Nutr Res Pract.
2007 Mar;1(1):65-69.
The associations between serum leptin, adiponectin and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in hypercholesterolemic patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Food and Nutrition, Kyungnam University, Masan 603-701, Korea.
- 2Yonsei Cardiovascular Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul 120-752, Korea. namsikc@yumc.yonsei.ac.kr
Abstract
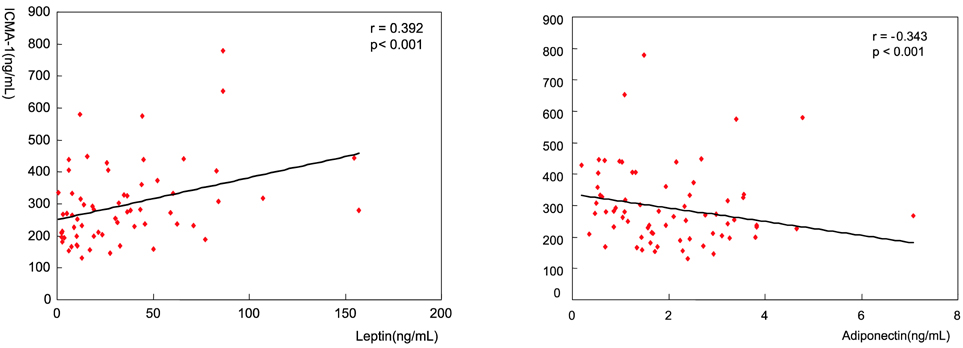
- We examined the associations between adiponectin or leptin and serum ICAM-1 levels in seventy-six hypercholesterolemic patients (mean age 59 yrs, 25 males and 51 females, LDL-cholesterol>=130mg/dL at screening). Blood lipid profiles and HOMA-IR derived from fasting glucose and insulin concentrations were determined. Serum levels of adiponectin, leptin and ICAM-1 were analyzed using ELISA. The results showed that serum levels of leptin were positively associated with serum levels of ICAM-1 independent of age, sex and BMI (r =0.392, p<0.001). Serum levels of adiponectin were negatively associated with serum levels of ICAM-1 independent of age, sex and BMI (r =-0.343, p<0.005). Stepwise multiple linear regression analysis showed that serum leptin was an independent factor to be associated with serum ICAM-1 levels after adjusting for age, sex, BMI, alcohol intake, smoking status, blood lipids such as total cholesterol, triglyceride, HDL cholesterol and LDL cholesterol and HOMA-IR (p<0.001). With respect to adiponectin, its association with serum ICAM-1 was attenuated but still significant when further adjustments were made for age, sex, BMI, alcohol intake, smoking status, blood lipids such as total cholesterol, triglyceride, HDL cholesterol and LDL cholesterol and HOMA-IR (p<0.005). In conclusion, this study suggests that adiponectin and leptin are associated with endothelial derived inflammation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adipokines
Adiponectin*
Cholesterol
Cholesterol, HDL
Cholesterol, LDL
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Fasting
Female
Glucose
Humans
Hypercholesterolemia
Inflammation
Insulin
Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1*
Leptin*
Linear Models
Male
Smoke
Smoking
Triglycerides
Adipokines
Adiponectin
Cholesterol
Cholesterol, HDL
Cholesterol, LDL
Glucose
Insulin
Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1
Leptin
Smoke
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ahima RS. Central actions of adipocyte hormones. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2005. 16:307–313.
Article2. Berg AH, Combs TP, Du X, Brownlee M, Scherer PE. The adipocyte secreted protein Acrp30 enhances hepatic insulin action. Nat Med. 2001. 7:947–953.
Article3. Berg AH, Scherer PE. Adipose tissue, inflammation, and cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. 2005. 96:939–949.
Article4. Chan JL, Bullen J, Stoyneva V, Depaoli AM, Addy C, Mantzoros CS. Recombinant methionyl human leptin administration to achieve high physiologic or pharmacologic leptin levels does not alter circulating inflammatory marker levels in humans with leptin sufficiency or excess. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005. 90:1618–1624.
Article5. Chandran M, Ciaraldi T, Philips SA, Henry RR. Adiponectin: more than just another fat cell hormone. Diabetes Care. 2003. 26:2442–2450.
Article6. Cines DB, Pollak ES, Buck CA, Loscalzo J, Zimmerman GA, McEver RP, Pober JS, Wick TM, Konkle BA, Schwartz BS, Barnathan ES, McCrae KR, Hug BA, Schmidt AM, Stern DM. Endothelial cells in physiology and in the pathophysiology of vascular disorders. Blood. 1998. 91:3527–3561.7. de Courten M, Zimmet P, Hodge A, Collins V, Nicolson M, Staten M. Hyperleptinaemia: the missing link in the metabolic syndrome? Diabet Med. 1997. 14:200–208.
Article8. Fantuzzi G. Adipose tissue, adipokines, and inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005. 115:911–919.
Article9. Glowinska B, Urban M, Peczynska J, Florys B. Soluble adhesion molecules (sICAM-1, sVCAM-1) and selectins (sE selectin, sP selectin, sL selectin) levels in children and adolescents with obesity, hypertension, and diabetes. Metabolism. 2005. 54:1020–1026.
Article10. Hackman A, Abe Y, Insull W Jr, Pownall H, Smith L, Dunn K, Gotto AM Jr, Ballantyne CM. Levels of soluble cell adhesion molecules in patients with dyslipidemia. Circulation. 1996. 93:1334–1338.
Article11. Hopkins AM, Baird AW, Nusrat A. ICAM-1: targeted docking for exogenous as well as endogenous ligands. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2004. 56:763–778.
Article12. Hu E, Liang P, Spiegelman BM. Adipo Q is a novel adipo-specific gene dysregulated in obesity. J Biol Chem. 1996. 271:10697–10703.13. Ikata J, Wakatsuki T, Oishi Y, Oki T, Ito S. Leukocyte counts and concentrations of soluble adhesion molecules as predictors of coronary atherosclerosis. Coron Artery Dis. 2004. 11:445–449.
Article14. Karaduman M, Sengul A, Oktenli C, Pekel A, Yesilova Z, Musabak U, Sanisoglu SY, Gunay C, Baysan O, Kocar IH, Tatar H, Ozata M. Tissue levels of adiponectin, tumour necrosis factor-alpha, soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and heart-type fatty acid-binding protein in human coronary atherosclerotic plaques. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2006. 64:196–202.
Article15. Kawanami D, Maemura K, Takeda N, Harada T, Nojiri T, Imai Y, Manabe I, Utsunomiya K, Nagai R. Direct reciprocal effects of resistin and adiponectin on vascular endothelial cells: a new insight into adipocytokine-endothelial cell interactions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004. 314:415–419.
Article16. Kent JW Jr, Comuzzie AG, Mahaney MC, Almasy L, Rainwater DL, VandeBerg JL, MacCluer JW, Blangero J. Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 concentration is genetically correlated with insulin resistance, obesity, and HDL concentration in Mexican Americans. Diabetes. 2004. 53:2691–2695.
Article17. Kevil CG, Patel RP, Bullard DC. Essential role of ICAM-1 in mediating monocyte adhesion to aortic endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2001. 281:C1442–C1447.
Article18. Kougias P, Chai H, Lin PH, Yao Q, Lumsden AB, Chen C. Effects of adipocyte-derived cytokines on endothelial functions: implication of vascular disease. J Surg Res. 2005. 126:121–129.
Article19. Lau DC, Dhillon B, Yan H, Szmitko PE, Verma S. Adipokines: molecular links between obesity and atheroslcerosis. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005. 288:H2031–H2041.
Article20. Libby P, Ridker PM, Maseri A. Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circulation. 2002. 105:1135–1143.
Article21. Libby P. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature. 2002. 420:868–874.
Article22. Lyon CJ, Law RE, Hsueh WA. Minireview: adiposity, inflammation, and atherogenesis. Endocrinology. 2003. 144:2195–2200.
Article23. Mathews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and b-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia. 1985. 28:412–419.
Article24. Okamoto Y, Kihara S, Ouchi N, Nishida M, Arita Y, Kumada M, Ohashi K, Sakai N, Shimomura I, Kobayashi H, Terasaka N, Inaba T, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y. Adiponectin reduces atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Circulation. 2002. 106:2767–2770.
Article25. Ouchi N, Kihara S, Arita Y, Maeda K, Kuriyama H, Okamoto Y, Hotta K, Nishida M, Takahashi M, Nakamura T, Yamashita S, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y. Novel modulator for endothelial adhesion molecules: adipocyte-derived plasma protein adiponectin. Circulation. 1999. 100:2473–2476.26. Peelman F, Waelput W, Iserentant H, Lavens D, Eyckerman S, Zabeau L, Tavernier J. Leptin: linking adipocyte metabolism with cardiovascular and autoimmune diseases. Prog Lipid Res. 2004. 43:283–301.
Article27. Skilton MR, Nakhla S, Sieveking DP, Caterson ID, Celermajer DS. Pathophysiological levels of the obesity related peptides resistin and ghrelin increase adhesion molecule expression on human vascular endothelial cells. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2005. 32:839–844.
Article28. van deS tolpe A, van der Saag PT. Intercellular adhesion molecule-1. J Mol Med. 1996. 74:13–33.
Article29. van der Vleuten GM, Veerkamp MJ, van Tits LJ, Toenhake H, den Heijer M, Stalenhoef AF, de Graaf J. Elevated leptin levels in subjects with familial combined hyperlipidemia are associated with the increased risk for CVD. Atherosclerosis. 2005. 183:355–360.
Article30. van der Vleuten GM, van Tits LJ, den Heijer M, Lemmers H, Stalenhoef AF, de Graaf J. Decreased adiponectin levels in familial combined hyperlipidemia patients contribute to the atherogenic lipid profile. J Lipid Res. 2005. 46:2398–2404.
Article31. van Haelst PL, van Doormaal JJ, Asselbergs FW, van Roon AM, Veeger NJ, Henneman MM, Smit AJ, Tervaert JW, May JF, Gans RO. Correlates of endothelial function and their relationship with inflammation in patients with familial hypercholesterolaemia. Clin Sci (Lond). 2003. 104:627–632.
Article32. Wallace AM, McMahon AD, Packard CJ, Kelly A, Shepherd J, Gaw A, Sattar N. Plasma leptin and the risk of cardiovascular disease in the west of Scotland coronary prevention study (WOSCOPS). Circulation. 2001. 104:3052–3056.
Article33. Witkowska AM. Soluble ICAM-1: a marker of vascular inflammation and lifestyle. Cytokine. 2005. 31:127–134.
Article34. Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Waki H, Imai Y, Shimozawa N, Hioki K, Uchida S, Ito Y, Takakuwa K, Matsui J. Globular adiponectin protected ob/ob mice from diabetes and ApoE-deficient mice from atherosclerosis. J Biol Chem. 2003. 278:2461–2468.
Article35. Zeitler H, Ko Y, Zimmermann C, Nickenig G, Glanzer K, Walger P, Sachinidis A, Vetter H. Elevated serum concentrations of soluble adhesion molecules in coronary artery disease and acute myocardial infarction. Eur J Med Res. 1997. 2:389–394.36. Ziccardi P, Nappo F, Giugliano G, Esposito K, Marfella R, Cioffi M, D'Andrea F, Molinari AM, Giugliano D. Reduction of inflammatory cytokine concentrations and improvement of endothelial functions in obese women after weight loss over one year. Circulation. 2002. 105:804–809.
Article37. Zimmet P, Hodge A, Nicolson M, Staten M, de Courten M, Moore J, Morawiecki A, Lubina J, Collier G, Alberti G, Dowse G. Serum leptin concentration, obesity and insulin resistance in Western cross sectional study. Br Med J. 1996. 313:965–969.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The relationship between serum adiponectin and inflammatory cytokines in obese Korean juveniles
- Expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in human primary lung cancers
- The Relationship between Progression of Coronary Artery Stenosis and Serum Adiponectin, ICAM(Intercellular Adhesion Molecule)-1 Level
- Expression of Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 and E-Selectin in Gastric Cancer and Their Clinical Significance
- Hydromorphone attenuates intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expressions induced by lipopolysaccharide on HCT-116 human colon cancer cells