J Gastric Cancer.
2012 Sep;12(3):140-148.
Expression of Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 and E-Selectin in Gastric Cancer and Their Clinical Significance
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ppongttai@gmail.com
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Among cell adhesion molecules, serum levels of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and E-selectin are known to be correlated with the metastatic potential of gastric cancer. In the present study, the authors investigated the expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and E-selectin in gastric cancer tissues and cultured gastric cancer cells, and examined their clinical value in gastric cancer.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
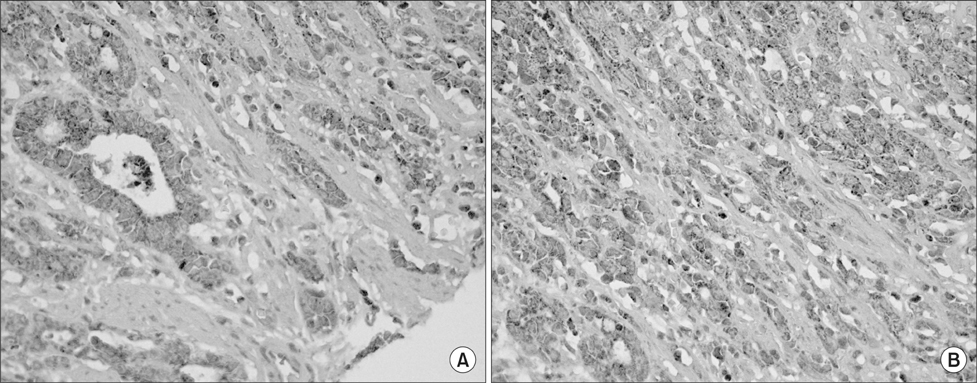
The protein was extracted from gastric cancer tissues and cultured gastric cancer cells (MKN-28 and Kato-III) and the expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and E-selectin was examined by western blotting. The clinical significance of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and E-selectin was explored, using immunohistochemical staining of specimens from 157 gastric cancer patients.
RESULTS
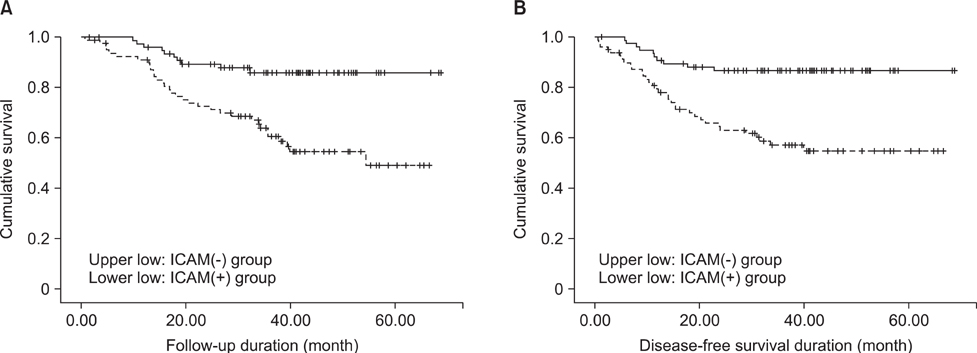
In western blot analysis, the expressions of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in gastric cancer tissues and cultured gastric cancer cells were increased, however, E-selectin in gastric cancer tissues and cells were not increased. Among 157 gastric cancer patients, 79 patients (50%) were intercellular adhesion molecule-1 positive and had larger tumor size, an increased depth of tumor invasion, lymph node metastasis and perineural invasion. The intercellular adhesion molecule-1 positive group showed a higher incidence of tumor recurrence (40.5%), and a poorer 3-year survival than the negative group (54.9 vs. 85.9%, respectively).
CONCLUSIONS
Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 is overexpressed in gastric cancer tissues and cultured gastric cancer cells, whereas E-selectin is not overexpressed. Increased expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in gastric cancer could be related to the aggressive nature of the tumor, and has a poor prognostic effect on gastric cancer.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ohene-Abuakwa Y, Pignatelli M. Adhesion molecules as diagnostic tools in tumor pathology. Int J Surg Pathol. 2000. 8:191–200.
Article2. Fidler IJ. Critical determinants of metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol. 2002. 12:89–96.
Article3. Picker LJ, Butcher EC. Physiological and molecular mechanisms of lymphocyte homing. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992. 10:561–591.
Article4. Sommers CL, Thompson EW, Torri JA, Kemler R, Gelmann EP, Byers SW. Cell adhesion molecule uvomorulin expression in human breast cancer cell lines: relationship to morphology and invasive capacities. Cell Growth Differ. 1991. 2:365–372.5. Maeda K, Kang SM, Sawada T, Nishiguchi Y, Yashiro M, Ogawa Y, et al. Expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and prognosis in colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep. 2002. 9:511–514.
Article6. Ogawa Y, Hirakawa K, Nakata B, Fujihara T, Sawada T, Kato Y, et al. Expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in invasive breast cancer reflects low growth potential, negative lymph node involvement, and good prognosis. Clin Cancer Res. 1998. 4:31–36.7. Rothlein R, Mainolfi EA, Czajkowski M, Marlin SD. A form of circulating ICAM-1 in human serum. J Immunol. 1991. 147:3788–3793.8. Wang P, Vánky F, Li SL, Patarroyo M, Klein E. Functional characteristics of the intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (CD54) expressed on cytotoxic human blood lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1990. 131:366–380.
Article9. Sánchez-Rovira P, Jimenez E, Carracedo J, Barneto IC, Ramirez R, Aranda E. Serum levels of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) in patients with colorectal cancer: inhibitory effect on cytotoxicity. Eur J Cancer. 1998. 34:394–398.
Article10. Tsujisaki M, Imai K, Hirata H, Hanzawa Y, Masuya J, Nakano T, et al. Detection of circulating intercellular adhesion molecule-1 antigen in malignant diseases. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991. 85:3–8.
Article11. Natali P, Nicotra MR, Cavaliere R, Bigotti A, Romano G, Temponi M, et al. Differential expression of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 in primary and metastatic melanoma lesions. Cancer Res. 1990. 50:1271–1278.12. Koyama S, Ebihara T, Fukao K. Expression of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) during the development of invasion and/or metastasis of gastric carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1992. 118:609–614.
Article13. Bevilacqua M, Butcher E, Furie B, Furie B, Gallatin M, Gimbrone M, et al. Selectins: a family of adhesion receptors. Cell. 1991. 67:233.
Article14. Bevilacqua MP, Nelson RM. Selectins. J Clin Invest. 1993. 91:379–387.
Article15. Majuri ML, Mattila P, Renkonen R. Recombinant E-selectin-protein mediates tumor cell adhesion via sialyl-Le(a) and sialyl-Le(x). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992. 182:1376–1382.
Article16. Ramphal JY, Hiroshige M, Lou B, Gaudino JJ, Hayashi M, Chen SM, et al. Ligand interactions with E-selectin. Identification of a new binding site for recognition of N-acyl aromatic glucosamine substituents of sialyl Lewis X. J Med Chem. 1996. 39:1357–1360.
Article17. Fujihara T, Yashiro M, Inoue T, Sawada T, Kato Y, Ohira M, et al. Decrease in ICAM-1 expression on gastric cancer cells is correlated with lymph node metastasis. Gastric Cancer. 1999. 2:221–225.
Article18. Yashiro M, Sunami T, Hirakawa K. CD54 expression is predictive for lymphatic spread in human gastric carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci. 2005. 50:2224–2230.
Article19. Yoo NC, Chung HC, Chung HC, Park JO, Rha SY, Kim JH, et al. Synchronous elevation of soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) correlates with gastric cancer progression. Yonsei Med J. 1998. 39:27–36.
Article20. Benekli M, Güllü IH, Tekuzman G, Savaş MC, Hayran M, Hasçelik G, et al. Circulating intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and E-selectin levels in gastric cancer. Br J Cancer. 1998. 78:267–271.
Article21. Ke JJ, Shao QS, Ling ZQ. Expression of E-selectin, integrin beta1 and immunoglobulin superfamily member in human gastric carcinoma cells and its clinicopathologic significance. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. 12:3609–3611.
Article22. Maruo Y, Gochi A, Kaihara A, Shimamura H, Yamada T, Tanaka N, et al. ICAM-1 expression and the soluble ICAM-1 level for evaluating the metastatic potential of gastric cancer. Int J Cancer. 2002. 100:486–490.
Article23. Staunton DE, Marlin SD, Stratowa C, Dustin ML, Springer TA. Primary structure of ICAM-1 demonstrates interaction between members of the immunoglobulin and integrin supergene families. Cell. 1988. 52:925–933.
Article24. Dustin ML, Rothlein R, Bhan AK, Dinarello CA, Springer TA. Induction by IL 1 and interferon-gamma: tissue distribution, biochemistry, and function of a natural adherence molecule (ICAM-1). J Immunol. 1986. 137:245–254.25. Staunton DE, Dustin ML, Erickson HP, Springer TA. The arrangement of the immunoglobulin-like domains of ICAM-1 and the binding sites for LFA-1 and rhinovirus. Cell. 1990. 61:243–254.
Article26. Schmidt RE, Bartley G, Levine H, Schlossman SF, Ritz J. Functional characterization of LFA-1 antigens in the interaction of human NK clones and target cells. J Immunol. 1985. 135:1020–1025.27. Dustin ML, Springer TA. Role of lymphocyte adhesion receptors in transient interactions and cell locomotion. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991. 9:27–66.
Article28. Vánky F, Wang P, Patarroyo M, Klein E. Expression of the adhesion molecule ICAM-1 and major histocompatibility complex class I antigens on human tumor cells is required for their interaction with autologous lymphocytes in vitro. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1990. 31:19–27.
Article29. Santarosa M, Favaro D, Quaia M, Spada A, Sacco C, Talamini R, et al. Expression and release of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in renal-cancer patients. Int J Cancer. 1995. 62:271–275.
Article30. Amedei A, Benagiano M, della Bella C, Niccolai E, D'Elios MM. Novel immunotherapeutic strategies of gastric cancer treatment. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011. 2011:437348.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Allicin Reduces Adhesion Molecules and NO Production Induced by gamma irradiation in Human Endothelial Cells
- The Expression of the Adhesion Molecules on Interfacial Membrane fromthe Aseptically Loosened Failed Femoral Stems in Revisional Hip Arthroplasty
- Expression of Adhesion Molecules in IgA Nephropathy, Diffuse Crescentic Glomerulonephritis, and Minimal Change Disease
- Enhanced Expression of Cell Adhesion Molecules in the Aorta of Diabetic Mice is Mediated by gp91phox-derived Superoxide
- Expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in human primary lung cancers