Nutr Res Pract.
2008 Sep;2(3):178-183.
Anthropometric indices and selected nutrient intakes of young children in Kwangju, Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nutrition and Health Sciences, University of Nebraska, Lincoln, NE 68583-0806, USA. jdriskell@unl.edu
- 2Department of Food & Nutrition, Duksung Women's University, 419 Ssangmun-dong, Dobong-gu, Seoul 132-714, Korea.
Abstract
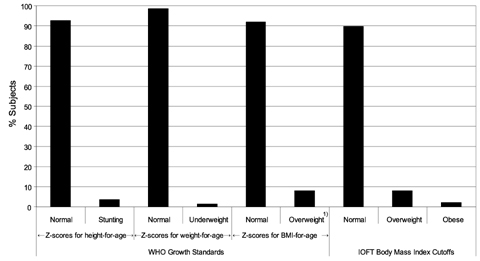
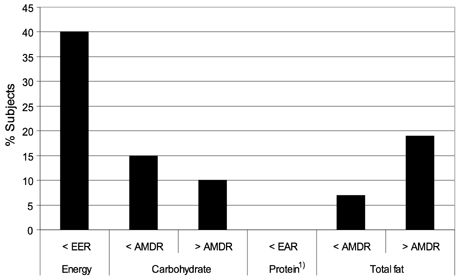
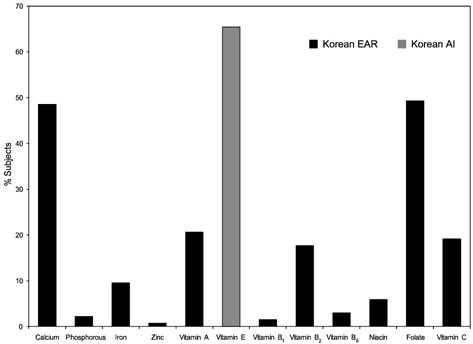
- The assessment of children's nutritional intakes is important because any nutritional inadequacies or toxicities may have adverse consequences. Studies on the nutritional intakes of Korean children are limited. The aims of this study were to determine anthropometric indices, estimate selected nutrient intakes of young Korean children, and compare these intakes with current Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans. This study included 136 healthy children (65 boys, 71 girls), 2-6 y old, living in Kwangju, Korea. Weights and heights were measured. Three consecutive 24-h food recalls were obtained. According to International Obesity TaskForce BMI cutoffs, 8% were overweight and 2% were obese. The energy intakes of 40% were < Korean Estimated Energy Requirements, while all subjects consumed > or = Korean Estimated Average Requirement (EAR) for protein. The majority of the children consumed > Korean EAR for iron, zinc, vitamin B1, vitamin B2, vitamin B6, and niacin. Vitamin E intakes of 65% of the Korean children were < Korean Adequate Intake, and approximately half of the subjects had < Korean EAR for calcium and for folate. Many young children in Kwangju, Korea, likely have inadequate status of calcium, folate, and vitamin E.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. British Medical Association. Preventing Childhood Obesity. 2005. London, UK: London, British Medical Association.2. The 2008 World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. 2008. Accessed on 03/14/2008. https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/index.html.3. Choi MJ, Yoon J. The effect of eating habits and nutrient intake on the physical growth indices in preschool children. Korean Journal of Community Nutrition. 2003. 8:3–14.4. Cole TJ, Bellizzi MC, Flegal KM, Dietz WH. Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: international survey. BMJ. 2000. 320:1240–1243.
Article5. De Onis M, Onyango AW, Borghi E, Siyam A, Nishida C, Siekmann J. Development of a WHO growth reference for school-aged children and adolescents. Bull World Health Organ. 2007. 85:660–667.
Article6. Gibson RS. Principles of Nutritional Assessment. 2005. 2nd ed. New York, USA: Oxford University Press.7. Giraud DW, Kim YN, Cho YO, Driskell JA. Vitamin E inadequacy observed in a group of 2-6 year old children living in Kwangju, Republic of Korea. Int J Vitam Nutr. (in press).8. Hammer LD, Kraemer HC, Wilson DM, Ritter PL, Dornbusch SM. Standardized percentile curves of body-mass index for children and adolescents. Am J Dis Child. 1991. 145:259–263.
Article9. Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Selenium, and Carotenoids. 2002. Washington, DC, USA: National Academy Press.10. Joung H, Lee MH, Choi YS, Cho SH. Baseline dietary behaviors of children for nutritional management programs at child care centers in Korea. The Korean Journal of Nutrition. 2000. 33:890–900.11. Kang KJ. A study on food habits, nutrient intakes and nutritional quality of preschool children in Seoul. Korean Journal of Community Nutrition. 2005. 10:471–483.12. Kim YK, Chyun JH. Nutrition intakes and relations to the obesity and prevalence of anemia in preschool children living in metropolitan area of Korea. Korean J Dietary Culture. 2001. 16:451–462.13. Kim YN, Giraud DW, Driskell JA. Tocopherol and carotenoid contents of selected Korean cooked combination foods. Nutrition Science. 2006. 9:323–329.14. Kim YN, Giraud DW, Driskell JA. Tocopherol and carotenoid contents of selected Korean fruits and vegetables. J Food Compost Anal. 2007a. 20:458–465.
Article15. Kim YN, Giraud DW, Cho YO, Driskell JA. Vitamin A inadequacy observed in a group of 2-6 year old children living Kwangju, Republic of Korea. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 2007b. 77:311–319.
Article16. Kim YN, Lee JY, Driskell JA. Marginal folate inadequacy observed in a group of young children in Kwangju, Korea. Nutrition Research and Practice. 2007c. 1:120–125.
Article17. Lim HJ. A study on the food habit and the evaluation of nutrient intake of preschool children in Pusan. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 1999. 28:1369–1379.18. Matsushita Y, Yoshiike N, Kaneda F, Yochita K, Takimoto H. Trends in childhood obesity in Japan over the last 25 years from the National Nutrition Survey. Obes Res. 2004. 12:205–214.
Article19. Ministry for Health and Welfare/Korea Health Industry Development Institute. The Third Korea National Health & Nutrition Examination Survey. 2006. Seoul, Republic of Korea: Korea Health Industry Development Institute.20. National Institute of Health and Nutrition. The 2002 National Nutrition Survey in Japan. Jpn J Nutr Diet. 2004. 62:37–44.21. National Rural Living Science Institute. Food Composition Table. 2001. 6th ed. Suwon, Korea: Rural Development Administration.22. Rosner B. Fundamentals of Biostatistics. 2000. 5th ed. CA, USA: Duxdury, Pacific Grove.23. Serra-Majem L, Ribas-Barba L, Pérez-Rodrigo C, Bartrina JA. Nutrient adequacy in Spanish children. Br J Nutr. 2006. 96:S49–S57.24. Shin KO, Yoo YY, Park HS. Study on the eating habits and growth development in Korean preschool children. The Korean Journal of Nutrition. 2005. 38:455–464.25. The Korean Nutrition Society. Recommended Dietary Allowances for Koreans. 2000. 7th ed. Seoul, Republic of Korea: Joungang Press.26. The Korean Nutrition Society. Computer Aided Nutritional Analysis Program for Professionals. 2002. Seoul, Republic of Korea: The Korean Nutrition Society.27. The Korean Nutrition Society. Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans. 2005. Seoul, Republic of Korea: The Korean Nutrition Society.28. National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference, release 18. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service. 2005. Accessed on 09/2005 to 10/2005. http://www.nal.usda.gov/fnic/foodcomp/Data/.29. World Health Organization. Physical Status: The Use and Interpretation of Anthropometry: Report of a WHO Expert Committee. 1995. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization.30. World Health Organization. WHO Child Growth Standards: Length/Height-for-Age, Weight-for-Age, Weight-for-Length, Weightfor- Height and Body Mass Index-for-Age: Methods and Development. 2006. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization.31. World Health Organization/Food and Agriculture Organization. Vitamin and Mineral Requirements in Human Nutrition. 2004. 2nd ed. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effect of Taste Preference on Anthropometric Measurements and Nutrient intakes in Children
- Survey on Nutritional Status of Pre-school Children in Asan Measured by Anthropometric and Nutrient Intake Analysis
- Anthropometric and Nutrition Status of Institutional Children
- Comparison of Nutrient Intakes between Disabled Children(Mental Retardation, Autism and Cerebral Palsy) and Non-disabled Children: Comparison According to the Types of Handicap
- Nutritional Status of School Lunch-Supported Elementary School Children in Gyeongbuk Rural Area