Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
2014 Jun;17(2):121-124.
Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid for Cholestasis due to Bile Duct Paucity
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. baedori@hanafos.com
- 2Department of Radiology, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of General Surgery, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
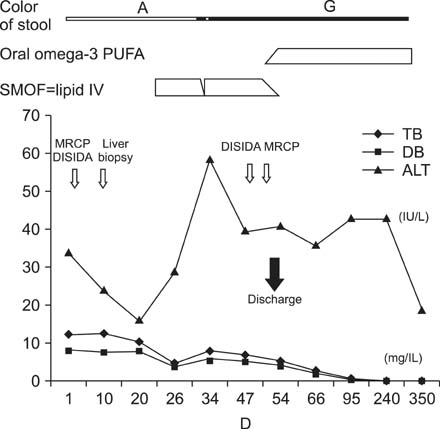
- Omega (omega)-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids appear to be effective in preventing and treating parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease, and several mechanisms were proposed for this observation. An 8-week-old male infant with cholestasis and acholic stool was diagnosed non-syndromic intrahepatic interlobular bile duct paucity by open-wedge liver biopsy. Initially he was treated with usual supportive medical therapy, including ursodeoxycholic acid. However, the clinical status and laboratory tests did not improve. Omega (omega)-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (initially intravenous administration and oral administration later), were started and his liver function, including aminotransferase level and bilirubin levels normalized, and the ivory stool color turned green. We report the possible effectiveness of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids as a potent choleretic agent for non-syndromic intrahepatic interlobular bile duct paucity, a very rare structural pediatric hepatic disease.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. de Meijer VE, Gura KM, Le HD, Meisel JA, Puder M. Fish oil-based lipid emulsions prevent and reverse parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease: the Boston experience. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2009; 33:541–547.
Article2. Rollins MD, Scaife ER, Jackson WD, Meyers RL, Mulroy CW, Book LS. Elimination of soybean lipid emulsion in parenteral nutrition and supplementation with enteral fish oil improve cholestasis in infants with short bowel syndrome. Nutr Clin Pract. 2010; 25:199–204.
Article3. Gura KM, Lee S, Valim C, Zhou J, Kim S, Modi BP, et al. Safety and efficacy of a fish-oil-based fat emulsion in the treatment of parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease. Pediatrics. 2008; 121:e678–e686.
Article4. Alwayn IP, Gura K, Nosé V, Zausche B, Javid P, Garza J, et al. Omega-3 fatty acid supplementation prevents hepatic steatosis in a murine model of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Pediatr Res. 2005; 57:445–452.
Article5. Clarke SD, Jump DB. Dietary polyunsaturated fatty acid regulation of gene transcription. Annu Rev Nutr. 1994; 14:83–98.
Article6. Bagga D, Wang L, Farias-Eisner R, Glaspy JA, Reddy ST. Differential effects of prostaglandin derived from omega-6 and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on COX-2 expression and IL-6 secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003; 100:1751–1756.
Article7. Calder PC. Mechanisms of action of (n-3) fatty acids. J Nutr. 2012; 142:592S–599S.
Article8. Serhan CN, Hong S, Gronert K, Colgan SP, Devchand PR, Mirick G, et al. Resolvins: a family of bioactive products of omega-3 fatty acid transformation circuits initiated by aspirin treatment that counter proinflammation signals. J Exp Med. 2002; 196:1025–1037.9. Bérard AM, Dumon MF, Darmon M. Dietary fish oil up-regulates cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase mRNA in mouse liver leading to an increase in bile acid and cholesterol excretion. FEBS Lett. 2004; 559:125–128.
Article10. Ramaprasad TR, Srinivasan K, Baskaran V, Sambaiah K, Lokesh BR. Spray-dried milk supplemented with alpha-linolenic acid or eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid decreases HMG Co A reductase activity and increases biliary secretion of lipids in rats. Steroids. 2006; 71:409–415.
Article11. Mercer DF, Hobson BD, Fischer RT, Talmon GA, Perry DA, Gerhardt BK, et al. Hepatic fibrosis persists and progresses despite biochemical improvement in children treated with intravenous fish oil emulsion. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2013; 56:364–369.
Article12. Lee S, Kim S, Le HD, Meisel J, Strijbosch RA, Nose V, et al. Reduction of hepatocellular injury after common bile duct ligation using omega-3 fatty acids. J Pediatr Surg. 2008; 43:2010–2015.
Article13. Chen CC, Ho CY, Chaung HC, Tain YL, Hsieh CS, Kuo FY, et al. Fish omega-3 fatty acids induce liver fibrosis in the treatment of bile duct-ligated rats. Dig Dis Sci. 2013; 58:440–447.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Use of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids to Treat Inspissated Bile Syndrome: A Case Report
- Clinical Evaluation of Syndromic and Nonsyndromic Intrahepatic Bile Duct Paucity
- The Clinicopathological Parameters for Making the Differential Diagnosis of Neonatal Cholestasis
- Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Children
- Association between Omega Fatty Acid Intake and Suicidality : Sex Differences in the General Korean Population