Tuberc Respir Dis.
2008 Nov;65(5):400-404.
Pseudomembranous Aspergillus Tracheobronchitis in an Immunocompetent Patient
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. sicha@knu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
Abstract
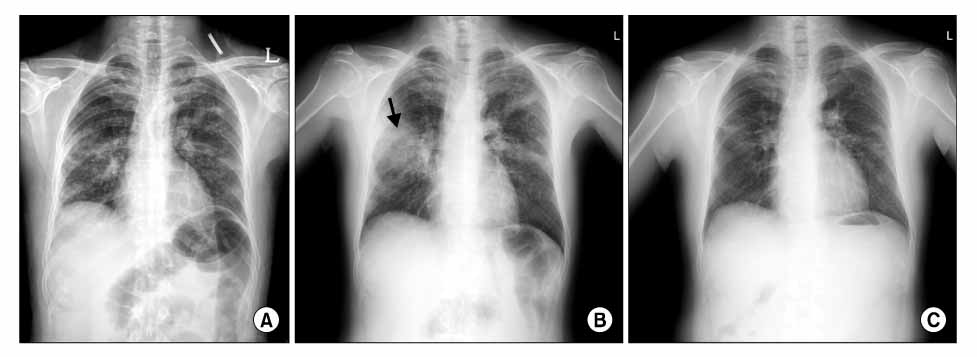
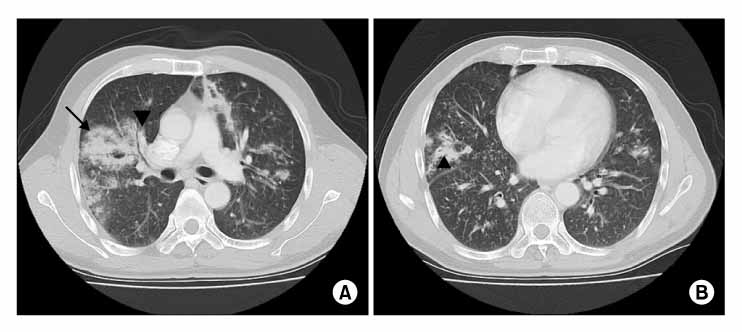
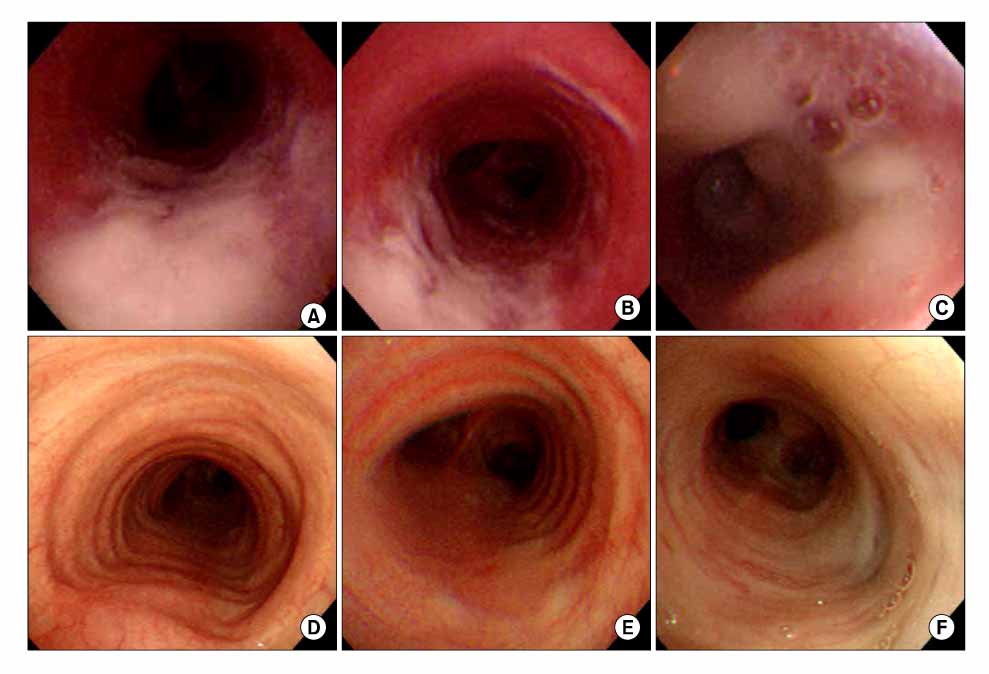
- Aspergillus tracheobronchitis (ATB), a variant of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis, is characterized by extensive tracheobronchitis and pseudomembrane formation. ATB usually occurs in immunocompromised patients with a high fatality rate. We report a case of ATB in a previously healthy patient who responded well to antifungal therapy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Soubani AO, Chandrasekar PH. The clinical spectrum of pulmonary aspergillosis. Chest. 2002. 121:1988–1999.2. Sharma OP, Chwogule R. Many faces of pulmonary aspergillosis. Eur Respir J. 1998. 12:705–715.3. Routsi C, Platsouka E, Prekates A, Rontogianni D, Paniara O, Roussos C. Aspergillus bronchitis causing atelectasis and acute respiratory failure in an immunocompromised patient. Infection. 2001. 29:243–244.4. Routsi C, Kaltsas P, Bessis E, Rontogianni D, Kollias S, Roussos C. Airway obstruction and acute respiratory failure due to Aspergillus tracheobronchitis. Crit Care Med. 2004. 32:580–582.5. Tasci S, Glasmacher A, Lentini S, Tschubel K, Ewig S, Molitor E, et al. Pseudomembranous and obstructive Aspergillus tracheobronchitis - optimal diagnostic strategy and outcome. Mycoses. 2006. 49:37–42.6. Machida U, Kami M, Kanda Y, Takeuchi K, Akahane M, Yamaguchi I, et al. Aspergillus tracheobronchitis after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1999. 24:1145–1149.7. van Assen S, Bootsma GP, Verweij PE, Donnelly JP, Raemakers JM. Aspergillus tracheobronchitis after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2000. 26:1131–1132.8. Boots RJ, Paterson DL, Allworth AM, Faoagali JL. Successful treatment of post-influenza pseudomembranous necrotising bronchial aspergillosis with liposomal amphotericin, inhaled amphotericin B, gamma interferon and GM-CSF. Thorax. 1999. 54:1047–1049.9. Franco J, Munoz C, Vila B, Marin J. Pseudomembranous invasive tracheobronchial aspergillosis. Thorax. 2004. 59:452.10. Nicholson AG, Sim KM, Keogh BF, Corrin B. Pseudomembranous necrotising bronchial aspergillosis complicating chronic airways limitation. Thorax. 1995. 50:807–808.11. Chang SM, Kuo HT, Lin FJ, Tzen CY, Sheu CY. Pseudomembranous tracheobronchitis caused by Aspergillus in immunocompromised patients. Scand J Infect Dis. 2005. 37:937–942.12. Denning DW. Commentary: unusual manifestations of aspergillosis. Thorax. 1995. 50:812–813.13. Bulpa PA, Dive AM, Garrino MG, Delos MA, Gonzalez MR, Evrard PA, et al. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients with invasive pulmonary aspergillosis: benefits of intensive care? Intensive Care Med. 2001. 27:59–67.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pseudomembranous Aspergillus Tracheobronchitis: Case Report of a Rare Manifestation of Airway Invasive Aspergillosis
- A Case of Severe Pseudomembranous Tracheobronchitis Complicated by Co-infection of Influenza A (H1N1) and Staphylococcus aureus in an Immunocompetent Patient
- A Case of Pseudomembranous Necrotizing Bronchial Aspergillosis in An Old Age Host
- A Case of Pseudomembranous Aspergillus Tracheobronchitis in a Patient with Diabetes Mellitus
- Airway Obstruction and Respiratory Failure Due to Aspergillus Tracheobronchitis