Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis.
2012 Sep;22(3):224-231.
Nationwide Survey on the Prevalence of Allergic Diseases according to Region and Age
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. sonbk@inha.ac.kr
- 2Environmental Health Center, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
It is widely known that allergic diseases progress through a sequential course known as the allergic march. However, there have been no recent reports in Korea regarding the progress of allergic diseases based on the medical claim data of the National Health Insurance Corporation.
METHODS
Medical claim data of 2005 and 2008 from the National Health Insurance Corporation were used. Data was classified according to the administrative districts of metropolitan cities and provinces, and divided according to age in increments of 5 years.
RESULTS
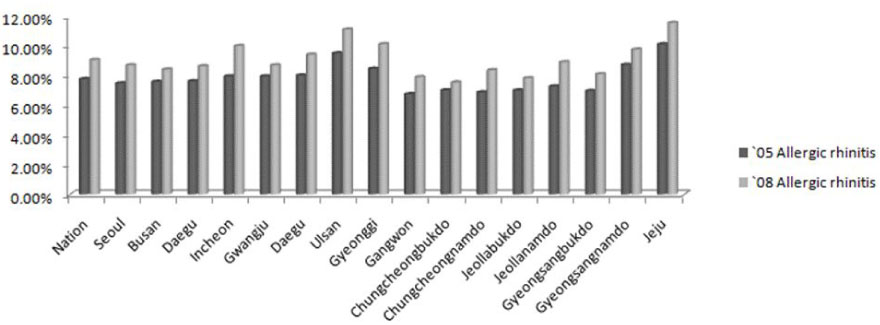
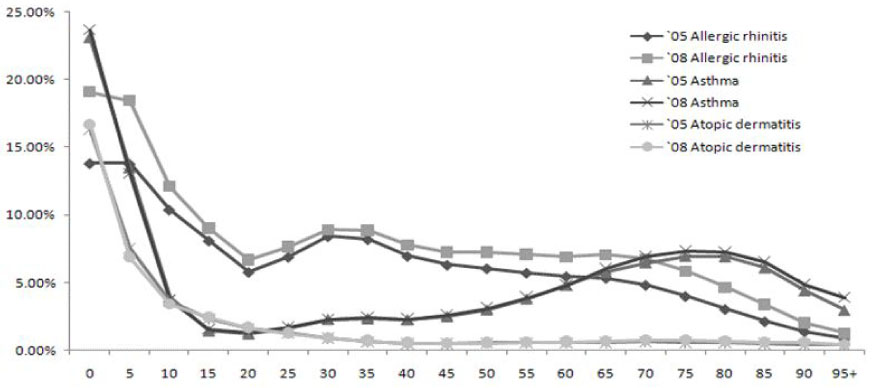
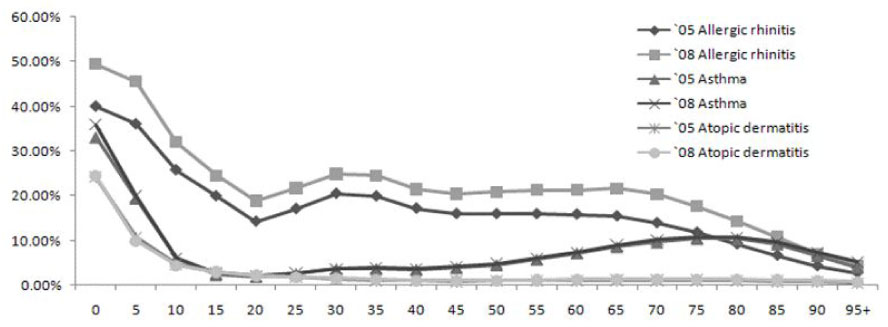
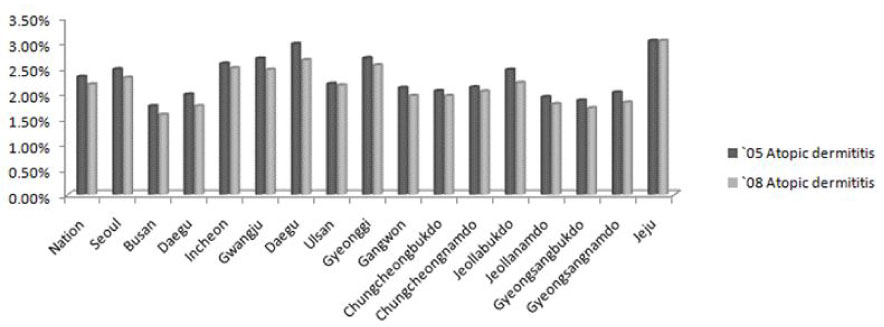
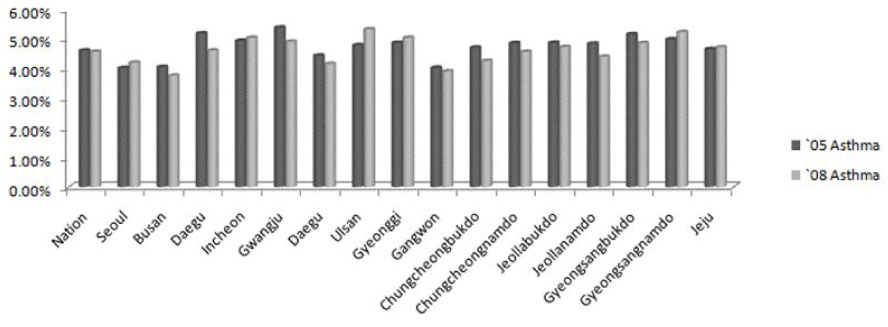
According to the nationwide survey on the prevalence of allergic diseases according to region, the prevalence of allergic diseases increased in 2008 compared to 2005. Especially, the prevalence of allergic rhinitis significantly rises in all regions. When comparing the prevalence of allergic diseases according to age, there was no significant difference in the prevalence of atopic dermatitis and asthma between 2005 and 2008. In contrast, allergic rhinitis demonstrated a rise of more than 5% in all age groups.
CONCLUSION
According to the nationwide survey on the prevalence of allergic diseases using the medical claim data from the National Health Insurance Corporation, the prevalence of allergic rhinitis had significantly increased in 2008 compared to 2005. More survey studies should be conducted in the future using the medical claim data of the National Health Insurance Corporation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. The International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC) Steering Committee. Worldwide variation in prevalence of symptoms of asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and atopic eczema: ISAAC. Lancet. 1998. 351:1225–1232.2. Asher MI, Montefort S, Bjorksten B, Lai CK, Strachan DP, Weiland SK, et al. Worldwide time trends in the prevalence of symptoms of asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and eczema in childhood: ISAAC Phases One and Three repeat multicountry cross-sectional surveys. Lancet. 2006. 368:733–743.
Article3. Eder W, Ege MJ, von Mutius E. The asthma epidemic. N Engl J Med. 2006. 355:2226–2235.
Article4. Lee SI, Shin MH, Lee HB, Lee JS, Son BK, Koh YY, et al. Prevalences of symptoms of asthma and other allergic diseases in Korean children: a nationwide questionnaire survey. J Korean Med Sci. 2001. 16:155–164.
Article5. Hong SJ, Kim SW, Oh JW, Rah YH, Ahn YM, Kim KE, et al. The validity of the ISAAC Written Questionnaire and the ISAAC Video Questionnaire (AVQ 3.0)for predicting asthma associated with bronchial hyperreactivity in a group of 13-14 year old Korean schoolchildren. J Korean Med Sci. 2003. 18:48–52.
Article6. Oh JW, Kim KE, Pyun BY, Lee HR, Choung JT, Hong SJ, et al. Nationwide study for epidemiological change of atopic dermatitis in school aged children between 1995 and 2000 and kindergarten aged children in 2003 in Korea. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2003. 13:227–237.7. Oh JW, Pyun BY, Choung JT, Ahn KM, Kim CH, Song SW, et al. Epidemiological change of atopic dermatitis and food allergy in school-aged children in Korea between 1995 and 2000. J Korean Med Sci. 2004. 19:716–723.
Article8. Hong SJ, Lee MS, Sohn MH, Shim JY, Han YS, Park KS, et al. Self-reported prevalence and risk factors of asthma among Korean adolescents: 5-year follow-up study, 1995-2000. Clin Exp Allergy. 2004. 34:1556–1562.
Article9. Virnig BA, McBean M. Administrative data for public health surveillance and planning. Annu Rev Public Health. 2001. 22:213–230.
Article10. Kim JY. Using national health insurance data to vitalize the evidence-based health care: the current status and tasks. The Korean society for preventive medicine winter symposium. 2007. 2007 Feb 13; Seoul: The Korean society for preventive medicine;1–28.11. Peat JK, van den Berg RH, Green WF, Mellis CM, Leeder SR, Woolcock AJ. Changing prevalence of asthma in Australian children. BMJ. 1994. 308:1591–1596.
Article12. Hong SJ, Ahn KM, Lee SY, Kim KE. The prevalences of asthma and allergic diseases in Korean children. Korean J Pediatr. 2008. 51:343–350.
Article13. Hong SJ. Korean ISSAC Study Group of Korean Association of Allergy and Respiratory Disease; Report of Korean ISAAC epidemiology study for asthma and allergic diseases in children. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2007. 17:Suppl 1. 56–66.14. Motheral BR, Fairman KA. The use of claims databases for outcomes research: rationale, challenges, and strategies. Clin Ther. 1997. 19:346–366.
Article15. Wennberg J, Gittelsohn A. Small area variations in health care delivery. Science. 1973. 182:1102–1108.
Article16. Jencks SF, Huff ED, Cuerdon T. Change in the quality of care delivered to Medicare beneficiaries, 1998-1999 to 2000-2001. JAMA. 2003. 289:305–312.
Article17. Jiang HJ, Friedman B, Begun JW. Factors associated with high-quality/low-cost hospital performance. J Health Care Finance. 2006. 32:39–52.18. Park BJ, Sung JH, Park KD, Seo SW, Kim SH. (Report of Research service project in 2002 by Seoul University College of Medicine Health Insurance Review&Assessment service). Plan on improving the validity of the type of disease in health insurance and establishment of its application. 2003. Seoul: Seoul National University School of Medicine.19. Kim JY. Basis of using health insurance data, strategic, and assignment from the computation of health statistic. The 4th statistically innovation forum; Facts and figures on utilization of insurance statistics and pension statistics. 2005. Seoul: National Medicine Health Insurance.20. Pladevall M, Williams LK, Potts LA, Divine G, Xi H, Lafata JE. Clinical outcomes and adherence to medications measured by claims data in patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2004. 27:2800–2805.
Article21. Powell KE, Diseker RA 3rd, Presley RJ, Tolsma D, Harris S, Mertz KJ, et al. Administrative data as a tool for arthritis surveillance: estimating prevalence and utilization of services. J Public Health Manag Pract. 2003. 9:291–298.22. Hennessy S, Bilker WB, Knauss JS, Margolis DJ, Kimmel SE, Reynolds RF, et al. Cardiac arrest and ventricular arrhythmia in patients taking antipsychotic drugs: cohort study using administrative data. BMJ. 2002. 325:1070.
Article23. Tirschwell DL, Longstreth WT Jr. Validating administrative data in stroke research. Stroke. 2002. 33:2465–2470.
Article24. Hux JE, Ivis F, Flintoft V, Bica A. Diabetes in Ontario: determination of prevalence and incidence using a validated administrative data algorithm. Diabetes Care. 2002. 25:512–516.25. Hammar N, Alfredsson L, Rosen M, Spetz CL, Kahan T, Ysberg AS. A national record linkage to study acute myocardial infarction incidence and case fatality in Sweden. Int J Epidemiol. 2001. 30:Suppl 1. S30–S34.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ten-Year trends and prevalence of asthma, allergic rhinitis, and atopic dermatitis among the Korean population, 2008–2017
- Changing Prevalence of Allergic Diseases in the Asia-Pacific Region
- Higher anxiety, stress, and suicidal behaviors in allergic adolescents: A Nationwide Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-Based Survey 2022
- The Prevalence of Atopic Dermatitis, Asthma, and Allergic Rhinitis and the Comorbidity of Allergic Diseases in Children
- A Survey of Allergic Diseases in University Students of Bangkok, Thailand