Tuberc Respir Dis.
2013 Jul;75(1):25-27.
Normalization of Elevated CA 19-9 Level after Treatment in a Patient with the Nodular Bronchiectatic Form of Mycobacterium abscessus Lung Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. wjkoh@skku.edu
Abstract
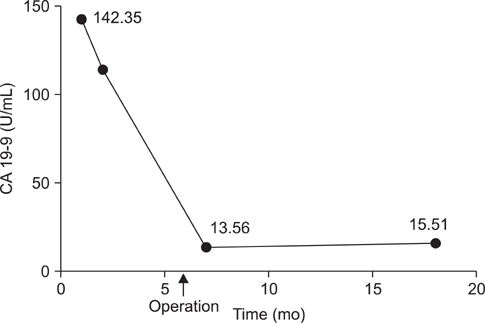
- Carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA 19-9) is a widely-used tumor marker in patients with pancreatic cancer. However, some patients with respiratory disease also exhibit elevated serum CA 19-9 levels. We report a case of normalization of elevated serum CA 19-9 levels after treatment of the nodular bronchiectatic form of Mycobacterium ab scessus lung disease. A 40-year-old man visited our hospital because of chronic cough and sputum. A computed tomography scan revealed severe bronchiectasis in the right upper and right middle lobes. Nontuberculous mycobacteria were repeatedly isolated and identified as M. abscessus. The serum CA 19-9 level was elevated to 142.35 U/mL (normal range, <37 U/mL). Surgical resection was performed because of failure of sputum conversion after antibiotic treatment. The serum CA 19-9 level returned to the normal range after surgery. This case suggested that serum CA 19-9 levels could be elevated in patients with the nodular bronchiectatic form of M. abscessus lung disease.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lamerz R. Role of tumour markers, cytogenetics. Ann Oncol. 1999; 10:Suppl 4. 145–149.2. Okusaka T, Yamada T, Maekawa M. Serum tumor markers for pancreatic cancer: the dawn of new era? JOP. 2006; 7:332–336.3. Kodama T, Satoh H, Ishikawa H, Ohtsuka M. Serum levels of CA19-9 in patients with nonmalignant respiratory diseases. J Clin Lab Anal. 2007; 21:103–106.4. Koh WJ, Jeon K, Lee NY, Kim BJ, Kook YH, Lee SH, et al. Clinical significance of differentiation of Mycobacterium massiliense from Mycobacterium abscessus. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011; 183:405–410.5. Griffith DE, Aksamit T, Brown-Elliott BA, Catanzaro A, Daley C, Gordin F, et al. An official ATS/IDSA statement: diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of nontuberculous mycobacterial diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007; 175:367–416.6. Jeon K, Kwon OJ, Lee NY, Kim BJ, Kook YH, Lee SH, et al. Antibiotic treatment of Mycobacterium abscessus lung disease: a retrospective analysis of 65 patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009; 180:896–902.7. Mukae H, Hirota M, Kohno S, Komori K, Fukushima K, Hiratani K, et al. Elevation of tumor-associated carbohydrate antigens in patients with diffuse panbronchiolitis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993; 148:744–751.8. Huh JH, Lee SM, Koo TH, Shin BC, Um SJ, Yang DK, et al. A case of bronchiectasis with high serum CA19-9. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2008; 64:383–386.9. Kim HR, Lee CH, Kim YW, Han SK, Shim YS, Yim JJ. Increased CA 19-9 level in patients without malignant disease. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2009; 47:750–754.10. Shimizu Y, Hamada T, Tanaka Y, Sasaki A, Nemoto T. Colocalization of CA19-9 and KL-6 to epithelial cells in dilated bronchioles in a patient with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis complicated by diffuse alveolar damage. Respirology. 2002; 7:281–284.11. Yamazaki Y, Kubo K, Takamizawa A, Yamamoto H, Honda T, Sone S. Markers indicating deterioration of pulmonary Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare infection. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999; 160:1851–1855.12. Bulut I, Arbak P, Coskun A, Balbay O, Annakkaya AN, Yavuz O, et al. Comparison of serum CA 19.9, CA 125 and CEA levels with severity of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Med Princ Pract. 2009; 18:289–293.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Diagnosis and treatment of nontuberculous mycobacterial lung disease
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Lung Disease
- Comparison of Clinical and Radiographic Characteristics between Nodular Bronchiectatic Form of Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Lung Disease and Diffuse Panbronchiolitis
- Sequential Bilateral Lung Resection in a Patient with Mycobacterium Abscessus Lung Disease Refractory to Medical Treatment
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Lung Disease