Nutr Res Pract.
2010 Apr;4(2):163-172.
Assessment of foodservice quality and identification of improvement strategies using hospital foodservice quality model
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Food and Nutrition, Seoul Women's University, 623 Hwarangro, Nowon-gu, Seoul 139-774, Korea. klee@swu.ac.kr
- 2Nutrition Team, Korea University, Guro Hospital, Seoul 152-703, Korea.
Abstract
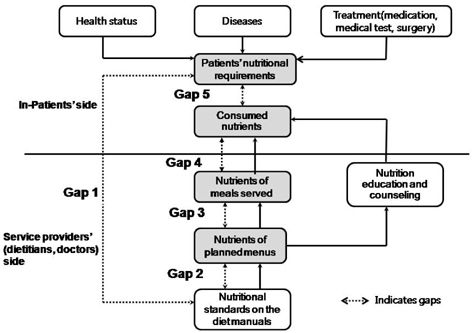
- The purposes of this study were to assess hospital foodservice quality and to identify causes of quality problems and improvement strategies. Based on the review of literature, hospital foodservice quality was defined and the Hospital Foodservice Quality model was presented. The study was conducted in two steps. In Step 1, nutritional standards specified on diet manuals and nutrients of planned menus, served meals, and consumed meals for regular, diabetic, and low-sodium diets were assessed in three general hospitals. Quality problems were found in all three hospitals since patients consumed less than their nutritional requirements. Considering the effects of four gaps in the Hospital Foodservice Quality model, Gaps 3 and 4 were selected as critical control points (CCPs) for hospital foodservice quality management. In Step 2, the causes of the gaps and improvement strategies at CCPs were labeled as "quality hazards" and "corrective actions", respectively and were identified using a case study. At Gap 3, inaccurate forecasting and a lack of control during production were identified as quality hazards and corrective actions proposed were establishing an accurate forecasting system, improving standardized recipes, emphasizing the use of standardized recipes, and conducting employee training. At Gap 4, quality hazards were menus of low preferences, inconsistency of menu quality, a lack of menu variety, improper food temperatures, and patients' lack of understanding of their nutritional requirements. To reduce Gap 4, the dietary departments should conduct patient surveys on menu preferences on a regular basis, develop new menus, especially for therapeutic diets, maintain food temperatures during distribution, provide more choices, conduct meal rounds, and provide nutrition education and counseling. The Hospital Foodservice Quality Model was a useful tool for identifying causes of the foodservice quality problems and improvement strategies from a holistic point of view.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hong WS, Kim HJ, Ryu KA. Case study on the analysis of patients' plate waste results. Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition. 1996. 12:339–345.2. Kim MY, Kim KJ, Lee KE. In-patients' food consumption and perception on foodservice quality at hospitals. Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association. 2008. 14:87–96.3. Hong WS, Kirk D. The analysis of edible plate wastes in 11 hospitals in the UK. J Foodserv Manage. 1995. 9:115–123.4. Demir C, Celik YJ. Determinants of patient satisfaction in a military teaching hospital. J Healthcare Qual. 2002. 24:30–34.
Article5. Sheehan-Smith L. Key facilitators and best practices of hotel-style room service in hospitals. J Am Diet Assoc. 2006. 106:581–586.
Article6. Kleeb T. Service excellence: unit-based service objectives in CQI. Hospitals. 1998. 66:50–54.7. Lau C, Greogire MB. Quality ratings of a hospital foodservice department by inpatients and postdischarge patients. J Am Diet Assoc. 1998. 98:1303–1307.
Article8. Parasuraman A, Zeithaml VA, Berry LL. A conceptual model of service quality and its implications for future research. J Marketing. 1985. 49:41–50.
Article9. American Society for Quality [Internet]. c2010. cited 2010 January 30. Milwaukee: Glossary;Available from: http://www.asq.org/glossary/index.html.10. Parasuraman A, Zeithaml VA, Berry LL. Servqual: a multiple-item scale for measuring consumer perceptions of service quality. J Retailing. 1988. 64:12–40.11. Jung SH, Yeom HS, Sohn CM. The improvement of hospital food service in quality and customer satisfaction by using 6-sigma strategy. Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association. 2007. 13:331–334.12. O'Hara PA, Harper DW, Kangas M, Bubeau J, Borsutzky C, Lemire N. Taste, temperature, and presentation predict satisfaction with foodservices in a Canadian continuing care hospital. J Am Diet Assoc. 1997. 97:401–405.13. Kim YS, Lyu ES. Evaluation of Patients' Satisfaction with Foodservice of mid-size hospitals in Busan area. Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition. 2003. 32:1153–1156.
Article14. Lee HY, Chang SH, Yang IS. Development of quality assessment tool and application to customer-oriented hospital foodservice management. The Korean Journal of Nutrition. 2004. 37:329–338.15. Lim HS, Yang IS, Cha JA. Analysis of patient satisfaction and factors influencing satisfaction on hospital foodservice quality. Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association. 1999. 5:29–47.16. Gregoire MB, Spears MC. Foodservice Organizations: A Managerial and Systems Approach. 2007. 6th ed. Upper Saddle River (NJ): Pearson Prentice Hall;204. 249.17. Mowe M, Bohmer T. The prevalence of undiagnosed proteincalorie undernutrition in a population of hospitalized elderly patients. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2002. 39:1089–1092.
Article18. Thomas D, Zdrowski C, Wilson M, Conright K, Lewis C, Tarig S, Morley J. Malnutrition in subacute care. Am J Clin Nutr. 2002. 75:308–313.
Article19. McNab H, Restivo R, Ber L. Dietetic quality assurance practices in Chicago area hospitals. J Am Diet Assoc. 1987. 85:635–637.20. Tobias A, Van Itallie T. Nutritional problems of hospitalized patients. J Am Diet Assoc. 1977. 71:253–257.21. Yang IS, Kim SJ, Lee HY, Cha JA. The indepth analysis of plate waste for DM diet served in general hospital. The Korean Journal of Nutrition. 2002. 35:394–401.22. Yang IS, Kim JL, Lee HY. An assessment of factors affecting plate waste and its effects in normal and soft diets provided from hospital foodservice. Korean Journal of Community Nutrition. 2001. 6:830–836.23. Kwak TK, Lyu ES, Lee HS, Ryu K, Choi SK, Hong WS, Jang MR, Shin ES, Moon HK, Jang HJ, Park SJ, Choi EH, Lee KE. Institutional Foodservice Operations. 2008. Seoul: Shinkwang Publishing Co.;156–166.24. Kim HJ, Jang EJ, Hong WS. Task analysis on foodservice, clinical nutrition service in hospital dietetic association. Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association. 2000. 6:148–160.25. Watters CA, Sorensen J, Fiala A, Wismer W. Exploring patient satisfaction with foodservice through focus groups and meal rounds. J Am Diet Assoc. 2003. 103:1347–1349.
Article26. Jung JH. A survey on nutritive value of general hospital diet and appetite of hospitalized patients in Pusan city. Journal of Korean Home Economics Education Association. 1986. 24:65–74.27. Dupertuis YM, Genton L, Kossovsky MP, Kyle UG, Raguso CA, Pichard C. Food intake in 1707 hospitalized patients: a prospective comprehensive hospital survey. Clin Nutr. 2003. 22:115–123.
Article28. Kandiah J, Stinnett L, Lutton D. Visual plate waste in hospitalized patients: length of stay and diet order. J Am Diet Assoc. 2006. 106:1663–1666.
Article29. Kim HJ, Jang UJ, Hong WS. A case study of food quality in a hospital foodservice system: with special reference to patient satisfaction. The Korean Journal of Nutrition. 1996. 29:348–356.30. McLymont V, Cox S, Stell F. Improving patient meal satisfaction with room service meal delivery. J Nurs Care Qual. 2003. 18:27–37.
Article31. Cox SA. Improving hospital foodservice. Food Technol. 2006. 60:28–36.32. Folio D, O'Sullivan-Maillet J, Touger-Decker R. The spoken menu concept of patient foodservice delivery systems increases overall patient satisfaction, therapeutic and tray accuracy, and is cost neutral for food and labor. J Am Diet Assoc. 2002. 102:546–548.
Article33. Lambert LG, Boudreaux J, Conklin M, Yadrick K. Are new meal distribution systems worth the effort for improving patient satisfaction with foodservice? J Am Diet Assoc. 1999. 9:1112–1114.
Article34. Gam SO, Park JR, Kim MJ, Lee MK, Shin KH. The study of patients satisfaction and expectation of hospital foodservice. The Korean Journal of Nutrition. 2007. 40:281–287.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of Foodservice Quality on the Viewpoint of Personnel in Hospital Foodservice
- Development of Quality Assessment Tool and Application to Customer-Oriented Hospital Foodservice Management
- Identification of Quality Attributes of University Foodservice and Factors Required for the Improvement of Customer Satisfaction: A Case Study Using IPA Model
- Strategies for the Improvement of Customer Satisfaction on Foodservice through Identifying the Foodservice Quality Factors in Senior Care Facilities
- A Study on Service Quality and Customer Loyalty of Foodservice Industry