Lab Med Online.
2012 Apr;2(2):87-94.
Evaluation of a Modified Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Serum PIVKA-II Measurement
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine & Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. eskang@skku.edu
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The serum des-gamma-carboxyprothrombin (protein induced by vitamin K antagonist-II, PIVKA-II) is a useful tumor marker in addition to alpha-fetoprotein for diagnosing primary hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In this study, we evaluated the laboratory performance of a modified ELISA method for PIVKA-II measurement adopting an automated ELISA processor in comparison with conventional manual method and investigated its diagnostic performance in patients with HCC.
METHODS
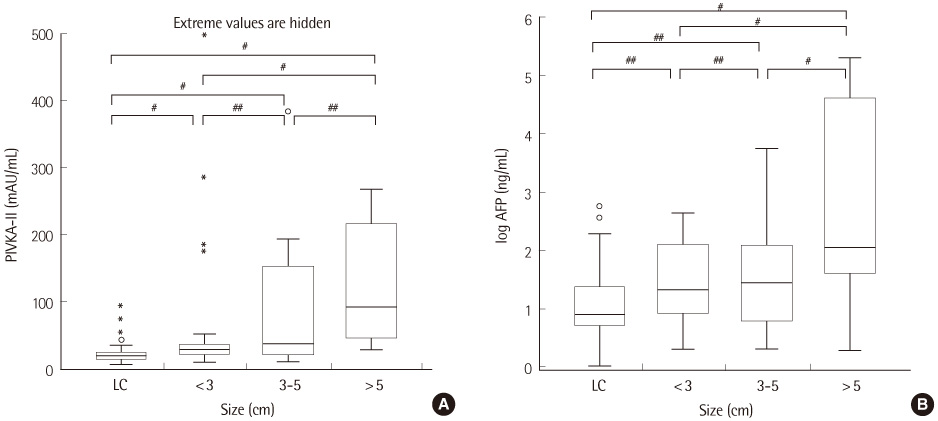
The laboratory performance of modified ELISA using PIVKA-II ELISA kit (Sanko Junyaku Co., Japan) was evaluated using control materials (10, 25, 500, 1,000 mAU/mL) and 208 patient samples according to the CLSI guidelines. In 93 HCC patients and 88 disease controls (30 chronic hepatitis and 58 liver cirrhosis), ROC curve, sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive values were analyzed.
RESULTS
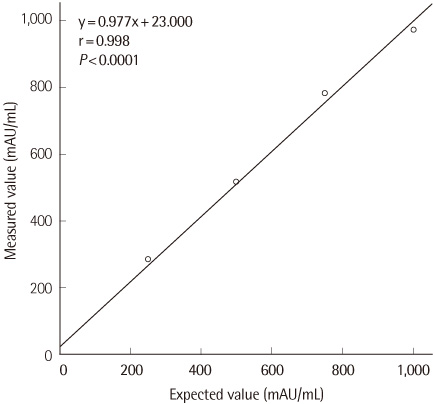
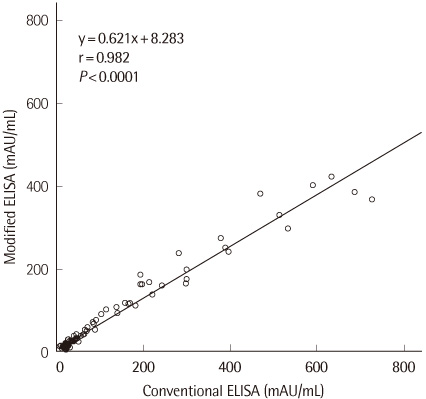
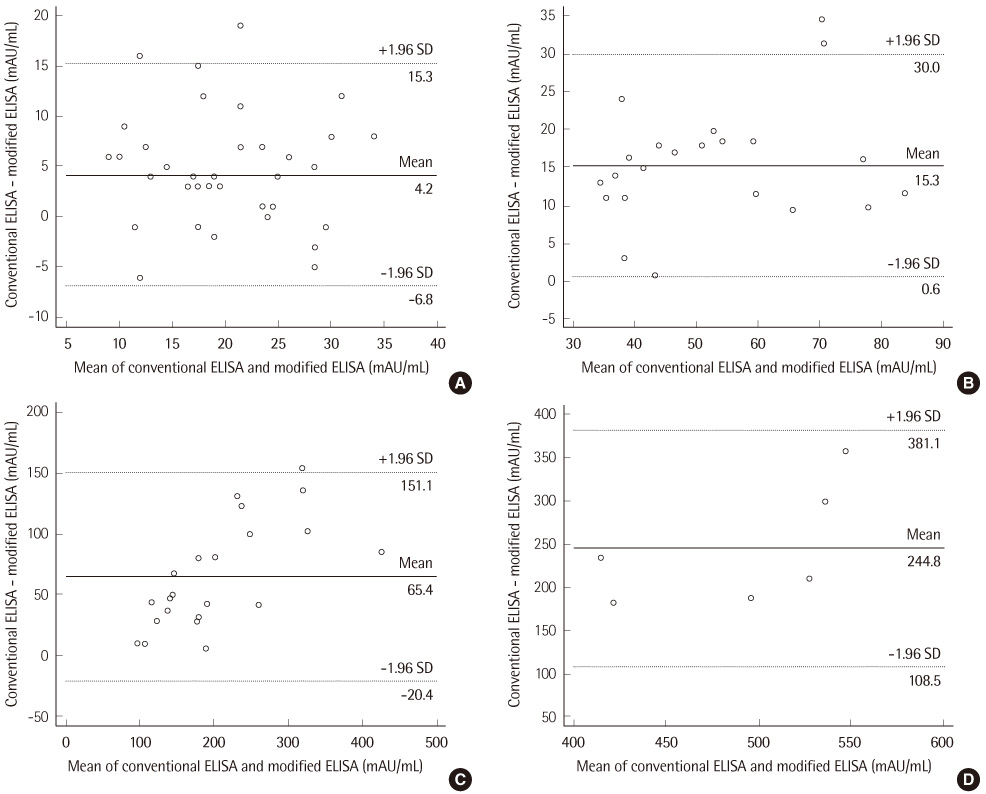
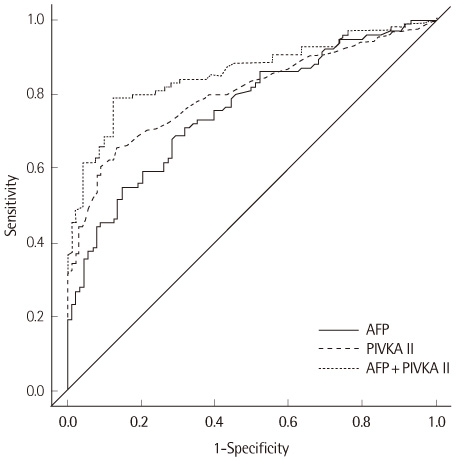
Total and within-run CVs for middle, high and very high level samples were less than 10%, while those of low level samples were over 10% (12.6% and 11.7%, respectively). The modified ELISA showed an excellent linearity (r>0.99) and low carryover rate (-0.14%). Although the correlation between the conventional and modified ELISAs was excellent (r=0.982), there was a proportional deviation of PIVKA-II levels (y intercept: 0.621). With a cut-off of 30 mAU/mL, the sensitivity and specificity of PIVKA-II for the diagnosis of HCC were 58% and 92%, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
PIVKA-II measurement by modified ELISA using an automated ELISA processor can improve the efficiency of laboratory in terms of turnaround time and labor intensiveness while maintaining reasonable sensitivity and specificity for the diagnosis of HCC.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wilson JF. Liver cancer on the rise. Ann Intern Med. 2005. 142:1029–1032.
Article2. Bosch FX, Ribes J, Díaz M, Cléries R. Primary liver cancer: worldwide incidence and trends. Gastroenterology. 2004. 127:5 Suppl 1. S5–S16.
Article3. National Cancer Informaion Center. Updated on Dec 2011. http://www.cancer.go.kr/cms/statics/incidence/index.html#1.4. Ikeda K, Saitoh S, Koida I, Arase Y, Tsubota A, Chayama K, et al. A multivariate analysis of risk factors for hepatocellular carcinogenesis: a prospective observation of 795 patients with viral and alcoholic cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1993. 18:47–53.
Article5. Hirai K, Aoki Y, Majima Y, Abe H, Nakashima O, Kojiro M, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of small hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Gastroenterol. 1991. 86:205–209.6. Okuda K. Hepatocellular carcinoma: recent progress. Hepatology. 1992. 15:948–963.
Article7. Sherman M. Alphafetoprotein: an obituary. J Hepatol. 2001. 34:603–605.
Article8. Weitz IC, Liebman HA. Des-gamma-carboxy (abnormal) prothrombin and hepatocellular carcinoma: a critical review. Hepatology. 1993. 18:990–997.
Article9. Nomura F, Ohnishi K, Tanabe Y. Clinical features and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma with reference to serum alpha-fetoprotein levels. Analysis of 606 patients. Cancer. 1989. 64:1700–1707.
Article10. Larson AE, Suttie JW. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase: evidence for a hydroperoxide intermediate in the reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978. 75:5413–5416.
Article11. Suttie JW. Recent advances in hepatic vitamin K metabolism and function. Hepatology. 1987. 7:367–376.
Article12. Liebman HA, Furie BC, Tong MJ, Blanchard RA, Lo KJ, Lee SD, et al. Des-gamma-carboxy (abnormal) prothrombin as a serum marker of primary hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1984. 310:1427–1431.
Article13. Koike Y, Shiratori Y, Sato S, Obi S, Teratani T, Imamura M, et al. Des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin as a useful predisposing factor for the development of portal venous invasion in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a prospective analysis of 227 patients. Cancer. 2001. 91:561–569.
Article14. Hagiwara S, Kudo M, Kawasaki T, Nagashima M, Minami Y, Chung H, et al. Prognostic factors for portal venous invasion in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol. 2006. 41:1214–1219.
Article15. Suehiro T, Sugimachi K, Matsumata T, Itasaka H, Taketomi A, Maeda T. Protein induced by vitamin K absence or antagonist II as a prognostic marker in hepatocellular carcinoma. Comparison with alpha-fetoprotein. Cancer. 1994. 73:2464–2471.
Article16. Fujiyama S, Morishita T, Sagara K, Sato T, Motohara K, Matsuda I. Clinical evaluation of plasma abnormal prothrombin (PIVKA-II) in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology. 1986. 33:201–205.17. Okuda H, Nakanishi T, Takatsu K, Saito A, Hayashi N, Watanabe K, et al. Measurement of serum levels of des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma by a revised enzyme immunoassay kit with increased sensitivity. Cancer. 1999. 85:812–818.
Article18. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. CLSI document EP5-A2. Evaluation of precision performance of quantitative measurement methods; approved guideline-second edition. 2008. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute.19. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. CLSI document EP6-A. Evaluation of the linearity of quantitative measurement procedures: a statistical approach; approved guideline. 2008. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute.20. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. CLSI document EP9-A2. Method comparison and bias estimation using patient samples; approved guideline-second edition. 2008. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute.21. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. CLSI document GP10-A. Assessment of the clinical accuracy of laboratory tests using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) Plots; approved guideline. 1995. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute.22. Marrero JA, Lok AS. Newer markers for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2004. 127:5 Suppl 1. S113–S119.
Article23. Beale G, Chattopadhyay D, Gray J, Stewart S, Hudson M, Day C, et al. AFP, PIVKAII, GP3, SCCA-1 and follisatin as surveillance biomarkers for hepatocellular cancer in non-alcoholic and alcoholic fatty liver disease. BMC Cancer. 2008. 8:200.
Article24. Marrero JA, Feng Z, Wang Y, Nguyen MH, Befeler AS, Roberts LR, et al. Alpha-fetoprotein, des-gamma carboxyprothrombin, and lectin-bound alpha-fetoprotein in early hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2009. 137:110–118.
Article25. von Kries R, Shearer MJ, Widdershoven J, Motohara K, Umbach G, Göbel U. Des-gamma-carboxyprothrombin (PIVKA II) and plasma vitamin K1 in newborns and their mothers. Thromb Haemost. 1992. 68:383–387.
Article26. Wang CS, Lin CL, Lee HC, Chen KY, Chiang MF, Chen HS, et al. Usefulness of serum des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin in detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2005. 11:6115–6119.
Article27. Park TH, Park TS, Kim HH, Lee EY, Son HC, Kim SH. Combination assay of serum PIVKA-II and alpha-fetoprotein in primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Korean J Clin Pathol. 2001. 21:215–221.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Combination Assay of Serum PIVKA-II and Alpha-fetoprotein in Primary Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Evaluation of enzymum system@(ES-300) for enzyme linked immunosorbent assay: comparison with RIA and CLIA for T3, T4, fT4 and TSH
- Evaluation of enzymum system@(ES-300) for enzyme linked immunosorbent assay: comparison with RIA and CLIA for T3, T4, fT4 and TSH
- Detection of anti-borrelia burgdorferi antibody by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in Korea
- Validation of measurement of house dust mite-specific IgE antibodies in serum using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay