J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2001 Dec;8(4):520-526.
Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion in Multilevel Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Associated with Degenerative Scoliosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Sung-Ae General Hospital, Seoul, Korea. choknm@hanmir.com
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Pochun Joongmoon Medical School, Korea.
Abstract
-
STUDY DESIGN: In this study, 18 patients undergoing posterior lumbar interbody fusion for multilevel lumbar spinal stenosis associated with degenerative scoliosis were reviewed retrospectively.
OBJECTIVES
To assess the effectiveness of the cage-instrumented posterior lumbar interbody fusion in multilevel lumbar spinal stenosis associated with degenerative scoliosis. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: Degenerative lumbar scoliosis with the problems of neurogenic claudication, mechanical back pain and spinal deformity present a challenge for treatment.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We reviewed 18 surgical cases of multilevel lumbar spinal stenosis with degenerative scoliosis from March 1995 to April 2000 with an average follow up period of 2.9 years. We assessed the radiographic results of scoliotic angle correction and sagittal angle correction of the maximum curve and fused segment and disc height restoration. Clinical results were evaluated according to the Kirkaldy-Willis criteria.
RESULTS
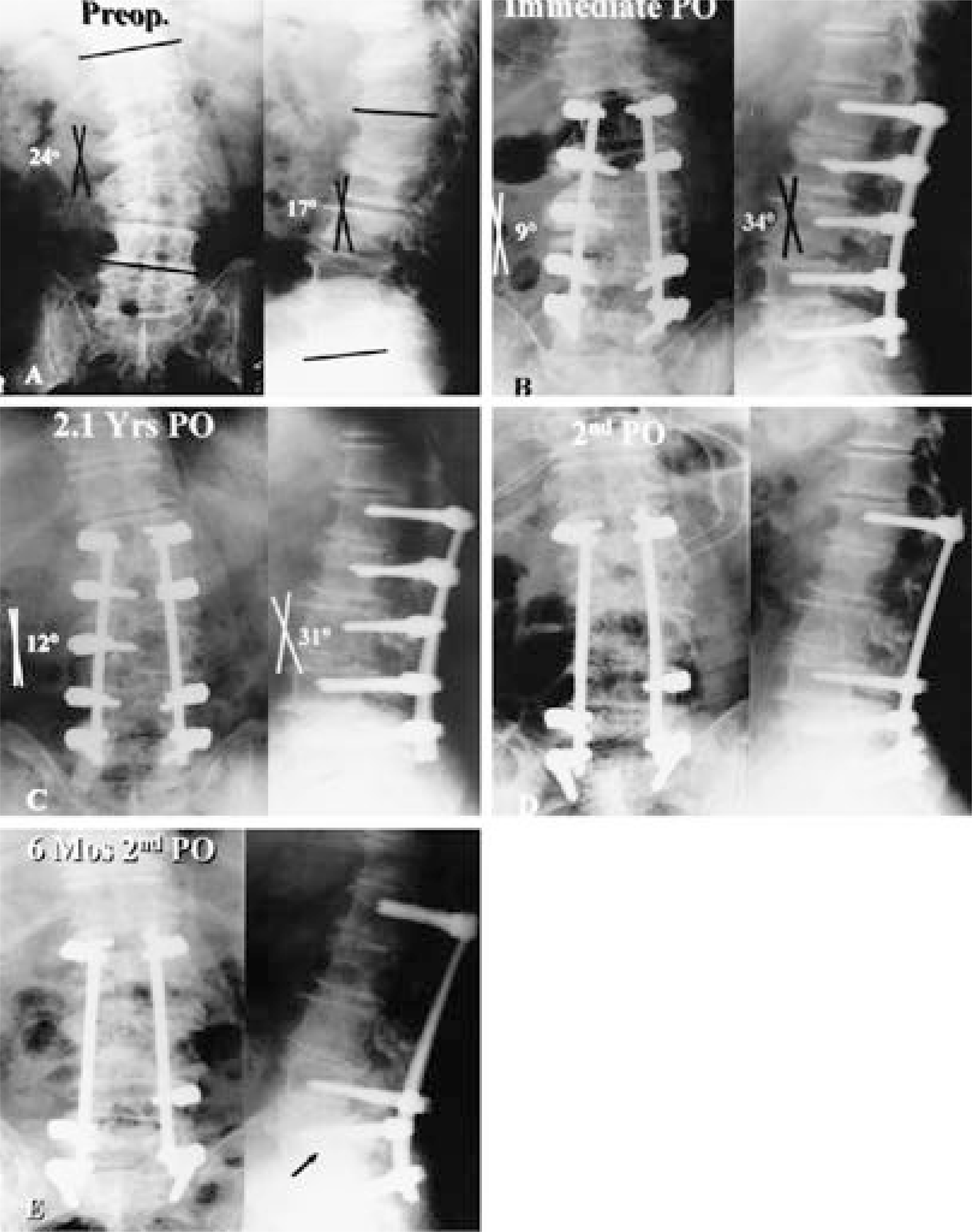
Mean scoliotic angle at preoperative, postoperative and final follow-up (maximum curve/fused segment) was 17.7-6.1-7.3degree /15.0-5.8-6.1degree respectively. Mean sagittal angle corresponding to each period was 12.1-34.1-32.7degree /8.3-27.0-26.0degree respectively. Mean disc height corresponding to each period was 22.9-42.4-40.5% respectively. The clinical result was analyzed as 15 satisfactory (83.3%), 3 fair (16.7%) and no poor. Fusion success was achieved in all patients. There were no serious complications except one case of fusion extension distally and no significant curve progression within follow-up period.
CONCLUSIONS
The cage-posterior lumbar interbody fusion in multilevel lumbar spinal stenosis with degenerative scoliosis was effective for correction of scoliotic and sagittal deformity and restoration of disc height with resultant foraminal patency, provided relatively high clinical success and in situ fusion success in all cases even over multiple fusion levels, and can be an alternative among surgical treatments of this complex disease.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Benner B, Ehni G. Degenerative lumbar scoliosis. Spine. 4:548–553. 1979.
Article2). Booth KC, Birdwell KH, Lenke LG, Baldus CR, Blanke KM. Complications and predictive factors for the successful treatment of flat back deformity (Fixed sagittal imbalance). Spine. 24:1712–1720. 1999.3). Brantigan JW, Steffee AD, Lewis ML, Quinn LM, Persenaire JM. Lumbar interbody fusion using the Brantigan I/F Cage for posterior lumbar interbody fusion and the variable pedicle screw placement system. Spine. 25:1437–1446. 2000.
Article4). Brantley AGU, Mayfield JK, Clark KR. The effect of pedicle screw fit-An in vitro study. Spine. 19:1752–1758. 1994.5). Carlson GD, Abitbol JJ, Anderson DR. Screw fixation in the human sacrum - An in vitro study of the biomechanics of fixation. Spine. 17:S196–203. 1992.6). Cho DY, Kim EH, Koh ES, Cho KN. Loss of the sagittal angle in the instrumented segments after pedicular screw fixation of the degenerative lumbar diseases. J of Korean Orthop Assoc. 30:481–489. 1997.
Article7). Cho JL, Yoon WK, Kwon OJ. Comparison of the clinical results between short and long segment fusion in lumbar spinal disorders. J of Korean Spine Surg. 2:47–55. 1995.8). Cinotti G, Postacchini F, Weinstein JN. Lumbar spinal stenosis and diabetes. Outcome of surgical decompression. J Bone Joint Surg[Br]. 76:215–219. 1994.
Article9). Ebstein JA, Epstein BS, Jones MD. Symptomat ic lumbar scoliosis with degenerative changes in the elderly. Spine. 4:542–547. 1979.10). Enker P, Steffee AD. Interbody fusion and instrumentation. Clin Orthp. 300:90–101. 1994.
Article11). Grubb SA, Lipscomb HJ. Diagnostic findings in painful adult scoliosis. Spine. 7:518–527. 1992.
Article12). Grubb SA, Lipscomb HJ. Results of lumbosacral fusion for degenerative disc disease with and without instrumentation- two to five year followup. Spine. 17:349–355. 1992.13). Grubb SA, Lipscomb HJ, Coonrad RW. Degenerative adult onset scoliosis. Spine. 13:241–245. 1988.
Article14). Grubb SA, Lipscomb HJ, Suh PB. Results of surgical treatment of painful adult scoliosis. Spine. 19:1619–1627. 1994.
Article15). Ha KY, Kim KW, Park SJ, Choi YS. Correction of curve and determination of fixation segment in degenerative lumbar scoliosis. J of Korean Spine Surg. 7:211–218. 2000.16). Ha KY, Moon MS, Paek SY. Effect of instrumental stabilization and fusion of degenerative lumbar scoliosis on unfused adjacent segment. J of Korean Spine Surg. 2:270–278. 1995.17). Kim EH, Cho DY, Kim JH. A clinical analysis of long segment fusion with pedicle screw in degenerative lumbar spine. J of Korean Spine Surg. 6:388–396. 1999.18). Kim EH, Lee KB, Cho DY. A comparison of flexible and rigid rods system in transpedicular screw fixation of degenerative lumbar spine. J of Korean Orthop Assoc. 34:103–110. 1999.19). Kirkaldy-Willis WH, Paine KWE, Cauchix , Graeme M. Lumbar spinal stenosis. Clin Orthp. 99:30–50. 1974.20). Kostuik J. Decision making in adult scoliosis. Spine. 4:521–526. 1979.
Article21). Marchesi DG, Aebi M. Pedicle fixation devices in the treatment of adult lumbar scoliosis. Spine. 17:S304–S309. 1992.
Article22). Okuyama K, Sato K, Abe E, Inaba H, Shimada Y, Murai H. Stability of transpedicle screwing for the osteoporotic spine-An in vitro study of the mechanical stability. Spine. 18:2240–2245. 1993.23). Postacchini F. Spine update. Surgical management of lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine. 24:1043–1047. 1999.24). Pritchett JW, Bortel DT. Degenerative symptomatic lumbar scoliosis. Spine. 18:700–703. 1993.
Article25). San Martino A, D'Andria FM, San Martino C. The surgical treatment of nerve root compression caused by scoliosis of the lumbar spine. Spine. 8:261–265. 1983.
Article26). Simmons ED (Jr.), Simmons EH. Spinal stenosis with scoliosis. Spine. 17:S117–S120. 1992.
Article27). Wiltse LL. Surgery for intervertebral disk disease of the lumbar spine. Spine. 16:839–845. 1991.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Minimally Invasive Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Indications, Outcomes and Complications
- Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion with Selective Biportal Endoscopic Posterior Decompression for Multilevel Lumbar Degenerative Diseases
- Clinical Comparison between Decompression and Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion in Chronic Lower Back Pain Involving Degenerative Disc Disease and Spinal Stenosis
- Result of Pedicle Screw Fixation in Lumbar Stenosis with: A Comparison of Degenerative Type Lumbar Stenosis with Spondylolisthetic type Lumbar Stenosis
- Anterior Interbody Fusion for Lower Lumbar Spinal Diseases