Nutr Res Pract.
2014 Apr;8(2):165-171.
Beneficial effects of natural Jeju groundwaters on lipid metabolism in high-fat diet-induced hyperlipidemic rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1School of Pharmacy, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 800 Dongchuan Road, Shanghai 200240, China. yxwang@sjtu.edu.cn
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Groundwater is believed to possess many beneficial effects due to its natural source of various minerals. In this study, we examined the effects of natural Jeju groundwater S1 (Samdasoo(TM)), S2 and S3 pumped up from different locations of Jeju Island, Korea, along with local tap water, on body weight gain, serum lipids and lipoproteins, and liver histopathology in high-fat diet-induced hyperlipidemic rats.
MATERIALS/METHODS
Rats were randomly and equally divided into 6 groups. Different water samples were supplied to the hyperlipidemic rats as their daily drinking water and the widely-used anti-hyperlipidemic drug simvastatin was used as a positive control. Body weight, serum lipids and lipoproteins were measured weekly. Liver weight, liver index and liver histopathology were examined after the execution of the rats.
RESULTS
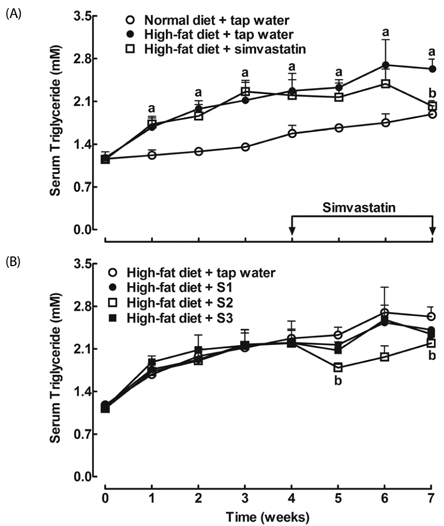
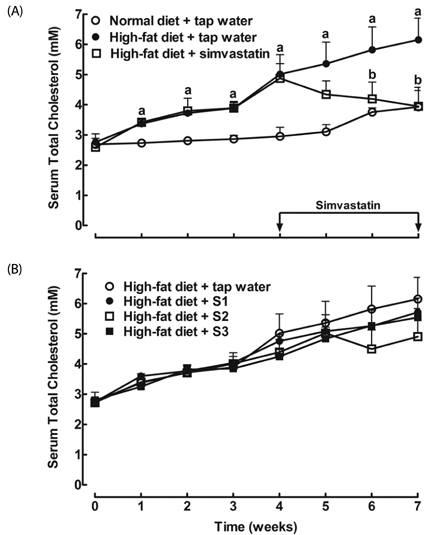
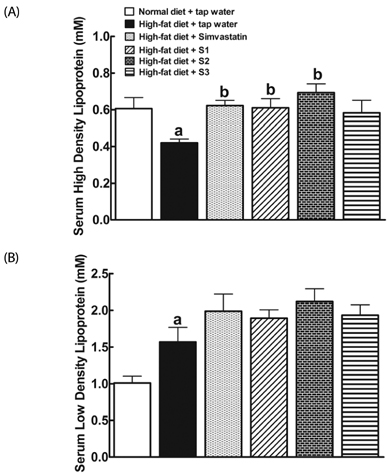
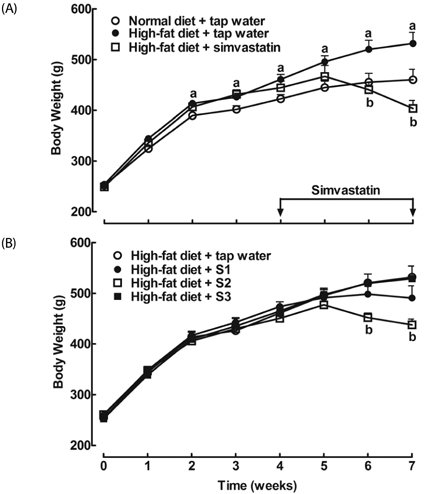
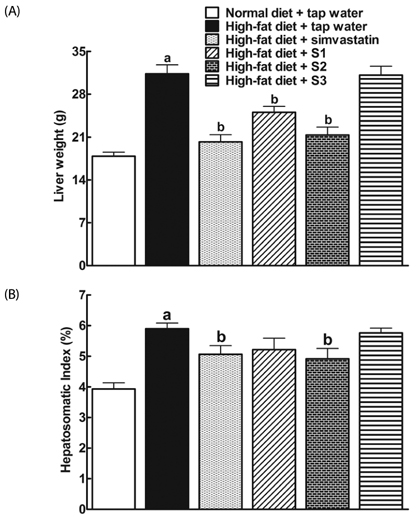
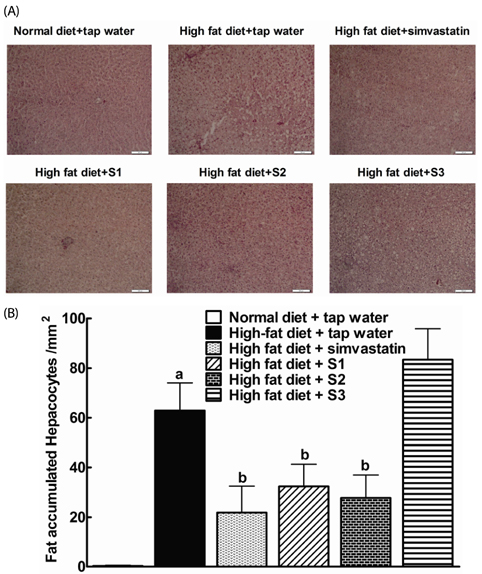
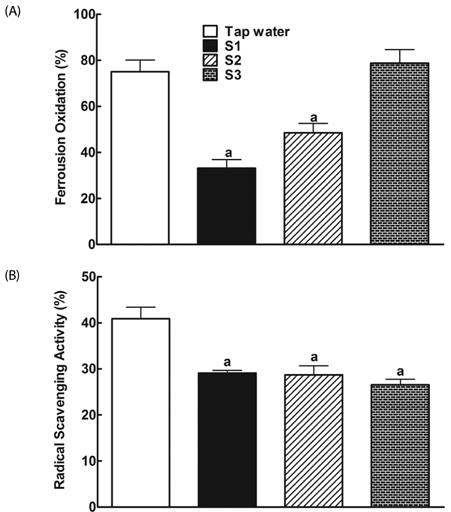
After drinking Jeju groundwaters for two months, S2 but not S3 significantly reduced weight growth and serum triglycerides levels and increased high density lipoprotein-C (HDL-C) without affecting total cholesterol or LDL-C. S1 and particularly S2 significantly reduced the severity of liver hypertrophy and steatosis. All Groundwaters had much higher contents of vanadium (S3>S2>S1>>tap water) whereas S1 and S2 but not S3 markedly blocked autoxidation of ferrous ions.
CONCLUSION
Jeju Groundwater S1 and particularly S2 exhibit protective effects against hyperlipidemia and fatty liver and hypothesize that the beneficial effect of Jeju Groundwaters may be contributed from blockade of autoxidation of ferrous ions rather than their high contents of vanadium.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Edmunds WM, Smedley PL. Groundwater geochemistry and health: an overview. Geol Soc Lond Spec Publ. 1996; 113:91–105.
Article2. Borgman RF, Lightsey SF. Effects of synthesized hard water and of cadmium in the drinking water upon lipid metabolism and cholelithiasis in rabbits. Am J Vet Res. 1982; 43:1432–1435.3. Porter LP, Borgman RF, Lightsey SF. Effects of water hardness upon lipid and mineral metabolism in rabbits. Nutr Res. 1988; 8:31–45.
Article4. Denke MA, Fox MM, Schulte MC. Short-term dietary calcium fortification increases fecal saturated fat content and reduces serum lipids in men. J Nutr. 1993; 123:1047–1053.5. Diersen-Schade DA, Richard MJ, Jacobson NL. Effects of dietary calcium and fat on cholesterol in tissues and feces of young goats. J Nutr. 1984; 114:2292–2300.
Article6. Yacowitz H, Fleischman AI, Amsden RT, Bierenbaum ML. Effects of dietary calcium upon lipid metabolism in rats fed saturated or unsaturated fat. J Nutr. 1967; 92:389–392.
Article7. Bhattacharyya AK, Thera C, Anderson JT, Grande F, Keys A. Dietary calcium and fat. Effect on serum lipids and fecal excretion of cholesterol and its degradation products in man. Am J Clin Nutr. 1969; 22:1161–1174.8. Shahkhalili Y, Murset C, Meirim I, Duruz E, Guinchard S, Cavadini C, Acheson K. Calcium supplementation of chocolate: effect on cocoa butter digestibility and blood lipids in humans. Am J Clin Nutr. 2001; 73:246–252.
Article9. Tolman EL, Barris E, Burns M, Pansini A, Partridge R. Effects of vanadium on glucose metabolism in vitro. Life Sci. 1979; 25:1159–1164.10. Hwang SL, Chang HW. Natural vanadium-containing Jeju ground water stimulates glucose uptake through the activation of AMP-activated protein kinase in L6 myotubes. Mol Cell Biochem. 2012; 360:401–409.
Article11. Curran GL. Effect of certain transition group elements on hepatic synthesis of cholesterol in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1954; 210:765–770.
Article12. Curran GL, Costello RL. Reduction of excess cholesterol in the rabbit aorta by inhibition of endogenous cholesterol synthesis. J Exp Med. 1956; 103:49–56.
Article13. Pepato MT, Magnani MR, Kettelhut IC, Brunetti IL. Effect of oral vanadyl sulfate treatment on serum enzymes and lipids of streptozotocin-diabetic young rats. Mol Cell Biochem. 1999; 198:157–161.14. Noh JR, Gang GT, Kim YH, Yang KJ, Lee CH, Na OS, Kim GJ, Oh WK, Lee YD. Desalinated underground seawater of Jeju Island (Korea) improves lipid metabolism in mice fed diets containing high fat and increases antioxidant potential in t-BHP treated HepG2 cells. Nutr Res Pract. 2010; 4:3–10.
Article15. Trinder P. Determination of glucose in blood using glucose oxidase with an alternative oxygen acceptor. Ann Clin Biochem. 1969; 6:24–27.
Article16. Bachorik PS, Ross JW. National Cholesterol Education Program recommendations for measurement of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol: executive summary. The National Cholesterol Education Program Working Group on Lipoprotein Measurement. Clin Chem. 1995; 41:1414–1420.
Article17. Collins R, Armitage J, Parish S, Sleight P, Peto R. Heart Protection Study Collaborative Group. Effects of cholesterol-lowering with simvastatin on stroke and other major vascular events in 20536 people with cerebrovascular disease or other high-risk conditions. Lancet. 2004; 363:757–767.
Article18. Pedersen TR, Kjekshus J, Berg K, Haghfelt T, Faergeman O, Faergeman G, Pyörälä K, Miettinen T, Wilhelmsen L, Olsson AG, Wedel H. Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study Group. Randomised trial of cholesterol lowering in 4444 patients with coronary heart disease: the Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study (4S). 1994. Atheroscler Suppl. 2004; 5:81–87.
Article19. Azarnoff DL, Curran GL. Site of vanadium inhibition of cholesterol biosynthesis. J Am Chem Soc. 1957; 79:2968–2969.
Article20. Kruszewski M. The role of labile iron pool in cardiovascular diseases. Acta Biochim Pol. 2004; 51:471–480.
Article21. Pietrangelo A. Iron, oxidative stress and liver fibrogenesis. J Hepatol. 1998; 28:Suppl 1. 8–13.
Article22. Mateo-Gallego R, Calmarza P, Jarauta E, Burillo E, Cenarro A, Civeira F. Serum ferritin is a major determinant of lipid phenotype in familial combined hyperlipidemia and familial hypertriglyceridemia. Metabolism. 2010; 59:154–158.
Article23. Bristow-Craig HE, Strain JJ, Welch RW. Iron status, blood lipids and endogenous antioxidants in response to dietary iron levels in male and female rats. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 1994; 64:324–329.24. George DK, Goldwurm S, MacDonald GA, Cowley LL, Walker NI, Ward PJ, Jazwinska EC, Powell LW. Increased hepatic iron concentration in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is associated with increased fibrosis. Gastroenterology. 1998; 114:311–318.
Article25. Hsiao TJ, Chen JC, Wang JD. Insulin resistance and ferritin as major determinants of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in apparently healthy obese patients. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2004; 28:167–172.
Article26. Uysal S, Armutcu F, Aydogan T, Akin K, Ikizek M, Yigitoglu MR. Some inflammatory cytokine levels, iron metabolism and oxidan stress markers in subjects with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Clin Biochem. 2011; 44:1375–1379.
Article27. Bozzini C, Girelli D, Olivieri O, Martinelli N, Bassi A, De Matteis G, Tenuti I, Lotto V, Friso S, Pizzolo F, Corrocher R. Prevalence of body iron excess in the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Care. 2005; 28:2061–2063.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Dietary Fat and Genistein on Lipid Metabolism and Antioxidant Activity in Hyperlipidemic Male Rats induced High Fat Diet
- Anti-obesity effect of Korean Hamcho (Salicornia herbacea L.) powder on high-fat diet-induced obese rats
- Effects of Cheonggukjang on Lipid Metabolism in Hyperlipidemic Female Rats
- Effects of Genistein Supplementation on Fatty Liver and Lipid Metabolism in Rats Fed High Fat Diet
- Effect of Chlorella vulgaris on lipid metabolism in Wistar rats fed high fat diet