Nutr Res Pract.
2007 Jun;1(2):89-93.
Establishing new principles for nutrient reference values (NRVs) for food labeling purposes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Beltsville Human Nutrition Research Center, Agricultural Research Service, United States Department of Agriculture, 10300 Baltimore Avenue, Beltsville, MD 20705, USA. allison.yates@ars.usda.gov
Abstract
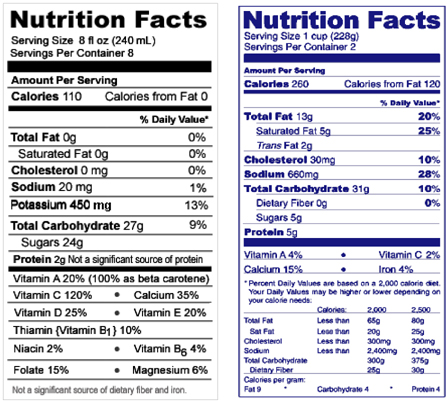
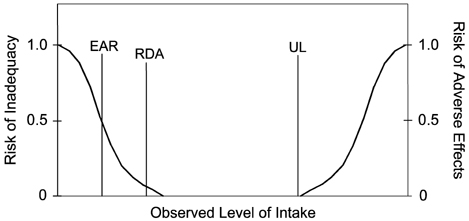
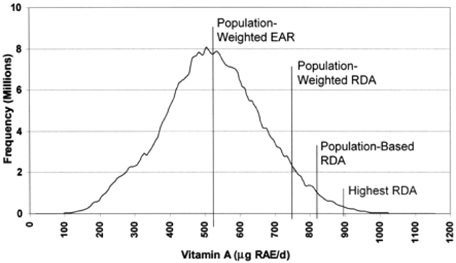
- Many countries such as The Republic of Korea have established their own nutritional standards, collectively termed Nutrient Reference Values(NRVs), and they vary due to the science which was reviewed, the purposes for which they are developed, and issues related to nutrition and food policy in the country. The current effort by the Codex Alimentarius Committee on Nutrition and Foods for Special Dietary Uses (CNFSDU) to update the NRVs that were established following the Helsinki Consultation in 1988 represents an opportunity to develop a set of reference values reflecting current scientific information to be used or adapted by many countries. This paper will focus on possible approaches to selecting or developing reference values which would serve the intended purpose for nutrition labeling to the greatest extent possible. Within the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (U.S. FDA) is currently reviewing regulations on nutrition labeling to better address current health issues, and is expected to enter into a process in the next few months to begin to explore how best to update nutrient Daily Values (DVs), most of which are still based on the Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs) of the Food and Nutrition Board, U.S. National Academy of Sciences, last reviewed and revised in 1968. In this presentation, I review the current purposes in the U.S. for nutrition labeling as identified in the 1938 Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act as amended, the scientific basis for current nutrition labeling regulations in the United States, and the recommendations made by the recent Committee on Use of Dietary Reference Intakes in Nutrition Labeling of the Institute of Medicine (2003) regarding how to use the DRIs in developing new DVs to be used on the label in the United States and Canada. Based on these reviews, I then provide examples of the issues that arise in comparing one approach to another. Much of the discussion focuses on the appropriate role of nutrient labeling within the Nutrition Facts panel, one of the three major public nutrition education tools in the United States (along with MyPyramid and Dietary Guidelines for Americans).
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. FAO/WHO/Ministry of Trade and Industry. Recommended nutrient reference values for food labeling purposes. Report of a Joint FAO/WHO Expert Consultation on recommended allowances of nutrients for food labelling purposes. 1988. Helsinki. Finland:2. Federal Register. 37 FR 6493-6497. 1972.3. Federal Register. 38 FR 2125-2132. 1973.4. Federal Register. 58 FR 2079-2205. 1993.5. Institute of Medicine (IOM). How should the recommended dietary allowances be revised? 1994. Washington DC. USA: Food and Nutrition Board. National Academy Press.6. IOM. Dietary reference intakes for calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, vitamin D, and fluoride. 1997. Washington DC. USA: Food and Nutrition Board. National Academy Press.7. IOM. Dietary reference intakes for vitamin C, vitamin E, selenium, and carotenoids. 2000. Washington DC. USA: Food and Nutrition Board. National Academy Press.8. IOM. Dietary reference intakes: guiding principles for nutrition labeling and fortification. 2003. Washington DC. USA: Food and Nutrition Board. The National Academies Press;[Available for review at www.nap.edu].9. National Research Council. Recommended dietary allowances. 1968. 7th ed. Washington DC. USA: Food and Nutrition Board. National Academy Press.10. Pennington JAT, Hubbard VS. Derivation of Daily Values used for nutrition labeling. J Am Diet Assoc. 1997. 97:1407–1412.
Article11. Tarasuk V. Use of population-weighted Estimated Average Requirements as a basis for Daily Values on food labels. Amer J Clin Nutr. 2006. 83:1217–1222.
Article12. Yates A. Which dietary reference intake is best suited to serve as the basis for nutrition labeling for daily values? J Nutr. 2006. 136:2457–2462.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Scientific Principles on the Revision and Addition of the Codex Nutrient Reference Values for Food Labelling Purposes
- The Scope of Population Groups and Nutrients for Codex Nutrient Reference Values
- Application of Dietary Reference Intakes for Codex Nutrient Reference Values
- A Study of Health Professionals Awareness, Satisfaction and Desirable Nutrition Labeling of Foods for Special Dietary Uses
- Development of Menu Labeling System (MLS) Using Nutri-API (Nutrition Analysis Application Programming Interface)