Tuberc Respir Dis.
2006 Jul;61(1):46-53.
The Effects of Intra-Abdominal Hypertension on the Prognosis of Critically Ill Patients in the Intensive Care Unit (ICU)
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Korea University, Seoul, Korea. kkhchest@korea.ac.kr
- 2Intensive Care Unit, Ansan Hospital, Korea University Medical Center, Korea.
- 3Intensive Care Unit, Guro Hospital, Korea University Medical Center, Korea.
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND: Intra-abdominal hypertension (IAH) is defined as the presence of either an intra-abdominal pressure (IAP) > or = 12 mmHg or an abdominal perfusion pressure (APP = mean arterial pressure - IAP) < or = 60 mmHg. Abdominal compartment syndrome (ACS) is defined as the presence of an IAP > or = 20 mmHg together with organ failure. The purpose of this study was to investigate the prevalence of IAH and ACS on the day of admission and the effects of these maladies on the prognosis of critically ill patients in the ICU.
METHODS
At the day of admission to the ICU, the IAP was recorded by measuring the intravesicular pressure via a Foley catheter. The APACHE II and III scores were checked and SAPS II was also scored during the days the patients were in the ICU. The primary end point was the prevalence of IAH and ACS at the day of admission and the correlation between them with the 28-days mortality rate. The measurement of IAP continued until the 7th day or the day when the patient was transferred to the general ward before 7th day, unless the patient died or a Foley catheter was removed before 7th day. Patients were observed until death or the 28th day.
RESULTS
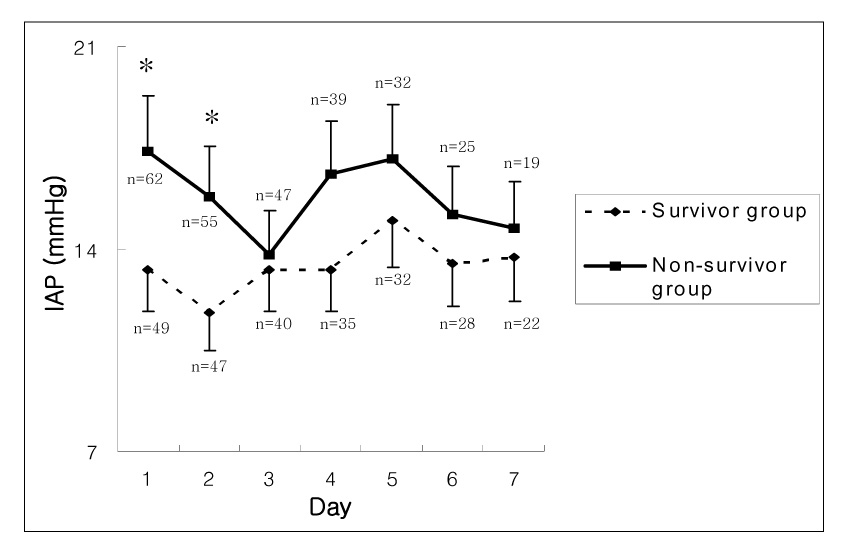
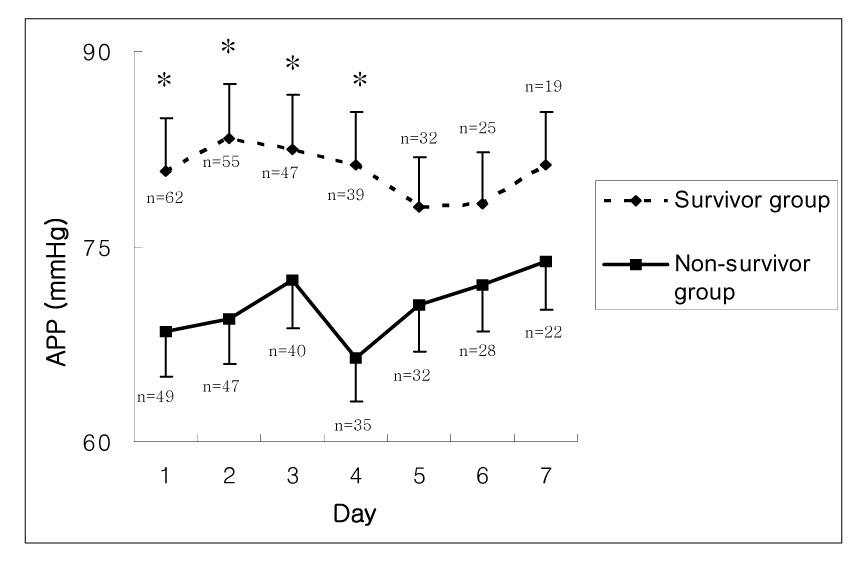
A total of 111 patients were enrolled. At the day of admission, the prevalence of IAH and ACS were 47.7% and 15.3%, respectively and the mean IAP was 15.1+/-8.5 mmHg. The rates of IAH for the survivor and the non-survivor groups were 56.5% and 71.4%, respectively, and these were not significantly different (p=0.593). Yet the rates of ACS between these two groups were significantly different (4/62, 6.5% vs. 13/49, 26.5%; Odds Ratio = 5.24, 95% CI = 1.58-17.30, p=0.004).
CONCLUSION
In the present study, the prevalence of IAH was 47.7% and the prevalence of ACS was 15.3% on the day of admission. ACS was associated with a poor outcome for the critically ill patients in the ICU.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sugerman HJ. Increased intra-abdominal pressure in obesity. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1998. 22:1138.2. Hering R, Wrigge H, Vorwerk R, Brensing KA, Schroder S, Zinserling J, et al. The effects of prone positioning on intraabdominal pressure and cardiovascular and renal function in patients with acute lung injury. Anesth Analg. 2001. 92:1226–1231.3. Duggan JE, Drummond GB. Abdominal muscle activity and intraabdominal pressure after upper abdominal surgery. Anesth Analg. 1989. 69:598–603.4. Navarro-Rodriguez T, Hashimoto CL, Carrilho FJ, Strauss E, Laudanna AA, Moraes-Filho JP. Reduction of abdominal pressure in patients with ascites reduces gastroesophageal reflux. Dis Esophagus. 2003. 16:77–82.5. Rosenthal RJ, Friedman RL, Kahn AM, Martz J, Thiagarajah S, Cohen D, et al. Reasons for intracranial hypertension and hemodynamic instability during acute elevations of intra-abdominal pressure: observations in a large animal model. J Gastrointest Surg. 1998. 2:415–425.6. Ishizaki Y, Itoh T, Shimomura K, Noie T, Abe H, Izezuki Y. Cardiovascular effects of increasedintra-abdominal pressure during pneumoperitoneum: preliminary report. Nippon Geka Gakkai Zasshi. 1991. 92:614.7. Rouby JJ, Puybasset L, Nieszkowska A, Lu Q. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: lessons from computed tomography of the whole lung. Crit Care Med. 2003. 31:S285–S295.8. Polat C, Aktepe OC, Akbulut G, Yilmaz S, Arikan Y, Dilek ON, et al. The effects of increased intra-abdominal pressure on bacterial translocation. Yonsei Med J. 2003. 44:259–264.9. Markou N, Grigorakos L, Myrianthefs P, Boutzouka E, Rizos M, Evagelopoulou P, et al. Venous pressure measurements in the superior and inferior vena cava: the influence of intra-abdominal pressure. Hepatogastroenterology. 2004. 51:51–55.10. Reddy VG. Prevention of postoperative acute renal failure. J Postgrad Med. 2002. 48:64–70.11. Sugrue M, Jones F, Deane SA, Bishop G, Bauman A, Hillman K. Intra-abdominal hypertension is an independent cause of postoperative renal impairment. Arch Surg. 1999. 134:1082–1085.12. Malbrain ML, Chiumello D, Pelosi P, Bihari D, Innes R, Ranieri VM, et al. Incidence and prognosis of intraabdominal hypertension in a mixed population of critically ill patients: a multiple-center epidemiological study. Crit Care Med. 2005. 33:315–322.13. Cheatham ML, White MW, Sagraves SG, Johnson JL, Block EF. Abdominal perfusion pressure: a superior parameter in the assessment of intra-abdominal hypertension. J Trauma. 2000. 49:621–626.14. Cheatham ML, Safcsak K. Intraabdominal pressure: a revised method for measurement. J Am Coll Surg. 1998. 186:594–595.15. Kron IL, Harman PK, Nolan SP. The measurement of intra-abdominal pressure as a criterion for abdominal re-exploration. Ann Surg. 1984. 199:28–30.16. Malbrain ML, Chiumello D, Pelosi P, Wilmer A, Brienza N, Malcangi V, et al. Prevalence of intra-abdominal hypertension in critically ill patients: a multicentre epidemiological study. Intensive Care Med. 2004. 30:822–829.17. Sugrue M. Abdominal compartment syndrome. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2005. 11:333–338.18. Knaus WA, Draper EA, Wagner DP, Zimmerman JE. APACHE II: a severity of disease classification system. Crit Care Med. 1985. 13:818–829.19. Knaus WA, Wagner DP, Draper EA, Zimmerman JE, Bergner M, Bastos PG, et al. The APACHE III prognostic system: risk prediction of hospital mortality for critically ill hospitalized adults. Chest. 1991. 100:1619–1636.20. le Gall JR, Lemeshow S, Saulnier F. A new Simplified Acute Physiology Score (SAPS II) based on a European/North American multicenter study. JAMA. 1993. 270:2957–2963.21. Malbrain ML. Different techniques to measure intra-abdominal pressure (IAP): time for a critical reappraisal. Intensive Care Med. 2004. 30:357–371.22. Malbrain ML. Is it wise not to think about intra-abdominal hypertension in the ICU? Curr Opin Crit Care. 2004. 10:132–145.23. Malbrain ML, Deeren D, de Potter TJ. Intra-abdominal hypertension in the critically ill: it is time to pay attention. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2005. 11:156–171.24. Doty JM, Oda J, Ivatury RR, Blocher CR, Christie GE, Yelon JA, et al. The effects of hemodynamic shock and increased intra-abdominal pressure on bacterial translocation. J Trauma. 2002. 52:13–17.25. Kotzampassi K, Metaxas G, Paramythiotis D, Pidonia I, Rekka H, Karamouzis M, et al. The influence of continuous seven-day elevated intra-abdominal pressure in the renal perfusion in cirrhotic rats. J Surg Res. 2003. 115:133–138.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Effects of Intra-Abdominal Pressure in Critically Ill Trauma Patients
- Prevention of Complications in Critically Ill Patients
- Effect of a Clinical Nursing Practice Guideline of Enteral Nutrition Care on the Duration of Mechanical Ventilator for Critically Ill Patients
- Admission Hyperglycemia Aggravates the Prognosis of Critically Ill Patients
- Sedation in the Critically Ill Patients