Tuberc Respir Dis.
2008 Aug;65(2):91-98.
Molecular Epidemiology and Antimicrobial Resistance of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Nasal Swab at Intensive Care Unit
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Konyang University, Daejeon, Korea. sk1609@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, College of Medicine, Konyang University, Daejeon, Korea.
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is the most common organism associated with nosocomial infections. MRSA infections are becoming increasing important because they have emerged no only as healthcare-associated (HA) infections but also as community-associated (CA) ones. This study examined the moleculo-epidemiology of MRSA, which was isolated from nasal swabs in the intensive care unit (ICU) at Konyang University Hospital. MRSA are classified into HA-MRSA and CA-MRSA.
METHODS
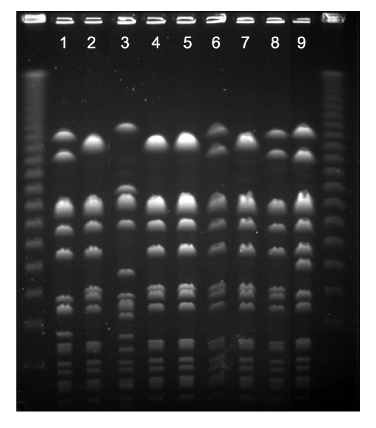
From June to September 2006, 353 patients who were admitted to the ICU in Konyang University Hospital were enrolled in this study. Single nasal swabs were obtained for culture in the ICU on the 1st day. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and the antimicrobial resistant patterns were analyzed between HA- and CA-MRSA. An antimicrobial sensitivity test was also performed.
RESULTS
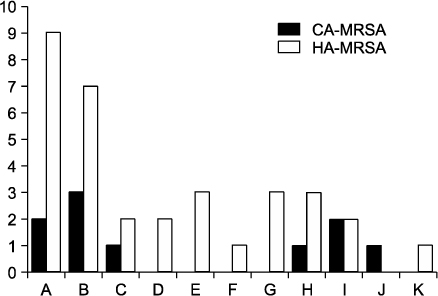
Forty two strains of MRSA were isolated from 353 patients (11.9%). Among the 42 isolates, HA-MRSA and CA-MRSA were found in 33 (78.6%), and 9 (21.4%), respectively. Eleven different PFGE types (type A to K) were identified. Types A (n=9) and B (n=7) were the most common for HA-MRSA, and types A (n=2) and B (n=2) were identified in CA-MRSA. The proportion of types A and B in CA-MRSA (44.4%) was similar to that in HA-MRSA (48.5%). The rates of resistance rates to erythromycin and ciprofloxacin were higher in HA-MRSA than in CA-MRSA.
CONCLUSION
The rate of isolation of MRSA in an ICU setting was 11.9%. HA-MRSA was isolated more frequently than CA-MRSA. The rate of resistance of HA-MRSA to erythromycin and ciprofloxacin was higher than that of CA-MRSA. Despite the small number of subjects, the main isolates (type A and B) of CA-MRSA were similar to those of HA-MRSA.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Diederen BM, Kluytmans JA. The emergence of infections with community-associated methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect. 2006. 52:157–168.2. Kim JM, Park ES, Jeong JS, Kim KM, Kim JM, Oh HS, et al. Multicenter surveillance study for nosocomial infections in major hospitals in Korea. Am J Infect Control. 2000. 28:454–458.3. From the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Four pediatric deaths from community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus--Minnesota and North Dakota, 1997-1999. JAMA. 1999. 282:1123–1125.4. Beam JW, Buckley B. Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: prevalence and risk factors. J Athl Train. 2006. 41:337–340.5. Wijaya L, Hsu LY, Kurup A. Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: overview and local situation. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 2006. 35:479–486.6. Park JY, Kim HO, Jeong YG, Kim S, Bae IG. Clinical characteristics and risk factors of community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections: comparison of community-acquired methicillin-susceptible staphylococcus aureus infections. Infect Chemother. 2006. 38:109–115.7. Kluytmans J, van Belkum A, Verbrugh H. Nasal carriage of Staphylococcus aureus: epidemiology, underlying mechanisms, and associated risks. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1997. 10:505–520.8. Wertheim HF, Vos MC, Ott A, van Belkum A, Voss A, Kluytmans JA, et al. Risk and outcome of nosocomial Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia in nasal carriers versus non-carriers. Lancet. 2004. 364:703–705.9. National Commitiee for Clinical Laboratory Standards (NCCLS). Standard M2-A4. Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically. 1990. Villanova, PA: NCCLS.10. Matushek MG, Bonten MJ, Hayden MK. Rapid preparation of bacterial DNA for pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J Clin Microbiol. 1996. 34:2598–2600.11. Tenover FC, Arbeit RD, Goering RV, Mickelsen PA, Murray BE, Persing DH, et al. Interpreting chromosomal DNA restriction patterns produced by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis: criteria for bacterial strain typing. J Clin Microbiol. 1995. 33:2233–2239.12. Mest DR, Wong DH, Shimoda KJ, Mulligan ME, Wilson SE. Nasal colonization with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus on admission to the surgical intensive care unit increased with the risk of infection. Anesth Analg. 1994. 78:644–650.13. Jung SI, Heo ST, Kim YS, Kim S, Peck KR, Kwon OJ, et al. Prevention of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus nasal carriage and infection by conventional method and intranasal fusidic acid. Korean J Nosocomial Infect Control. 2001. 6:33–40.14. Kim S, Kim CK, Lee H, Peck KR, Kwon J, Lee JH, et al. A study on modes of transmission and role of nasal carriage to subsequent infection with Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in medical ICU using PFGE. Korean J Nosocomial Infect Control. 1998. 3:1–10.15. Corbella X, Dominguez MA, Pujol M, Ayats J, Sendra M, Pallares R, et al. Staphylococcus aureus nasal carriage as a marker for subsequent staphylococcal infections in intensive care unit patients. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1997. 16:351–357.16. Lim MS, Marshall CL, Spelman D. Carriage of multiple subtypes of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by intensive care unit patients. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2006. 27:1063–1067.17. Kim OS, Yoon SW, Kang YJ, Kim YK, Lee NY, Lee JH, et al. Rate of nasal colonization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus at admission to a medical intensive care unit. Korean J Nosocomial Infect Control. 2007. 12:42–49.18. Song W, Lee TJ, Kim SJ, Park MJ, Lee KM. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in intensive care unit (ICU) patients: relation to nasal carriage of patients or ICU personnels. Korean J Clin Microbiol. 2001. 4:45–51.19. Pujol M, Pena C, Pallares R, Ariza J, Ayats J, Dominguez MA, et al. Nosocomial Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia among nasal carriers of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible strains. Am J Med. 1996. 100:509–516.20. Garrouste-Orgeas M, Timsit JF, Kallel H, Ben Ali A, Dumay MF, Paoli B, et al. Colonization with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in ICU patients: morbidity, mortality, and glycopeptide use. J Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2001. 22:687–692.21. Porter R, Subramani K, Thomas AN, Chadwick P. Nasal carriage of Staphylococcus aureus on admission to intensive care: incidence and prognostic significance. Intensive Care Med. 2003. 29:655–658.22. Faria NA, Oliveira DC, Westh H, Monnet DL, Larsen AR, Skov R, et al. Epidemiology of emerging methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Denmark: a nationwide study in a country with low prevalence of MRSA infection. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. 43:1836–1842.23. Wylie JL, Nowicki DL. Molecular epidemiology of community- and health care-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Manitoba, Canada. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. 43:2830–2836.24. Salgado CD, Farr BM, Calfee DP. Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a meta-analysis of prevalence and risk factors. Clin Infect Dis. 2003. 36:131–139.25. Onorato M, Borucki MJ, Baillargeon G, Paar DP, Freeman DH, Cole CP, et al. Risk factors for colonization or infection due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in HIV-positive patients: a retrospective case-control study. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 1999. 20:26–30.26. Merrer J, Santoli F, Appere de Vecchi C, Tran B, De Jonghe B, Outin H. "Colonization pressure" and risk of acquisition of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a medical intensive care unit. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2000. 21:718–723.27. Shopsin B, Kreiswirth BN. Molecular epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Emerg Infect Dis. 2001. 7:323–326.28. Trindade PA, McCulloch JA, Oliveira GA, Mamizuka EM. Molecular techniques for MRSA typing: current issues and perspectives. Braz J Infect Dis. 2003. 7:32–43.29. McDougal LK, Steward CD, Killgore GE, Chaitram JM, McAllister SK, Tenover FC. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis typing of oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from the United States: establishing a national database. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. 41:5113–5120.30. Huang H, Flynn NM, King JH, Monchaud C, Morita M, Cohen SH. Comparisons of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and hospital-associated MSRA infections in Sacramento, California. J Clin Microbiol. 2006. 44:2423–2427.31. Davis SL, Perri MB, Donabedian SM, Manierski C, Singh A, Vager D, et al. Epidemiology and outcomes of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection. J Clin Microbiol. 2007. 45:1705–1711.32. Park CW, Lee JS, Song JY, Kim CH, Eom JS, Cheong HJ, et al. Clinical and molecular epidemiologic study of community-acquired and hospital-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infection. J Korean Soc Chemother. 2002. 20:77–90.33. Jeong HY, Lee JE, Choi BK, Seo KW, Park SH, Kim YL, et al. Molecular epidemiology of community-associated antimicrobial-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Seoul, Korea (2003): pervasiveness of multidrug-resistant SCCmec type II methicillin-resistant S. aureus. Microb Drug Resist. 2007. 13:178–185.34. Hiramatsu K. Elucidation of mechanism of antibiotic resistance acquisition of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and determination of its whole genome nucleotide sequence. JMAJ. 2004. 47:153–159.35. Vandenesch F, Naimi T, Enright MC, Lina G, Nimmo GR, Heffernan H, et al. Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus carrying Panton-Valentine leukocidin genes: worldwide emergence. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003. 9:978–984.36. Lowy FD. Antimicrobial resistance: the example of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Invest. 2003. 111:1265–1273.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Detection of Multidrug Resistant Patterns and Associated - genes of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus ( MRSA ) Isolated from Clinical Specimens
- Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Infection in Neonates
- Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA)
- A case of multiple furunculosis caused by methicillin-resistant staphylococcs aureus
- Multilocus Sequence Typing of Clonal Changes of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Intensive Care Unit Patients: 1996 versus 2004