Korean J Nutr.
2010 Apr;43(2):197-206. 10.4163/kjn.2010.43.2.197.
Development of Menu Labeling System (MLS) Using Nutri-API (Nutrition Analysis Application Programming Interface)
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Food and Nutrition, University of Ulsan, Ulsan 680-749, Korea. smhong@ulsan.ac.kr
- 2Department of Computer Engineering & Information Technology, University of Ulsan, Ulsan 680-749, Korea.
- 3Department of Nutrition Policy, Korea Food and Drug Administration, Seoul 122-701, Korea.
- KMID: 2267984
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4163/kjn.2010.43.2.197
Abstract
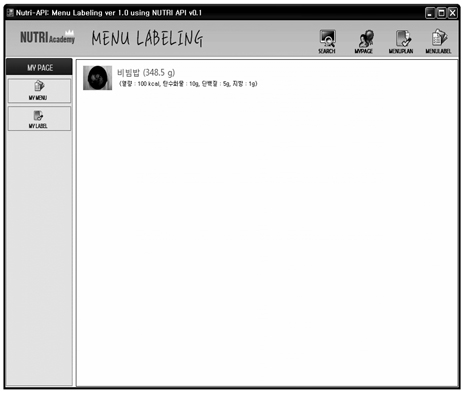
- Now a days, people eat outside of the home more and more frequently. Menu labeling can help people make more informed decisions about the foods they eat and help them maintain a healthy diet. This study was conducted to develop menu labeling system using Nutri-API (Nutrition Analysis Application Programming Interface). This system offers convenient user interface and menu labeling information with printout format. This system provide useful functions such as new food/menu nutrients information, retrieval food semantic service, menu plan with subgroup and nutrient analysis informations and print format. This system provide nutritive values with nutrient information and ratio of 3 major energy nutrients. MLS system can analyze nutrients for menu and each subgroup. And MLS system can display nutrient comparisons with DRIs and % Daily Nutrient Values. And also this system provide 6 different menu labeling formate with nutrient information. Therefore it can be used by not only usual people but also dietitians and restaurant managers who take charge of making a menu and experts in the field of food and nutrition. It is expected that Menu Labeling System (MLS) can be useful of menu planning and nutrition education, nutrition counseling and expert meal management.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
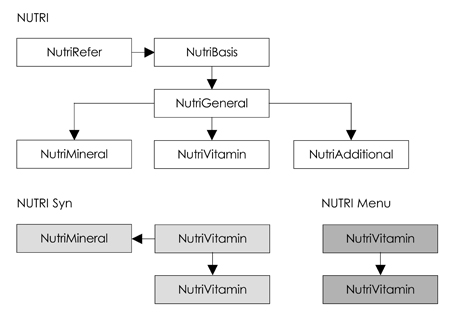
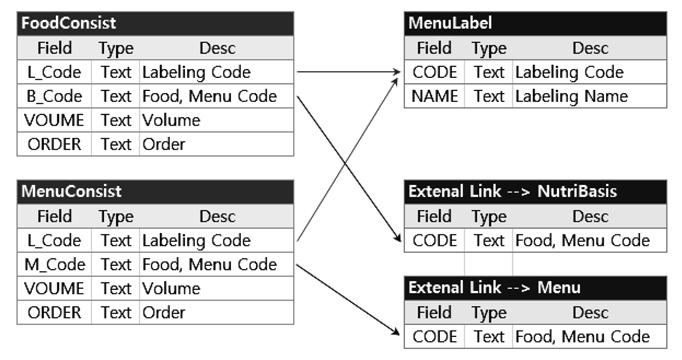
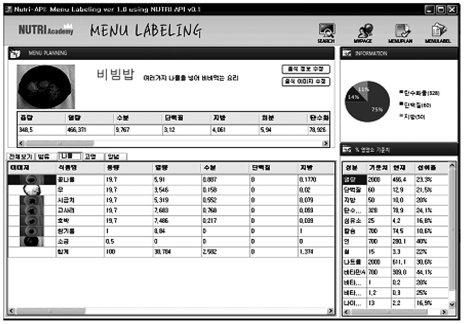
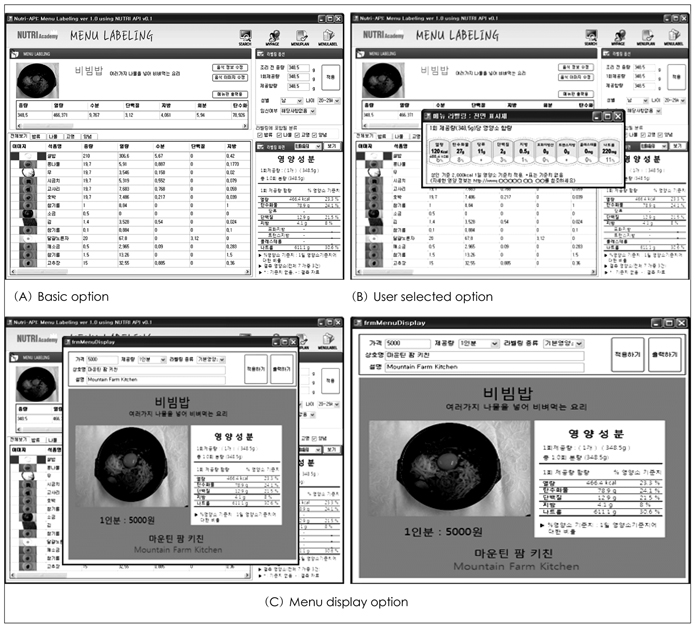
Figure
Reference
-
1. Korea Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Ministry for Health, Welfare and Family Affairs. National health & nutrition exanimation survey (KNHANES IV). 2008. 56–58.2. Food labeling Standards. Korea Food & Drug Administration. . Accessed on Jan 8; 2010. Available from: http://nutrition.kfda.go.kr.3. Kwon KI, Park SH, Lee JH, Kim JY, Yoo KS, Lee JS, Kim SY, Sung HI, Nam HS, Kim JW, Lee HY, Park HK, Kim MC. Prevalence, Nutrition Labeling and Claims, Processed, and Packaged Foods. Korean J Community Nutr. 2007. 12(2):206–213.4. Jun SM, Kwon SH, Park HK, Kim SH, Kwon KI, Jung HR. Consumer's Use and Demand of Restaurant Foods Nntrition Labeling. J Consumer studies. 2009. 20(2):279–303.5. The Household Income And Expenditure Trend Survey. Korea National Statistical Office. Accessed on Jan 6; 2010. Available from: http://www.nso.fo.kr.6. Hong SM. Menu Labeling and Recipe Standardization. 2009. Ulsan: UUP;9–13.7. Korea Health Industry Development Institute, Ministry for Health and Welfare. Report on 1998, National Health And Nutrition Survey (KNHANES I), Dietary intake survey. 1999. 271–272.8. Korea Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Ministry for Health and Welfare. National health & nutrition exanimation survey (KNHANES IV). 2008. 191.9. Hong SM. Research of promotion, advance and recognition for menu nutrition labeling of restaurants. Research Report of KFDA. 2009. Seoul: 45.10. Korea Food & Drug Administration. Food safety policies for children-safe foods, frank nutrition, healthy children. 2007.11. CSPI (Center for Science in the Public Interest) Menu Labeling. Accessed on Jan 6, 2010. Available from: http://www.cspinet.org/menulabeling/.12. US FDA. A Labeling Guide for Restaurants and Other Retail Establishments Selling Away-From-Home Foods. U.S. Office of Nutrition, Labeling, and Dietary Supplements. 2008.13. The Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, as amended by the Nutrition Labeling and Education Act of 1990 (NLEA)(Public Law101-535). 1990.14. USDA. USDA National nutrient database for standard reference, release 15. online. Nutrient data laboratory home page. Accessed on March 30; 2009. Available from: http://www.nal.usda.gov/fnic/foodcomp.15. Hong SM. Development of computer programs for nutrition counseling. Korean J Nutr. 1989. 22(4):275–289.16. Han JS, Rhee SH. A computerized nutrition counseling system for patients with diabetes. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 1993. 22(6):734–742.17. Kolasa KM, Miller MG. New developments in nutrition education using computer technology. J Nutr Educ. 1996. 28(1):7–14.
Article18. Peter GJ, Marling C, Sterling L. An artificial intelligence system for computer-assisted menu planning. J Am Diet Assoc. 1998. 98(9):1009–1014.
Article19. Kang HJ, Kim KJ, Kim I. A study on the computerized nutrition counseling program by food intake and exercise amount checking. Korean J Nutr. 1999. 32(5):598–607.20. Hong SM, Kim G. System for nutrition counseling and screening. J Community Nutr. 2005. 7(4):220–229.21. The Korean Nutrition Society. Computer aided nutritional analysis program (CAN-Pro, version 3.0). 2008. Seoul:22. Choi YS. Contents of domestic and overseas web pages related to nutrition and guides to build web nutrition information. J Korean Diet Assoc. 2000. 6(1):1–8.23. Hong SM, Hwang HJ. A study on the current situation and needs for the internet program of the nutrition computing. J Korean Diet Assoc. 2002. 8(1):9–18.24. Han JS, Jeong JH. A web-based internet program for nutrition counseling and diet management of patient with diabetes mellitus. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2004. 33(1):114–122.25. Hong SM, Kim G. Manipulation system for nutrition counseling based on internet. J Korean Diet Assoc. 2004. 10(3):284–292.26. Hong SM, Cho HS, Kim G. A basic study of food exchange database construction and search system (ENECC/E-Food Exchange) based on internet. J Korean Diet Assoc. 2003. 9(2):159–171.27. Hong SM, Cho HS, Kim G. Improvements in e-food exchange of commonly used foods and search system (ENECC/E-Food Exchange) based on internet. J Korean Diet Assoc. 2004. 10(2):129–142.28. Hong SM, Bae JH, Kim G, Choi JS, Kim YO. MenuGen: Menu planning and recommended menu search system for promotion of self sufficiency of Korean food. J Korean Diet Assoc. 2004. 10(3):272–283.29. National Rural Development Administration. MenuGen. Accessed on Jan 8; 2010. Available from: http://www.rrdi.go.kr/menugen.30. Hong SM, Cho JY, Lee JH, Kim G, Kim MC. NutriSonic web expert system for meal management and nutrition counseling with nutrient time-series analysis, e-food exchange and easy data transition. Nutr Res Pract. 2008. 2(2):121–129.
Article31. Hong SM. Web-site data base construction, nutritional menus development for children and web-site data base application, Rsearch Report of KFDA. 2007. Seoul: Republic of Korea;151–239.32. Hong SM. The construction and usage of low-sodium menu DB with smart web-based nutrition information service system (Smart Web-NISS) implementation. Research Report of KFDA. 2009. Seoul. Republic of Korea: 511–544.33. Korea Food & Drug Administration (2010): NutriEval. Accessed on Jan 8; 2010. Available from: http//nutrieval.kfda.go.kr.34. Jang YA. Development of Nutrition Panel Caluculating Program for Nutrition Labels using Food Composition Database. Research Report of KFDA. 2007. Seoul: 76.35. Korea Food & Drug Administration: FANTASY. Accessed Jan 8; 2010. from: http://kissna.kfda.go.kr.36. Korea Food & Drug Administration, KFDA food Nara. Accessed Jan 8; 2010. Available from: http://www.foodnara.go.kr.37. Hong SM. Nutrient database construction and program of activation for menu nutrition labeling of restaurants. Research Report of KFDA. 2008. Seoul. Republic of Korea: 39–120.38. Food And Beverage News. Accessed Jan 8; 2010. Available from: http://thinkfood.co.kr/main/php/search_view.php?idx=35233.39. National Rural Living Science Institute. Food composition table, seventh revision. 2006. Suwon:40. The Korean Nutrition Society. Dietary reference intakes for Koreans. 2005. Seoul:41. Hong SM, Cho JY, Park YJ, Kim MC, Kim G. NutriSyn: Knowledge Based Synonym Retrieval Service for Food and Dishes on the Web. J Korean Diet Assoc. 2009. 15(3):286–297.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Customers' Use of Menu Labeling in Restaurants and Their Perceptions of Menu Labeling Attributes
- Institutional Applications of Eclipse Scripting Programming Interface to Clinical Workflows in Radiation Oncology
- Effect of Motivations and Attitudes toward Nutrition Information on College Students' Use Intentions of Menu Labeling at University Dining Services
- Refactoring the Code for Visualizing Protein Database Information in a 3D Viewer for Software Reusability
- The Recognition and Requirement of Nutrition Labeling in Fast-Food Restaurants