Restor Dent Endod.
2016 Feb;41(1):44-54. 10.5395/rde.2016.41.1.44.
Antioxidant therapy enhances pulpal healing in bleached teeth
- Affiliations
-
- 1Dental Research Division, School of Dentistry, Paulista University, Sao Paulo, SP, Brazil.
- 2Department of Morphology, Piracicaba Dental School, University of Campinas, Piracicaba, SP, Brazil.
- 3Department of Physiology and Pathology, Araraquara School of Dentistry, University Estadual Paulista, Araraquara, SP, Brazil. casouzac@foar.unesp.br
- 4Department of Restorative Dentistry, Piracicaba Dental School, University of Campinas, Piracicaba, SP, Brazil.
- KMID: 2316963
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.1.44
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the histopathological effects of an antioxidant therapy on the pulp tissue of rat teeth exposed to a bleaching gel with 35% hydrogen peroxide.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Forty rats were subjected to oral ingestion by gavage of distilled water (DW) or ascorbic acid (AA) 90 min before the bleaching therapy. For the bleaching treatment, the agent was applied twice for 5 min each to buccal surfaces of the first right mandibular molars. Then, the animals were sacrificed at 6 hr, 24 hr, 3 day, or 7 day post-bleaching, and the teeth were processed for microscopic evaluation of the pulp tissue.
RESULTS
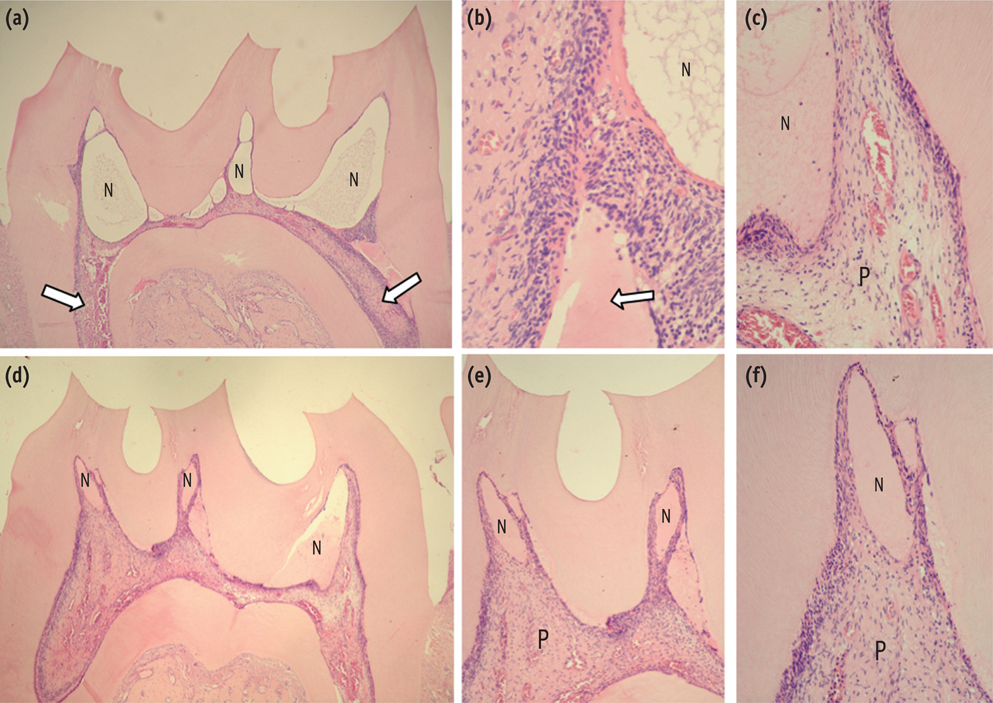
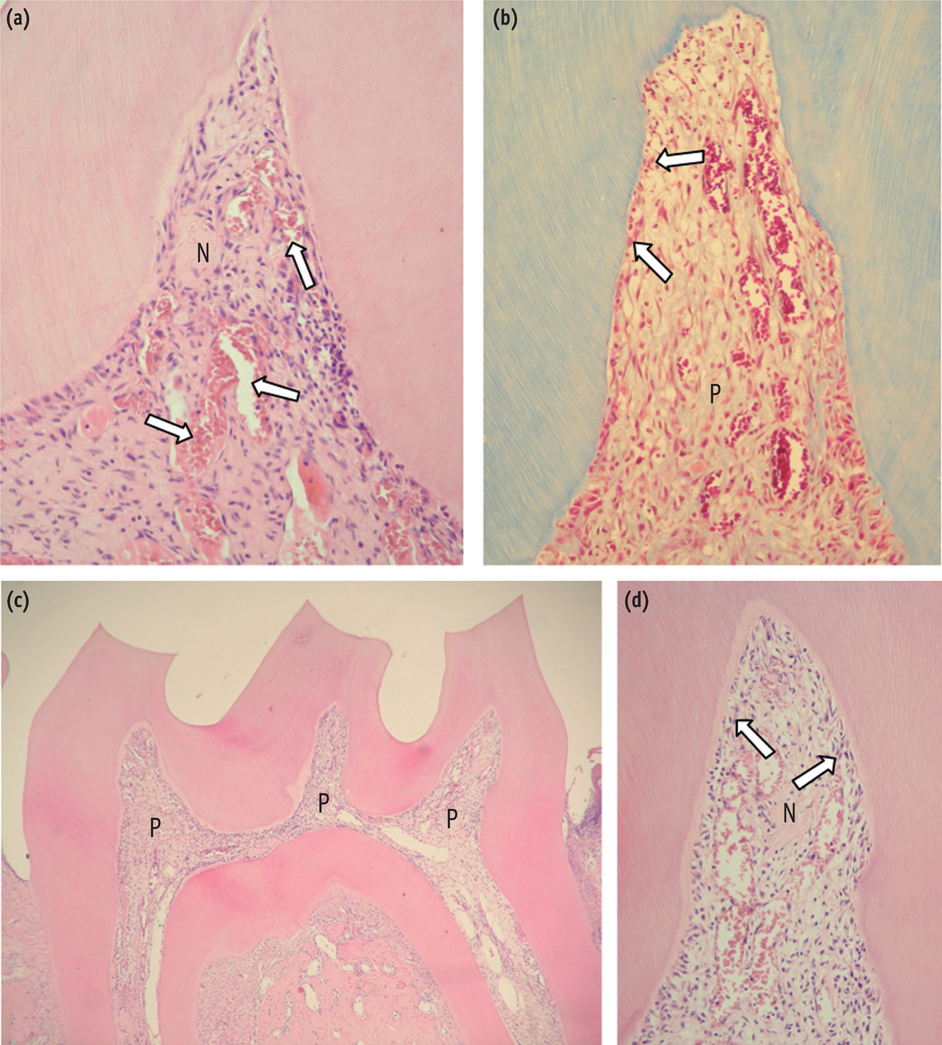
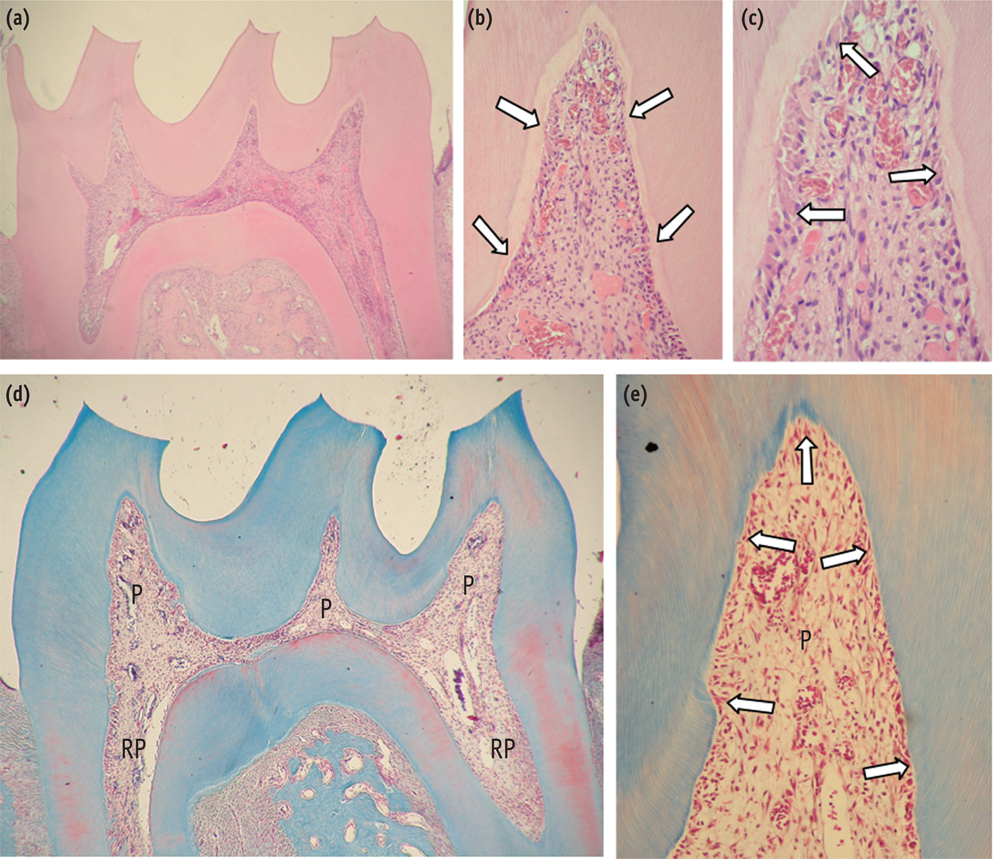
At 6 hr, the pulp tissue showed moderate inflammatory reactions in all teeth of both groups. In the DW and AA groups, 100% and 80% of teeth exhibited pulp tissue with significant necrosis and intense tissue disorganization, respectively. At 24 hr, the AA-treated group demonstrated a greater regenerative capability than the DW group, with less intense inflammatory reaction and new odontoblast layer formation in 60% of the teeth. For up to the 7 day period, the areas of pulpal necrosis were replaced by viable connective tissue, and the dentin was underlined by differentiated odontoblast-like cells in most teeth of both groups.
CONCLUSIONS
A slight reduction in initial pulpal damage during post-bleaching was promoted by AA therapy. However, the pulp tissue of AA-treated animals featured faster regenerative potential over time.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Can different agents reduce the damage caused by bleaching gel to pulp tissue? A systematic review of basic research
Letícia Aparecida Silva Batista, Alexandre Henrique dos Reis-Prado, Hebertt Gonzaga dos Santos Chaves, Lara Cancella de Arantes, Luís Fernando Santos Alves Morgan, Carolina Bosso André, Thaís Yumi Suzuki, Francine Benetti
Restor Dent Endod. 2023;48(4):e39. doi: 10.5395/rde.2023.48.e39.
Reference
-
1. Cintra LT, Benetti F, da Silva Facundo AC, Ferreira LL, Gomes-Filho JE, Ervolino E, Rahal V, Briso AL. The number of bleaching sessions influences pulp tissue damage in rat teeth. J Endod. 2013; 39:1576–1580.
Article2. Soares DG, Basso FG, Hebling J, de Souza Costa CA. Concentrations of and application protocols for hydrogen peroxide bleaching gels: effects on pulp cell viability and whitening efficacy. J Dent. 2014; 42:185–198.
Article3. Soares DG, Gonçalves Basso F, Hebling J, de Souza Costa CA. Effect of hydrogen-peroxide-mediated oxidative stress on human dental pulp cells. J Dent. 2015; 43:750–756.
Article4. Soares DG, Marcomini N, Basso FG, Pansani TN, Hebling J, de Souza Costa CA. Indirect cytocompatibility of a low-concentration hydrogen peroxide bleaching gel to odontoblast-like cells. Int Endod J. 2016; 49:26–36.
Article5. de Almeida LC, Costa CA, Riehl H, dos Santos PH, Sundfeld RH, Briso AL. Occurrence of sensitivity during at-home and in-office tooth bleaching therapies with or without use of light sources. Acta Odontol Latinoam. 2012; 25:3–8.6. Bonafe E, Bacovis CL, Iensen S, Loguercio AD, Reis A, Kossatz S. Tooth sensitivity and efficacy of in-office bleaching in restored teeth. J Dent. 2013; 41:363–369.
Article7. Costa CA, Riehl H, Kina JF, Sacono NT, Hebling J. Human pulp responses to in-office tooth bleaching. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010; 109:e59–e64.8. Paula E, Kossatz S, Fernandes D, Loguercio A, Reis A. The effect of perioperative ibuprofen use on tooth sensitivity caused by in-office bleaching. Oper Dent. 2013; 38:601–608.
Article9. Soares DG, Ribeiro AP, Lima AF, Sacono NT, Hebling J, de Souza Costa CA. Effect of fluoride-treated enamel on indirect cytotoxicity of a 16% carbamide peroxide bleaching gel to pulp cells. Braz Dent J. 2013; 24:121–127.
Article10. Reis A, Dalanhol AP, Cunha TS, Kossatz S, Loguercio AD. Assessment of tooth sensitivity using a desensitizer before light-activated bleaching. Oper Dent. 2011; 36:12–17.
Article11. Lima AF, Lessa FC, Hebling J, de Souza Costa CA, Marchi GM. Protective effect of sodium ascorbate on MDPC-23 odontoblast-like cells exposed to a bleaching agent. Eur J Dent. 2010; 4:238–244.12. Lima AF, Lessa FC, Mancini MN, Hebling J, Costa CA, Marchi GM. Transdentinal protective role of sodium ascorbate against the cytopathic effects of H2O2 released from bleaching agents. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010; 109:e70–e76.
Article13. Vargas Fda S, Soares DG, Basso FG, Hebling J, Costa CA. Dose-response and time-course of α-tocoferol mediating the cytoprotection of dental pulp cells against hydrogen peroxide. Braz Dent J. 2014; 25:367–371.14. de Paula EA, Kossatz S, Fernandes D, Loguercio AD, Reis A. Administration of ascorbic acid to prevent bleaching-induced tooth sensitivity: a randomized triple-blind clinical trial. Oper Dent. 2014; 39:128–135.
Article15. de Silveira Vargas F, Soares DG, Ribeiro AP, Hebling J, de Souza Costa CA. Protective effect of alphatocopherol isomer from vitamin E against the H2O2 induced toxicity on dental pulp cells. Biomed Res Int. 2014; 2014:895049.16. Lima AF, Fonseca FM, Freitas MS, Palialol AR, Aguiar FH, Marchi GM. Effect of bleaching treatment and reduced application time of an antioxidant on bond strength to bleached enamel and subjacent dentin. J Adhes Dent. 2011; 13:537–542.17. Whang HJ, Shin DH. Effects of applying antioxidants on bond strength of bleached bovine dentin. Restor Dent Endod. 2015; 40:37–43.
Article18. Park JY, Kwon TY, Kim YK. Effective application duration of sodium ascorbate antioxidant in reducing microleakage of bonded composite restoration in intracoronally-bleached teeth. Restor Dent Endod. 2013; 38:43–47.
Article19. Ekuni D, Tomofuji T, Sanbe T, Irie K, Azuma T, Maruyama T, Tamaki N, Murakami J, Kokeguchi S, Yamamoto T. Vitamin C intake attenuates the degree of experimental atherosclerosis induced by periodontitis in the rat by decreasing oxidative stress. Arch Oral Biol. 2009; 54:495–502.
Article20. Tomofuji T, Ekuni D, Sanbe T, Irie K, Azuma T, Maruyama T, Tamaki N, Murakami J, Kokeguchi S, Yamamoto T. Effects of vitamin C intake on gingival oxidative stress in rat periodontitis. Free Radic Biol Med. 2009; 46:163–168.
Article21. Sanbe T, Tomofuji T, Ekuni D, Azuma T, Irie K, Tamaki N, Yamamoto T, Morita M. Vitamin C intake inhibits serum lipid peroxidation and osteoclast differentiation on alveolar bone in rats fed on a high-cholesterol diet. Arch Oral Biol. 2009; 54:235–240.
Article22. Patra RC, Swarup D, Dwivedi SK. Antioxidant effects of alpha tocopherol, ascorbic acid and L-methionine on lead induced oxidative stress to the liver, kidney and brain in rats. Toxicology. 2001; 162:81–88.
Article23. Chandra Jagetia G, Rajanikant GK, Rao SK, Shrinath Baliga M. Alteration in the glutathione, glutathione peroxidase, superoxide dismutase and lipid peroxidation by ascorbic acid in the skin of mice exposed to fractionated gamma radiation. Clin Chim Acta. 2003; 332:111–121.
Article24. Nandi D, Patra RC, Swarup D. Effect of cysteine, methionine, ascorbic acid and thiamine on arsenic-induced oxidative stress and biochemical alterations in rats. Toxicology. 2005; 211:26–35.
Article25. Jagetia GC, Rajanikant GK, Rao SK. Evaluation of the effect of ascorbic acid treatment on wound healing in mice exposed to different doses of fractionated gamma radiation. Radiat Res. 2003; 159:371–380.
Article26. Kaplan B, Gönül B, Dinçer S, Dincer Kaya FN, Babül A. Relationships between tensile strength, ascorbic acid, hydroxyproline, and zinc levels of rabbit full-thickness incision wound healing. Surg Today. 2004; 34:747–751.
Article27. Kadirvel R, Sundaram K, Mani S, Samuel S, Elango N, Panneerselvam C. Supplementation of ascorbic acid and alpha-tocopherol prevents arsenic-induced protein oxidation and DNA damage induced by arsenic in rats. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2007; 26:939–946.
Article28. Chandler NP. The radiographic assessment of pulp size: validity and clinical implications. N Z Dent J. 1989; 85:23–26.29. Kina JF, Huck C, Riehl H, Martinez TC, Sacono NT, Ribeiro AP, Costa CA. Response of human pulps after professionally applied vital tooth bleaching. Int Endod J. 2010; 43:572–580.
Article30. Roderjan DA, Stanislawczuk R, Hebling J, de Souza Costa CA, Soares DG, Reis A, Loguercio AD. Histopathological features of dental pulp tissue from bleached mandibular incisors. J Mater Sci Eng B. 2014; 6:178–185.31. Costa CA, Oliveira MF, Giro EM, Hebling J. Biocompatibility of resin-based materials used as pulpcapping agents. Int Endod J. 2003; 36:831–839.
Article32. Accorinte Mde L, Loguercio AD, Reis A, Muench A, de Araújo VC. Response of human pulp capped with a bonding agent after bleeding control with hemostatic agents. Oper Dent. 2005; 30:147–155.33. de Souza Costa CA, Hebling J, Scheffel DL, Soares DG, Basso FG, Ribeiro AP. Methods to evaluate and strategies to improve the biocompatibility of dental materials and operative techniques. Dent Mater. 2014; 30:769–784.
Article34. Kadirvel R, Sundaram K, Mani S, Samuel S, Elango N, Panneerselvam C. Supplementation of ascorbic acid and alpha-tocopherol prevents arsenic-induced protein oxidation and DNA damage induced by arsenic in rats. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2007; 26:939–946.
Article35. Moores J. Vitamin C: a wound healing perspective. Br J Community Nurs. 2013; Suppl. S6. S8. S11.
Article36. Levine M, Padayatty SJ, Espey MG. Vitamin C: a concentration-function approach yields pharmacology and therapeutic discoveries. Adv Nutr. 2011; 2:78–88.
Article37. Padayatty SJ, Sun H, Wang Y, Riordan HD, Hewitt SM, Katz A, Wesley RA, Levine M. Vitamin C pharmacokinetics: implications for oral and intravenous use. Ann Intern Med. 2004; 140:533–537.
Article38. Schmalz G, Smith AJ. Pulp development, repair, and regeneration: challenges of the transition from traditional dentistry to biologically based therapies. J Endod. 2014; 40:S2–S5.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pulp necrosis following luxated injury to teeth in a patient with uncontrolled type II diabetes mellitus: a case report
- Cases report of autotransplantation of immature teeth
- A STUDY ON THE HUMAN PULPAL RESPONSE TO DENTIN BONDING DESENSITIZER
- Orthodontic bonding to acid- or laser-etched prebleached enamel
- Evaluation of the periodontal and pulpal healing of replanted rat molars with doxycycline root conditioning