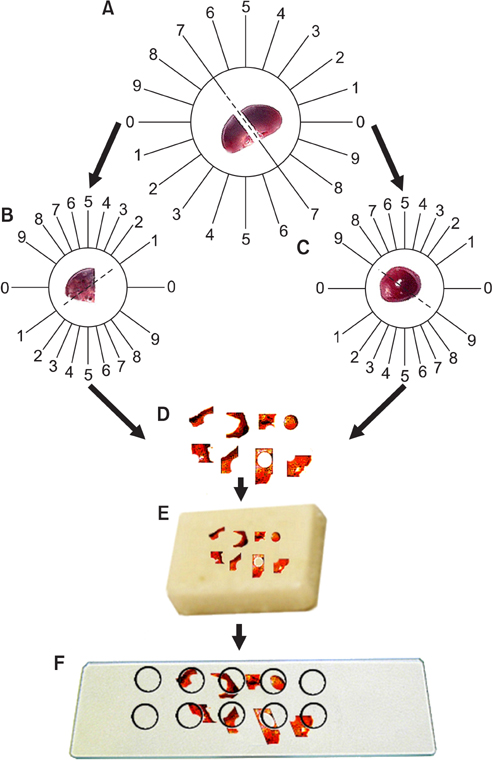
Korean J Urol.
2013 Apr;54(4):252-257.
Diosmin Reduces Calcium Oxalate Deposition and Tissue Degeneration in Nephrolithiasis in Rats: A Stereological Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Histomorphometry and Stereology Research Center, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Shiraz, Iran. karbalas@sums.ac.ir
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Kidney stones (nephrolithiasis) are a widespread disease. Thus, blocking stone formation and finding new therapeutic methods is an important area of study. Diosmin (a major component of the bile) is known to have antioxidant as well as renoprotective effects. The present investigation aimed to evaluate the effect of diosmin on renal tissue protection in rats with ethylene glycol-induced nephrolithiasis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The rats were randomly divided into three groups. Group one (control) did not receive any treatments. In groups two and three, nephrolithiasis was induced by 2.5% (V/V) ethylene glycol + 2.5% (W/V) ammonium chloride (2 mL/d). The second and the third groups received distilled water or diosmin (80 mg/kg/d) by gavage for 21 days.
RESULTS
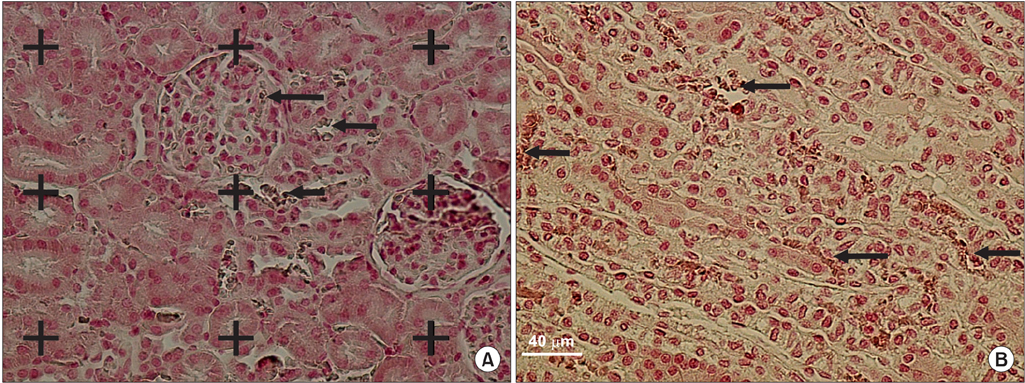
Stereological estimation of the renal structures revealed that the average volume of calcium oxalate (CaOx) in the nephrolithiasis+diosmin rats was -63% less than in the rats with untreated nephrolithiasis (p<0.01). The volume of the glomeruli, proximal and distal convoluted tubules, Henle's loop, collecting ducts, and vessels was reduced -32% to 58% after the induction of nephrolithiasis (p<0.001). In the nephrolithiasis+diosmin rats, on average, -70% to 96% of the glomeruli, proximal convoluted tubules, Henle's loop collecting ducts, and vessels remained intact (p<0.01). Degeneration of the cortical tissue was 5-fold that of the medulla. In the nephrolithiasis+diosmin rats, degeneration in the renal cortical tissue and medulla was reduced -70% and 44%, respectively, compared with that in the untreated nephrolithiasis group (p<0.01).
CONCLUSIONS
Diosmin reduces CaOx deposition and the degeneration of glomeruli and tubules in a rat model of nephrolithiasis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Tamamoto LC, Schmidt SJ, Lee SY. Sensory profile of a model energy drink with varying levels of functional ingredients-caffeine, ginseng, and taurine. J Food Sci. 2010. 75:S271–S278.2. Srinivasan S, Pari L. Ameliorative effect of diosmin, a citrus flavonoid against streptozotocin-nicotinamide generated oxidative stress induced diabetic rats. Chem Biol Interact. 2012. 195:43–51.3. Jean T, Bodinier MC. Mediators involved in inflammation: effects of Daflon 500 mg on their release. Angiology. 1994. 45(6 Pt 2):554–559.4. Labrid C. Pharmacologic properties of Daflon 500 mg. Angiology. 1994. 45(6 Pt 2):524–530.5. Rezai-Zadeh K, Douglas Shytle R, Bai Y, Tian J, Hou H, Mori T, et al. Flavonoid-mediated presenilin-1 phosphorylation reduces Alzheimer's disease beta-amyloid production. J Cell Mol Med. 2009. 13:574–588.6. Benavente-Garcia O, Castillo J. Update on uses and properties of citrus flavonoids: new findings in anticancer, cardiovascular, and anti-inflammatory activity. J Agric Food Chem. 2008. 56:6185–6205.7. Lopez M, Hoppe B. History, epidemiology and regional diversities of urolithiasis. Pediatr Nephrol. 2010. 25:49–59.8. Kohri K, Takada M, Katoh Y, Kataoka K, Iguchi M, Kurita T. Amino acids in urine and plasma of urolithiasis patients. Int Urol Nephrol. 1989. 21:9–16.9. Hyde DM, Tyler NK, Plopper CG. Morphometry of the respiratory tract: avoiding the sampling, size, orientation, and reference traps. Toxicol Pathol. 2007. 35:41–48.10. Bouskela E, Cyrino FZ, Lerond L. Leukocyte adhesion after oxidant challenge in the hamster cheek pouch microcirculation. J Vasc Res. 1999. 36:Suppl 1. 11–14.11. Li CY, Deng YL, Sun BH. Taurine protected kidney from oxidative injury through mitochondrial-linked pathway in a rat model of nephrolithiasis. Urol Res. 2009. 37:211–220.12. Scherle W. A simple method for volumetry of organs in quantitative stereology. Mikroskopie. 1970. 26:57–60.13. Nyengaard JR. Stereologic methods and their application in kidney research. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999. 10:1100–1123.14. Gundersen HJ, Bagger P, Bendtsen TF, Evans SM, Korbo L, Marcussen N, et al. The new stereological tools: disector, fractionator, nucleator and point sampled intercepts and their use in pathological research and diagnosis. APMIS. 1988. 96:857–881.15. Gundersen HJ, Bendtsen TF, Korbo L, Marcussen N, Moller A, Nielsen K, et al. Some new, simple and efficient stereological methods and their use in pathological research and diagnosis. APMIS. 1988. 96:379–394.16. Corley RA, Meek ME, Carney EW. Mode of action: oxalate crystal-induced renal tubule degeneration and glycolic acid-induced dysmorphogenesis: renal and developmental effects of ethylene glycol. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2005. 35:691–702.17. Saha S, Verma RJ. Bergenia ciliata extract prevents ethylene glycol induced histopathological changes in the kidney. Acta Pol Pharm. 2011. 68:711–715.18. Khan SR. Calcium oxalate crystal interaction with renal tubular epithelium, mechanism of crystal adhesion and its impact on stone development. Urol Res. 1995. 23:71–79.19. Tsujihata M. Mechanism of calcium oxalate renal stone formation and renal tubular cell injury. Int J Urol. 2008. 15:115–120.20. Ebisuno S, Kohjimoto Y, Tamura M, Ohkawa T. Adhesion of calcium oxalate crystals to Madin-Darby canine kidney cells and some effects of glycosaminoglycans or cell injuries. Eur Urol. 1995. 28:68–73.21. Scheid C, Koul H, Hill WA, Luber-Narod J, Kennington L, Honeyman T, et al. Oxalate toxicity in LLC-PK1 cells: role of free radicals. Kidney Int. 1996. 49:413–419.22. Wiessner JH, Hasegawa AT, Hung LY, Mandel NS. Oxalate-induced exposure of phosphatidylserine on the surface of renal epithelial cells in culture. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999. 10:Suppl 14. S441–S445.23. Thamilselvan S, Byer KJ, Hackett RL, Khan SR. Free radical scavengers, catalase and superoxide dismutase provide protection from oxalate-associated injury to LLC-PK1 and MDCK cells. J Urol. 2000. 164:224–229.24. Itoh Y, Yasui T, Okada A, Tozawa K, Hayashi Y, Kohri K. Preventive effects of green tea on renal stone formation and the role of oxidative stress in nephrolithiasis. J Urol. 2005. 173:271–275.25. Sarica K, Yagci F, Bakir K, Erbagci A, Erturhan S, Ucak R. Renal tubular injury induced by hyperoxaluria: evaluation of apoptotic changes. Urol Res. 2001. 29:34–37.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Oral administration of oxalate decarboxylase prevents hyperoxaluria and renal calcium oxalate stone formation in ethylene glycolinduced nephrolithiasis rats
- Effectiveness of Magnesium Oxide and Sodium Thiosulfate in Calcium Oxalate Crystallization
- Effect of Male Sex Hormones on Calcium Oxalate Nephrolithiasis in Ethylene Glycol-Treated Rats
- Management of Urinary Stone with Potassium Citrate
- Development of Animal Model of Nephrolithiasis