Lab Anim Res.
2016 Mar;32(1):70-73. 10.5625/lar.2016.32.1.70.
Rapid and efficient identification of the mouse leptin receptor mutation (C57BL/KsJ-db/db) by tetra-primer amplification refractory mutation system-polymerase chain reaction (ARMS-PCR) analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 11Laboratory Animal Center/Department of Medical Genetics, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Chuncheon, Korea. jgsuh@hallym.ac.kr
- 2Institute of Natural Medicine, Hallym University, Chuncheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2312156
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5625/lar.2016.32.1.70
Abstract
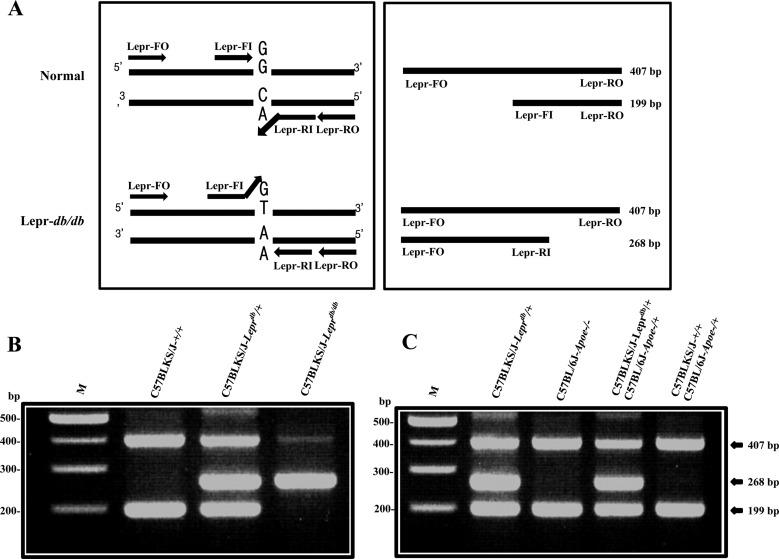
- The C57BLKS/J-Lepr(db) mouse has a point mutation in the leptin receptor gene and is one of the most useful animal model for non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus in human. Since the homozygote of C57BLKS/J-Lepr(db) mouse is infertile, detection of point mutation in the leptin receptor gene is important for efficient maintaining strains as well as mass production of homozygotes. To develop a rapid and efficient genotyping method for C57BLKS/J-Lepr(db) mouse, the tetra-primer amplification-refractory mutation system polymerase chain reaction (ARMS-PCR) was used. The 407 and 199 bp PCR products were amplified from normal (+/+) mice; while the 407 and 268 bp PCR products were amplified from homozygotes (db/db) mice; and the 407, 268, and 199 bp PCR products were amplified from heterozygotes (db/+) mice. This result showed that the tetra-primer ARMS-PCR analysis by us is suitable to detect point mutation of the leptin receptor gene. Taken together, our method will dramatically reduce animal use for maintenance of strains as well as production of homozygote in the C57BLKS/J-Lepr(db) strains.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chen H, Charlat O, Tartaglia LA, Woolf EA, Weng X, Ellis SJ, Lakey ND, Culpepper J, Moore KJ, Breitbart RE, Duyk GM, Tepper RI, Morgenstern JP. Evidence that the diabetes gene encodes the leptin receptor: identification of a mutation in the leptin receptor gene in db/db mice. Cell. 1996; 84(3):491–495. PMID: 8608603.
Article2. Coleman DL, Hummel KP. Symposium IV: Diabetic syndrome in animals. Influence of genetic background on the expression of mutations at the diabetes locus in the mouse. II. Studies on background modifiers. Isr J Med Sci. 1975; 11(7):708–713. PMID: 1099054.3. Horvat S, Bünger L. Polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) assay for the mouse leptin receptor (Lepr(db)) mutation. Lab Anim. 1999; 33(4):380–384. PMID: 10778787.
Article4. Newton CR, Graham A, Heptinstall LE, Powell SJ, Summers C, Kalsheker N, Smith JC, Markham AF. Analysis of any point mutation in DNA. The amplification refractory mutation system (ARMS). Nucleic Acids Res. 1989; 17(7):2503–2516. PMID: 2785681.
Article5. Ye S, Dhillon S, Ke X, Collins AR, Day IN. An efficient procedure for genotyping single nucleotide polymorphisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001; 29(17):E88. PMID: 11522844.
Article6. Oh SH, Nam H, Suh JG. A high resolution genetic mapping of the faded (fe) gene to a region between D10mit156 and D10mit193 on mouse chromosome 10. Lab Anim Res. 2013; 29(1):33–38. PMID: 23573106.7. Collins A, Ke X. Primer1: primer design web service for tetraprimer ARMS-PCR. Open Bioinforma J. 2012; 6:55–58.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Erratum: Rapid and efficient identification of the mouse leptin receptor mutation (C57BLKS/J-Lepr(db)) by tetra-primer amplification refractory mutation system-polymerase chain reaction (ARMS-PCR) analysis
- Rapid Apolipoprotein E Genotyping by the Multiplex Amplification Refractory Mutation System
- Non-amplification of an Allele of D8S1179 Locus Due to Point Mutation in Flanking Region
- Comparison between Two Sets of Primer for HBV-DNA by Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
- Comparison of Three Different Methods for Detection of IL28 rs12979860 Polymorphisms as a Predictor of Treatment Outcome in Patients with Hepatitis C Virus