Nutr Res Pract.
2013 Jun;7(3):172-177.
Effect of Phellius linteus water extract on benign prostatic hyperplasia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Food Science, International University of Korea, Gyeongnam 660-759, Korea.
- 2Department of Food and Nutrition, International University of Korea, 270 San, Sangmun, Munsan, Gyeongnam 660-759, Korea. jhappychoi@hanmail.net
Abstract
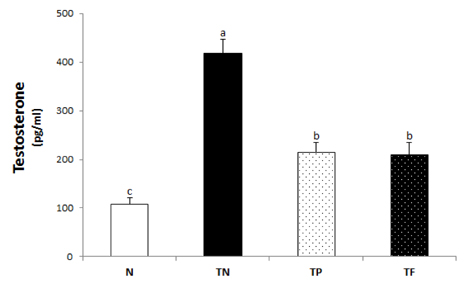
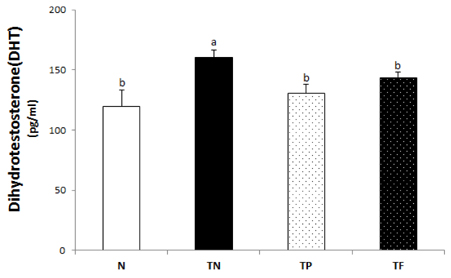
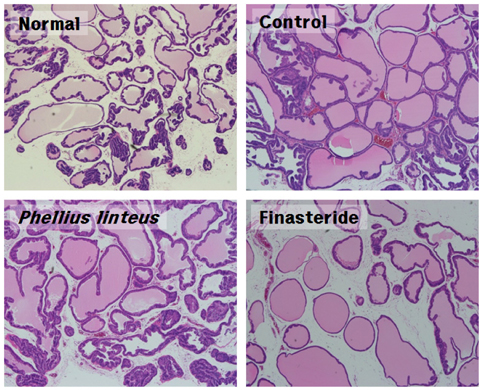
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is one of the most common diseases among elderly men. As the old-age population is increasing recently, it is to our interest to observe the growing BPH within them. In BPH, the dihydrotestosterone (DHT) acts as promotes prostate growth. It inhibits enzyme 5alpha-reductase that is involved in the conversion of testosterone to the DHT activity which reduces the excessive prostate growth. Through experiments, the effects of Phellius linteus water extract performed on the BPH rats were induced by testosterone treatments. For 12 weeks, Sprague-Dawley rats were treated with testosterone for the induction of BPH. Rats were divided into four experimental groups: the not treated group (N), the testosterone injection and D.W treatment group (TN), the testosterone injection and Phellinus linteus treatment group (TP) and testosterone injection and finasteride treatment group (TF). Prostate weight, volume and weight ratio in the TP group and the TF group were significantly lower than the TN group. Testosterone and DHT levels in the TN group were significantly higher than that of the N group. And the TP group was significantly decreased than that of the TN group. While prostates of control rats revealed severe acinar gland atrophy and stromal proliferation; the TP and TF groups showed trophic symptoms and were lined by flattened epithelial cells, thus, the stromal proliferation is relatively low as compared to the TN group. These suggest that Phellinus linteus water extracts may be an useful remedy for treating the benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wei JT, Calhoun E, Jacobsen SJ. Urologic diseases in America project: benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol. 2005; 173:1256–1261.
Article2. Zhang Y, Zhu C, Curado MP, Zheng T, Boyle P. Changing patterns of bladder cancer in the USA: evidence of heterogeneous disease. BJU Int. 2012; 109:52–56.
Article3. Parsons JK. Benign prostatic hyperplasia and male lower urinary tract symptoms: epidemiology and risk factors. Curr Bladder Dysfunct Rep. 2010; 5:212–218.
Article4. Arrighi HM, Metter EJ, Guess HA, Fozzard JL. Natural history of benign prostatic hyperplasia and risk of prostatectomy. The Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging. Urology. 1991; 38:4–8.
Article5. Miano R, De Nunzio C, Asimakopoulos AD, Germani S, Tubaro A. Treatment options for benign prostatic hyperplasia in older men. Med Sci Monit. 2008; 14:RA94–RA102.6. Clark RV, Hermann DJ, Cunningham GR, Wilson TH, Morrill BB, Hobbs S. Marked suppression of dihydrotestosterone in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia by dutasteride, a dual 5α-reductase inhibitor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004; 89:2179–2184.
Article7. Isaacs JT. Antagonistic effect of androgen on prostatic cell death. Prostate. 1984; 5:545–557.
Article8. Nixon P. New clinical trial of medical therapy for benign prostatic hyperplasia. Drug Benefit Trends. 1997; 9:44–45.9. Jang H, Ha US, Kim SJ, Yoon BI, Han DS, Yuk SM, Kim SW. Anthocyanin extracted from black soybean reduces prostate weight and promotes apoptosis in the prostatic hyperplasia-induced rat model. J Agric Food Chem. 2010; 58:12686–12691.
Article10. Isaacs JT, Coffey DS. Etiology and disease process of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Prostate Suppl. 1989; 2:33–50.
Article11. Tsuji T, Du W, Nishioka T, Chen L, Yamamoto D, Chen CY. Phellinus linteus extract sensitizes advanced prostate cancer cells to apoptosis in athymic nude mice. PLoS One. 2010; 5:e9885.
Article12. Sliva D. Medicinal mushroom Phellinus linteus as an alternative cancer therapy. Exp Ther Med. 2010; 1:407–411.
Article13. Kim HM, Han SB, Oh GT, Kim YH, Hong DH, Hong ND, Yoo ID. Stimulation of humoral and cell mediated immunity by polysaccharide from mushroom Phellinus linteus. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1996; 18:295–303.
Article14. Kojima H, Tanigawa N, Kariya S, Komemushi A, Shomura Y, Sawada S, Arai E, Yokota Y. A case of spontaneous regression of hepatocellular carcinoma with multiple lung metastases. Radiat Med. 2006; 24:139–142.
Article15. Suzuki S, Ohshima S. In : Mori K, editor. Influence of shiitake (Lentinus edodes) on human serum cholesterol. Mushroom Science 9: Proceedings of the 9th International Scientific Congress on the Cultivation of Edible Fungi; Tokyo: Mushroom Research Institute in Japan;1976. p. 463–647.16. Kim BC, Jeon WK, Hong HY, Jeon KB, Hahn JH, Kim YM, Numazawa S, Yosida T, Park EH, Lim CJ. The anti-inflammatory activity of Phellinus linteus (Berk. & M.A. Curt.) is mediated through the PKCdelta/Nrf2/ARE signaling to up-regulation of heme oxygenase-1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2007; 113:240–247.
Article17. Choi YH, Yan GH, Chai OH, Lim JM, Sung SY, Zhang X, Kim JH, Choi SH, Lee MS, Han EH, Kim HT, Song CH. Inhibition of anaphylaxis-like reaction and mast cell activation by water extract from the fruiting body of Phellinus linteus. Biol Pharm Bull. 2006; 29:1360–1365.
Article18. Steel RG, Torrie JH, Dickey DA. Principles and Procedures of Statistics: A Biometrical Approach. New York: McGraw-Hill;1996.19. Noh JR, Lee IK, Ly SY, Yang KJ, Gang GT, Kim YH, Hwang JH, Yun BS, Lee CH. A Phellinus baumii extract reduces obesity in high-fat diet-fed mice and absorption of triglyceride in lipid-loaded mice. J Med Food. 2011; 14:209–218.
Article20. Choi JS, Kim H, Jung MH, Hong S, Song J. Consumption of barley beta-glucan ameliorates fatty liver and insulin resistance in mice fed a high-fat diet. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2010; 54:1004–1013.
Article21. Song YS, Kim SH, Sa JH, Jin C, Lim CJ, Park EH. Antiangiogenic, antioxidant and xanthine oxidase inhibition activities of the mushroom Phellinus linteus. J Ethnopharmacol. 2003; 88:113–116.
Article22. Jeon TI, Hwang SG, Lim BO, Park DK. Extracts of Phellinus linteus grown on germinated brown rice suppress liver damage induced by carbon tetrachloride in rats. Biotechnol Lett. 2003; 25:2093–2096.
Article23. Liang CH, Syu JL, Mau JL. Antioxidant properties of solid-state fermented adlay and rice by Phellinus linteus. Food Chem. 2009; 116:841–845.
Article24. Zhu T, Guo J, Collins L, Kelly J, Xiao ZJ, Kim SH, Chen CY. Phellinus linteus activates different pathways to induce apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 2007; 96:583–590.
Article25. Cho SH, Han YH, Kim YS. Effects of bee venom herbal acupuncture on experimental rat model of benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Korean Orient Intern Med. 2010; 31:166–176.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Prominently Large Glans penis as a Possible sign of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- Ethanol Extract of Chaenomeles sinensis Inhibits the Development of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia by Exhibiting Anti-oxidant and Anti-inflammatory Effects
- Optimal Extraction Conditions of Anti-obesity Lipase Inhibitor from Phellinus linteus and Nutritional Characteristics of the Extracts
- The Effects of Abdominal Obesity on the Increased Prevalence Rate of Hypertension and Diabetes Mellitus in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Patients
- The influence of age and endocrine factors on the volume of benign prostatic hyperplasia