Tuberc Respir Dis.
2010 Jul;69(1):39-42.
A Case of Mycobacterium massiliense Infection Presenting as Pneumonia Resistant to Antibiotics in an Immunocompetent Host
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pulmonary & Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. shimts@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Thoracic Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
- Mycobacterium massiliense is newly identified rapid-growing nontuberculous mycobacterium, but there are no reports of this mycobacterium species being the cause of human illness. We describe one case of Mycobacterium massiliense infection presenting as antibiotic-resistant acute pneumonia that resulted in surgical treatment.
MeSH Terms
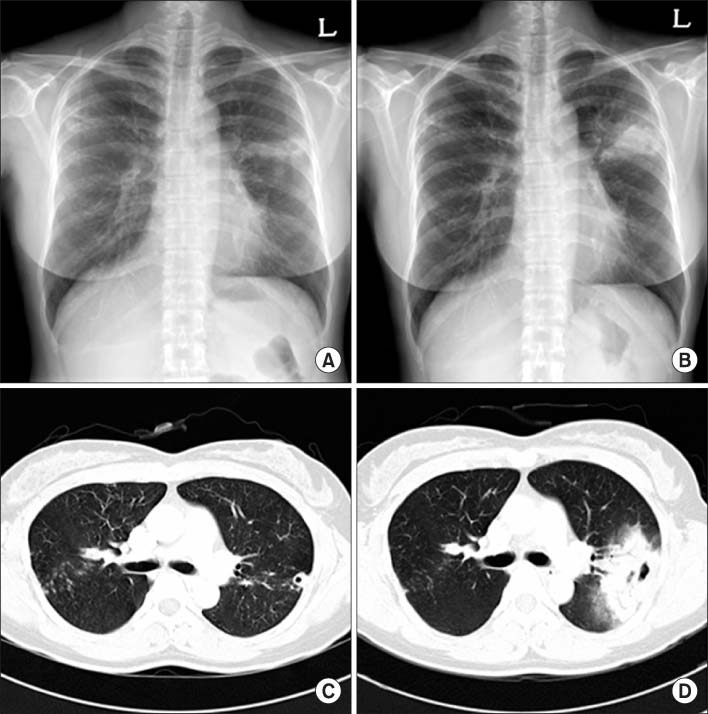
Figure
Reference
-
1. Adékambi T, Reynaud-Gaubert M, Greub G, Gevaudan MJ, La Scola B, Raoult D, et al. Amoebal coculture of "Mycobacterium massiliense" sp. nov. from the sputum of a patient with hemoptoic pneumonia. J Clin Microbiol. 2004. 42:5493–5501.2. Simmon KE, Pounder JI, Greene JN, Walsh F, Anderson CM, Cohen S, et al. Identification of an emerging pathogen, Mycobacterium massiliense, by rpoB sequencing of clinical isolates collected in the United States. J Clin Microbiol. 2007. 45:1978–1980.3. Viana-Niero C, Lima KV, Lopes ML, Rabello MC, Marsola LR, Brilhante VC, et al. Molecular characterization of Mycobacterium massiliense and Mycobacterium bolletii in isolates collected from outbreaks of infections after laparoscopic surgeries and cosmetic procedures. J Clin Microbiol. 2008. 46:850–855.4. Cardoso AM, Martins de Sousa E, Viana-Niero C, Bonfim de Bortoli F, Pereira das Neves ZC, Leão SC, et al. Emergence of nosocomial Mycobacterium massiliense infection in Goias, Brazil. Microbes Infect. 2008. 10:1552–1557.5. Kim HY, Yun YJ, Park CG, Lee DH, Cho YK, Park BJ, et al. Outbreak of Mycobacterium massiliense infection associated with intramuscular injections. J Clin Microbiol. 2007. 45:3127–3130.6. Lee H, Park HJ, Cho SN, Bai GH, Kim SJ. Species identification of mycobacteria by PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism of the rpoB gene. J Clin Microbiol. 2000. 38:2966–2971.7. Kim HY, Kook Y, Yun YJ, Park CG, Lee NY, Shim TS, et al. Proportions of Mycobacterium massiliense and Mycobacterium bolletii strains among Korean Mycobacterium chelonae-Mycobacterium abscessus group isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 2008. 46:3384–3390.8. Narita M, Ashkin D, Hollender ES, Pitchenik AE. Paradoxical worsening of tuberculosis following antiretroviral therapy in patients with AIDS. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998. 158:157–161.9. Yano S, Kobayashi K, Kato K, Tokuda Y, Ikeda T, Takeyama H. Paradoxical worsening of pulmonary Mycobacterium abscessus. Respir Med. 2007. 101:868–870.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Pulmonary and Endobronchial Mycobacterium avium Infection Presenting as an Acute Pneumonia in an Immunocompetent Patient
- Case of Mycobacterium Massiliense Infection Presenting as Recurrent Pneumonia in Sjogren's Syndrome
- A Case of Skin and Soft Tissue Infection by Mycobacterium massiliense
- Cutaneous Mycobacterium massiliense Infection Associated with Acupuncture
- A Fatal Case of Acute Respiratory Failure Caused by Mycobacterium massiliense