Korean J Urol.
2010 Jul;51(7):450-455.
Efficacy and Safety of Sunitinib on Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Single-Institution Experience
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. uro17@cnu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We assessed the efficacy and safety of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor sunitinib in Korean patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between September 2007 and December 2009, all twenty-one patients who had mRCC with a clear-cell component were retrospectively reviewed. Sunitinib was administered orally at a dose of 50 mg daily until disease progression or intolerance to treatment occurred. The primary end point of this study was the objective tumor response assessed by Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST), and the secondary end points were progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) rates as well as assessment of adverse effects.
RESULTS
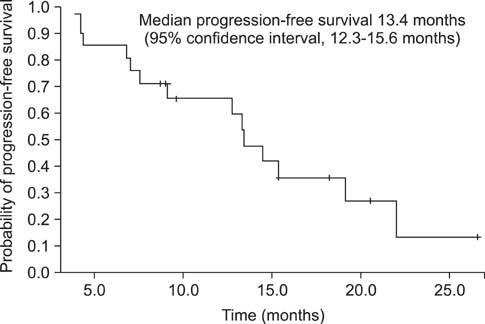
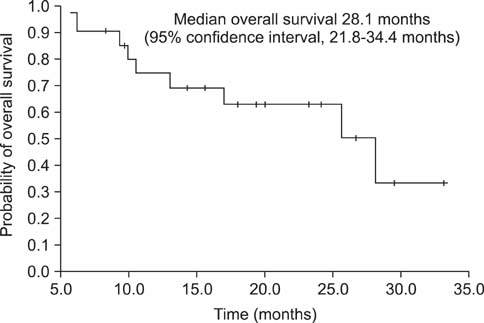
After a median of 17.4 months (range, 5.7-33.1 months) of treatment, 11 patients (52.4%) had an objective response with a complete response in 1 patient (4.8%), and a partial response in 10 patients (47.6%) as the best tumor response. The median PFS was 13.4 months (95% confidence interval [CI], range, 12.3-14.5 months), and the median OS was 28.1 months (95% CI, 21.8-34.4 months). All patients experienced adverse events of some sort, but the studied treatment protocol was well tolerated and most patients experienced reversible grade 1 or 2 toxicities.
CONCLUSIONS
Sunitinib was efficacious in the treatment of metastatic clear-cell RCC, and was well tolerated in Korean patients. Although sunitinib treatment-related adverse events such as hand-foot syndrome and facial/generalized edema were observed with a higher incidence than in Western trials, they were mainly mild to moderate, and readily managed.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005. 55:74–108.2. Lam JS, Leppert JT, Belldegrun AS, Figlin RA. Novel approaches in the therapy of metastatic renal cell carcinoma. World J Urol. 2005. 23:202–212.3. Motzer RJ, Russo P, Nanus DM, Berg WJ. Renal cell carcinoma. Curr Probl Cancer. 1997. 21:185–232.4. Janzen NK, Kim HL, Figlin RA, Belldegrun AS. Surveillance after radical or partial nephrectomy for localized renal cell carcinoma and management of recurrent disease. Urol Clin North Am. 2003. 30:843–852.5. Law TM, Motzer RJ, Mazumdar M, Sell KW, Walther PJ, O'Connell M, et al. Phase III randomized trial of interleukin-2 with or without lymphokine-activated killer cells in the treatment of patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. Cancer. 1995. 76:824–832.6. Linehan WM, Vasselli J, Srinivasan R, Walther MM, Merino M, Choyke P, et al. Genetic basis of cancer of the kidney: disease-specific approaches to therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. 10:6282S–6289S.7. Kim WY, Kaelin WG. Role of VHL gene mutation in human cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2004. 22:4991–5004.8. Mendel DB, Laird AD, Xin X, Louie SG, Christensen JG, Li G, et al. In vivo antitumor activity of SU11248, a novel tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeting vascular endothelial growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor receptors: determination of a pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationship. Clin Cancer Res. 2003. 9:327–337.9. Motzer RJ, Michaelson MD, Redman BG, Hudes GR, Wilding G, Figlin RA, et al. Activity of SU11248, a multitargeted inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor and platelet-derived growth factor receptor, in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2006. 24:16–24.10. Motzer RJ, Rini BI, Bukowski RM, Curti BD, George DJ, Hudes GR, et al. Sunitinib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. JAMA. 2006. 295:2516–2524.11. Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P, Michaelson MD, Bukowski RM, Rixe O, et al. Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007. 356:115–124.12. Motzer RJ, Bacik J, Schwartz LH, Reuter V, Russo P, Marion S, et al. Prognostic factors for survival in previously treated patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2004. 22:454–463.13. Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, Wanders J, Kaplan RS, Rubinstein L, et al. New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000. 92:205–216.14. Cohen HT, McGovern FJ. Renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2005. 353:2477–2490.15. Hudes G, Carducci M, Tomczak P, Dutcher J, Figlin R, Kapoor A, et al. Temsirolimus, interferon alfa, or both for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007. 356:2271–2281.16. Yang JC, Haworth L, Sherry RM, Hwu P, Schwartzentruber DJ, Topalian SL, et al. A randomized trial of bevacizumab, an anti-vascular endothelial growth factor antibody, for metastatic renal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003. 349:427–434.17. Escudier B, Eisen T, Stadler WM, Szczylik C, Oudard S, Siebels M, et al. Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007. 356:125–134.18. Bellmunt J, Flodgren P, Roigas J, Oudard S. Optimal management of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: an algorithm for treatment. BJU Int. 2009. 104:10–18.19. Chu TF, Rupnick MA, Kerkela R, Dallabrida SM, Zurakowski D, Nguyen L, et al. Cardiotoxicity associated with tyrosine kinase inhibitor sunitinib. Lancet. 2007. 370:2011–2019.20. Rini BI, Tamaskar I, Shaheen P, Salas R, Garcia J, Wood L, et al. Hypothyroidism in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with sunitinib. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2007. 99:81–83.21. Kollmannsberger C, Soulieres D, Wong R, Scalera A, Gaspo R, Bjarnason G. Sunitinib therapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: recommendations for management of side effects. Can Urol Assoc J. 2007. 1:2 Suppl. 41S–54S.22. Hong MH, Kim HS, Kim C, Ahn JR, Chon HJ, Shin SJ, et al. Treatment outcomes of sunitinib treatment in advanced renal cell carcinoma patients: a single cancer center experience in Korea. Cancer Res Treat. 2009. 41:67–72.23. Yoo C, Kim JE, Lee JL, Ahn JH, Lee DH, Lee JS, et al. The efficacy and safety of sunitinib in Korean patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma: high incidence of toxicity leads to frequent dose reduction. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2010. Epub ahead of print.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intolerance to Sunitinib Treatment in Hemodialysis Patients With Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Hypoglycemic Coma in a Patient with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Treated with Sunitinib
- Novel Sunitinib Strategy in Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma on Hemodialysis: Intermittent Dose of Sunitinib after Hemodialysis
- A Case of Sunitinib-Induced Destructive Thyroiditis
- A Case of Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma to the Maxillary Sinus Treated with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor