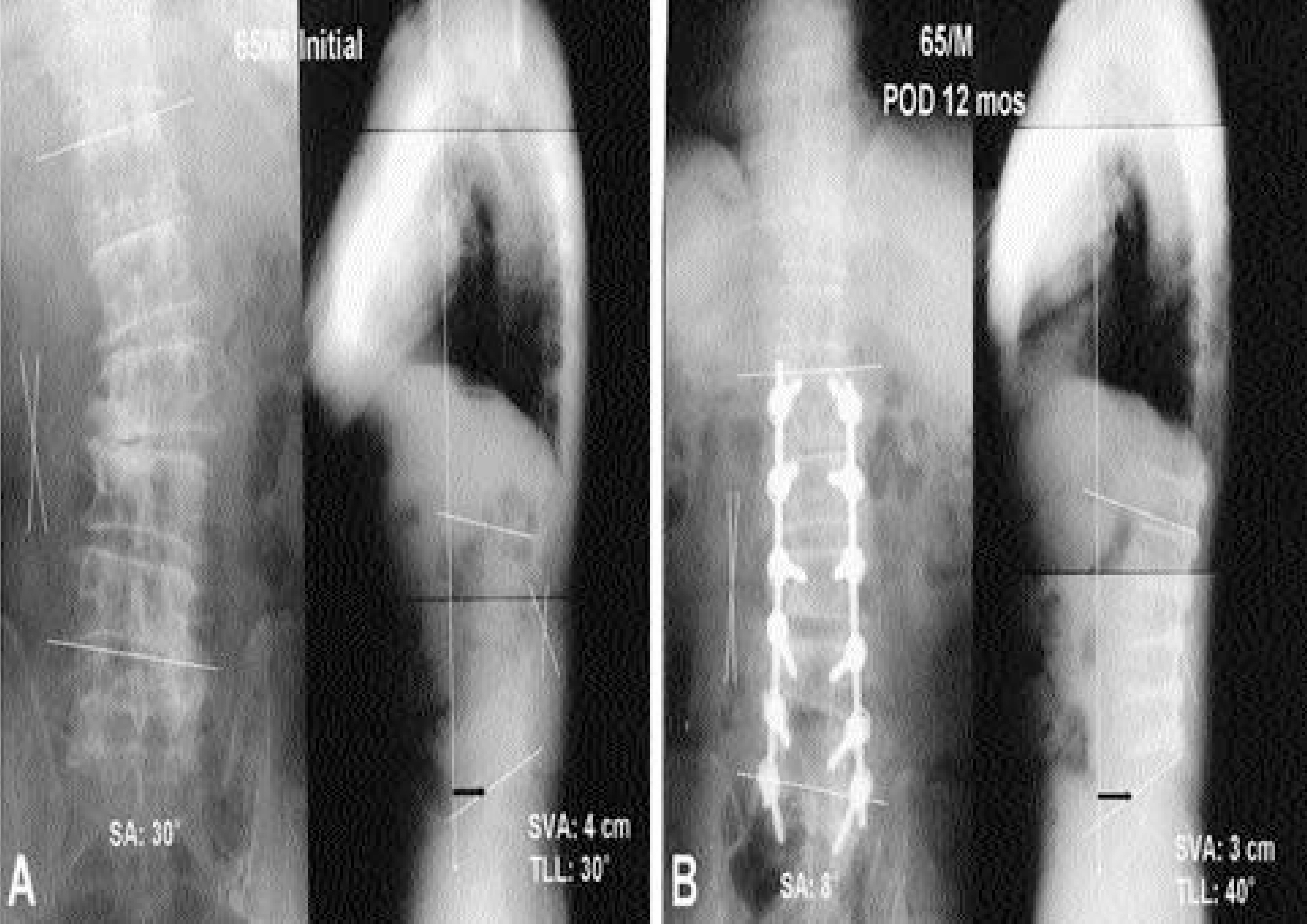
The scoliotic angles at preoperative, postoperative and follow-up were 15.0+/-4.9, 5.3+/-3.1 and 7.1+/-3.7 degrees retro-spectively. Total lumbar lordosis were 28.7+/-6.1, 40.6+/-7.3 and 35.1+/-10.2 degrees retrospectively. Sagittal vertical axis at preoperative and the last follow-up were 3.3+/-3.2 and 0.1 +/-3.3 cm retrospectively. According to Kirkaldy-Willis criteria, 6 cases were excellent, 24 cases good, 7 cases fair and 1 case poor. There was no statistical correlation between total lumbar lordosis and the clinical results (r=-0.061, p=0.717). Sagittal vertical axis was significantly correlated with the clinical results (r=0.519, p=0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
For improvement of surgical outcome of degenerative lumbar scoliosis, the sagittal vertical axis should be used as a parameter of sagittal alignment rather than the total lumbar lordosis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Bernhardt M, Bridwell KH. Segmental analysis of the sagittal plane alignment of the normal thoracic and lumbar spines and thoracolumbar junction. Spine. 14:717–721. 1989.
Article2). Booth KC, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Baldus CR, Blanke KM. Complications and predictive factors for the successful treatment of flatback deformity (fixed sagittal imbalance). Spine. 24:1712–1720. 1999.
Article3). Bradford DS. Adult scoliosis current conceps of treatment. Clin Orthop. 229:71–87. 1988.4). Bridwell KH. Degenerative scoliosis. Bridwell KH, DeWald RL, editors. The textbook of spinal surgery. 2nd ed.Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven;p. 777–795. 1997.5). Enker P, Steffee AD. Interbody fusion and instrumentation. Clin Orthop. 300:90–101. 1994.
Article6). Epstein JA, Epstein BS, Jones MD. Symtptpmatic lumbar scoliosis with degenerative changes in the elderly. Spine. 4:542–547. 1979.7). Farcy J-PC, Schwab FJ. Rationale for realignment surgery of the spine. The textbook of spinal surgery. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott;747. 1997.8). Gelb DE, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Blanke K, McEnery KW. An analysis of sagittal apinal alignment in 100 asymptomatic middle and older aged volunteers. Spine. 20:1351–1358. 1995.9). Grubb SA, Lipscomb HJ. Diagnostic findings in painful adult scoliosis. Spine. 17:518–527. 1992.
Article10). Grubb SA, Lipscomb HJ, Coonrad RW. Degenerative adult onset scoliosis. Spine. 13:241–245. 1988.
Article11). Grubb SA, Lipscomb HJ, Suh PB. Results of surgical treatment of painful adult scoliosis. Spine. 19:1619–1627. 1994.
Article12). Jackson RP, McManus AC. Radiographic analysis of sagittal plane alignment and balance in standing volunteers and patients with low back pain matched for age, sex, and size: a prospective controlled clinical study. Spine. 19:1611–1618. 1994.13). Kim YT, Lee CS, Kim JH, Kim JM, Park JH. Clinical features of degenerative scoliosis, J of Korean Spine Surg. 8:15–20. 2001.14). Korovessis R, Piperos G, Sidiropoulous P, Diamas A. Adult idiopathic lumbar scoliosis. A formula for pre -diction of progression and review of the literature. Spine. 19:1926–1932. 1993.15). Lee CS, Oh WH, Chung SS, Lee SG, Lee JY. Analysis of the sagittal alignment of normal spines, J of Korean Orthop Assoc. 34:949–954. 1999.16). Peterson MD, Jackson RP, McManus AC. Standing sagittal spinal balance, alignments and lumbopelvic relationships: Part I. A study of adult volunteers. Presented at the annual meeting of the. Scoliosis Research Society;Asheville, North Carolina, September 13-17. 1995.17). Pritchett JW, Bortel DT. Degenerative symptomatic lumbar scoliosis. Spine. 18:700–703. 1993.
Article18). Robin GC, Span Y, Steinberg R, Makin M, Menczel J. Scoliosis in the elderly: A follow up study. Spine. 7:355–359. 1982.19). Simmons ED, Simmons EH. Spinal stenosis with scoliosis. Spine. 17:117–120. 1992.
Article20). Stagnara P, DeMauroy JC, Dran G, Gonon GP, Costanzo G, Dimnet J, Pasquet A. Reciprocal angu -lation of vertebral bodies in a sagittal plane: Approach to references in the evaluation of kyphosis and lordosis. Spine. 7:335–342. 1982.21). Vedantam RV, Lenke LG, Keeney JA, Bridwell KH. Comparison of standing sagittal spinal aligment in asymptomatic adolescents and adults. Spine. 23:211–215. 1998.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Surgical Management of Spinal Stenosis with Degenerative Lumbar Scoliosis
- Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion in Multilevel Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Associated with Degenerative Scoliosis
- Surgical Treatment of Degenerative Lumbar Scoliosis with Multiple Spinal Stenosis
- Cotrel - Dubousset Pedicle Screw Fixation After Posterior Decompression of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
- Comparison of Sagittal Spinopelvic Alignment between Lumbar Degenerative Spondylolisthesis and Degenerative Spinal Stenosis