Tuberc Respir Dis.
2012 Feb;72(2):117-123.
Sedation in the Critically Ill Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Hanyang University Guri Hospital, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Guri, Korea. drterry@hanyang.ac.kr
Abstract
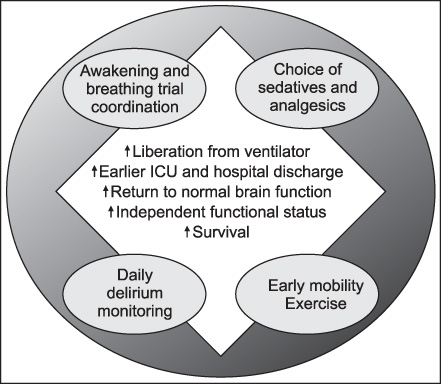
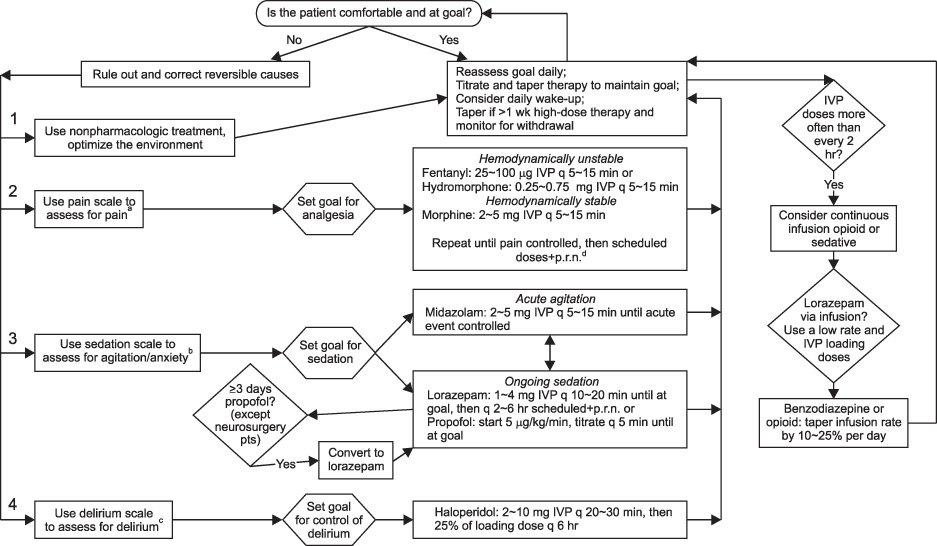
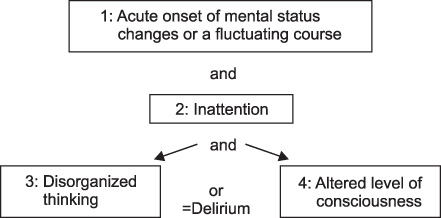
- Optimal level of sedation and analgesia is important for the comfort and safety of critically ill patients. However, suboptimal sedation is relatively common in the intensive care unit (ICU) and it could cause prolonged mechanical ventilation and ICU stay, also increase delirium and ICU acquired weakness and resultant decreased survival. Therefore, accurate assessment of the level of sedation and analgesia, maintaining adequate level of sedation, and daily evaluation of each patient and following adjustment could be important treatment strategy in critically ill patients. Recently, the strategy for sedation in the ICU is changing toward the direction of lowering sedation level or even "no sedation" with concurrent use of analgesics and the use of ultra short acting analgesics could be helpful in some patients. Clinicians should be aware of the importance of algorithmic approach including daily interruption of sedative and assessment of sedation level and especially in the patients under mechanical ventilation, organizational approaches such as the 'ABCDE' bundle could improve the management of critically ill patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jacobi J, Fraser GL, Coursin DB, Riker RR, Fontaine D, Wittbrodt ET, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the sustained use of sedatives and analgesics in the critically ill adult. Crit Care Med. 2002. 30:119–141.2. Jung SW, Kwon YS, Choi JC. Koh YS, editor. Clinical practice guidelines for the use of sedatives and analgesics. Clinical practice guideline of the Korean Society of Critical Care Medicine. 2009. Seoul: Medlang;6–19.3. Mehta S, Burry L, Martinez-Motta JC, Stewart TE, Hallett D, McDonald E, et al. A randomized trial of daily awakening in critically ill patients managed with a sedation protocol: a pilot trial. Crit Care Med. 2008. 36:2092–2099.4. Strøm T, Martinussen T, Toft P. A protocol of no sedation for critically ill patients receiving mechanical ventilation: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2010. 375:475–480.5. Morandi A, Brummel NE, Ely EW. Sedation, delirium and mechanical ventilation: the 'ABCDE' approach. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2011. 17:43–49.6. Sessler CN, Varney K. Patient-focused sedation and analgesia in the ICU. Chest. 2008. 133:552–565.7. Arias-Rivera S, Sáchez-Sánchez Mdel M, Santos-Díaz R, Gallardo-Murillo J, Sánchez-Izquierdo R, Frutos-Vivar F, et al. Effect of a nursing-implemented sedation protocol on weaning outcome. Crit Care Med. 2008. 36:2054–2060.8. Marshall J, Finn CA, Theodore AC. Impact of a clinical pharmacist-enforced intensive care unit sedation protocol on duration of mechanical ventilation and hospital stay. Crit Care Med. 2008. 36:427–433.9. Brook AD, Ahrens TS, Schaiff R, Prentice D, Sherman G, Shannon W, et al. Effect of a nursing-implemented sedation protocol on the duration of mechanical ventilation. Crit Care Med. 1999. 27:2609–2615.10. Riker RR, Picard JT, Fraser GL. Prospective evaluation of the Sedation-Agitation Scale for adult critically ill patients. Crit Care Med. 1999. 27:1325–1329.11. Devlin JW, Boleski G, Mlynarek M, Nerenz DR, Peterson E, Jankowski M, et al. Motor activity assessment scale: a valid and reliable sedation scale for use with mechanically ventilated patients in an adult surgical intensive care unit. Crit Care Med. 1999. 27:1271–1275.12. Arroliga AC, Thompson BT, Ancukiewicz M, Gonzales JP, Guntupalli KK, Park PK, et al. Use of sedatives, opioids, and neuromuscular blocking agents in patients with acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care Med. 2008. 36:1083–1088.13. Pisani MA, Murphy TE, Araujo KL, Slattum P, Van Ness PH, Inouye SK. Benzodiazepine and opioid use and the duration of intensive care unit delirium in an older population. Crit Care Med. 2009. 37:177–183.14. Maze M, Scarfini C, Cavaliere F. New agents for sedation in the intensive care unit. Crit Care Clin. 2001. 17:881–897.15. Gregoretti C, Moglia B, Pelosi P, Navalesi P. Clonidine in perioperative medicine and intensive care unit: more than an anti-hypertensive drug. Curr Drug Targets. 2009. 10:799–814.16. Precedex® (dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection) for intravenous use. 2010. cited 2010 Sep 10. Lake Forest, IL: Hospira, Inc.;Available from: http://www.precedex.com/wp-content/uploads/2010/02/Precedex_Full_PI.pdf.17. Turkmen A, Altan A, Turgut N, Vatansever S, Gokkaya S. The correlation between the Richmond agitation-sedation scale and bispectral index during dexmedetomidine sedation. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2006. 23:300–304.18. Pandharipande PP, Pun BT, Herr DL, Maze M, Girard TD, Miller RR, et al. Effect of sedation with dexmedetomidine vs lorazepam on acute brain dysfunction in mechanically ventilated patients: the MENDS randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2007. 298:2644–2653.19. Riker RR, Shehabi Y, Bokesch PM, Ceraso D, Wisemandle W, Koura F, et al. Dexmedetomidine vs midazolam for sedation of critically ill patients: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2009. 301:489–499.20. Reade MC, O'Sullivan K, Bates S, Goldsmith D, Ainslie WR, Bellomo R. Dexmedetomidine vs. haloperidol in delirious, agitated, intubated patients: a randomised open-label trial. Crit Care. 2009. 13:R75.21. Mirski MA, Lewin JJ 3rd, Ledroux S, Thompson C, Murakami P, Zink EK, et al. Cognitive improvement during continuous sedation in critically ill, awake and responsive patients: the Acute Neurological ICU Sedation Trial (ANIST). Intensive Care Med. 2010. 36:1505–1513.22. Wilhelm W, Kreuer S. The place for short-acting opioids: special emphasis on remifentanil. Crit Care. 2008. 12:Suppl 3. S5.23. Ouimet S, Kavanagh BP, Gottfried SB, Skrobik Y. Incidence, risk factors and consequences of ICU delirium. Intensive Care Med. 2007. 33:66–73.24. Spronk PE, Riekerk B, Hofhuis J, Rommes JH. Occurrence of delirium is severely underestimated in the ICU during daily care. Intensive Care Med. 2009. 35:1276–1280.25. Shehabi Y, Riker RR, Bokesch PM, Wisemandle W, Shintani A, Ely EW, et al. Delirium duration and mortality in lightly sedated, mechanically ventilated intensive care patients. Crit Care Med. 2010. 38:2311–2318.26. Griffiths RD, Hall JB. Intensive care unit-acquired weakness. Crit Care Med. 2010. 38:779–787.27. Morris PE, Goad A, Thompson C, Taylor K, Harry B, Passmore L, et al. Early intensive care unit mobility therapy in the treatment of acute respiratory failure. Crit Care Med. 2008. 36:2238–2243.28. Schweickert WD, Pohlman MC, Pohlman AS, Nigos C, Pawlik AJ, Esbrook CL, et al. Early physical and occupational therapy in mechanically ventilated, critically ill patients: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2009. 373:1874–1882.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pain Control and Sedation in Neuro Intensive Critical Unit
- Midazolam Infusion for Sedation in the ICU Patients
- The Efficacy of the COMFORT Scale in Assessing Optimal Sedation in Critically Ill Children Requiring Mechanical Ventilation
- Characteristics of Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients in Busan, Republic of Korea
- Prehospital transport of critically ill children via 119 emergency medical service providers: problems and improvement plan