Korean J Androl.
2012 Apr;30(1):45-51. 10.5534/kja.2012.30.1.45.
Comparison of Clinical Efficacy of Finasteride and Dutasteride as 5-alpha Reductase Inhibitor
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, College of Medicine, Konyang Universtiy, Daejeon, Korea. ovalboy@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2298808
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5534/kja.2012.30.1.45
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To compare the clinical therapeutic efficacy of finasteride and dutasteride as 5-alpha reductase inhibitor (5-ARI) in the medical treatment of benign prostate hyperplasia.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From July 2007 to July 2010, 354 benign prostatic hyperplasia patients with combination medication : alpha blocker plus 5-ARI were enrolled. These patients were classified into a finasteride medication group (F group) and dutasteride medication group (D group) retrospectively. We initially measured the total prostate volume (TPV), prostate specific antigen (PSA), International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS), quality of life score (QoL), maximal flow rate (Qmax), and post-void residual urine (PVR). After at least twelve months of medication, we rechecked these clinical parameters and during medication, side effects related to medication were also recorded.
RESULTS
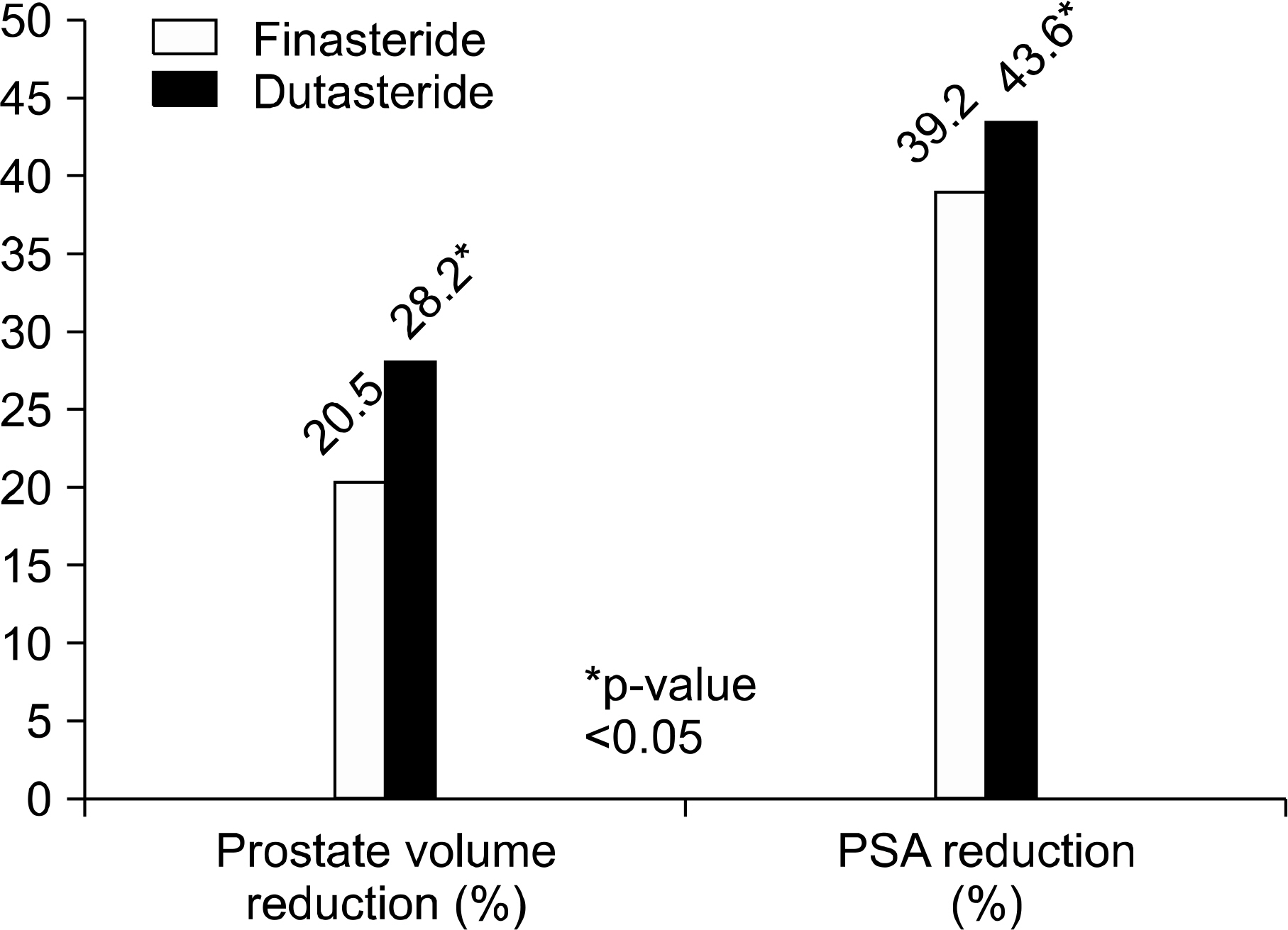
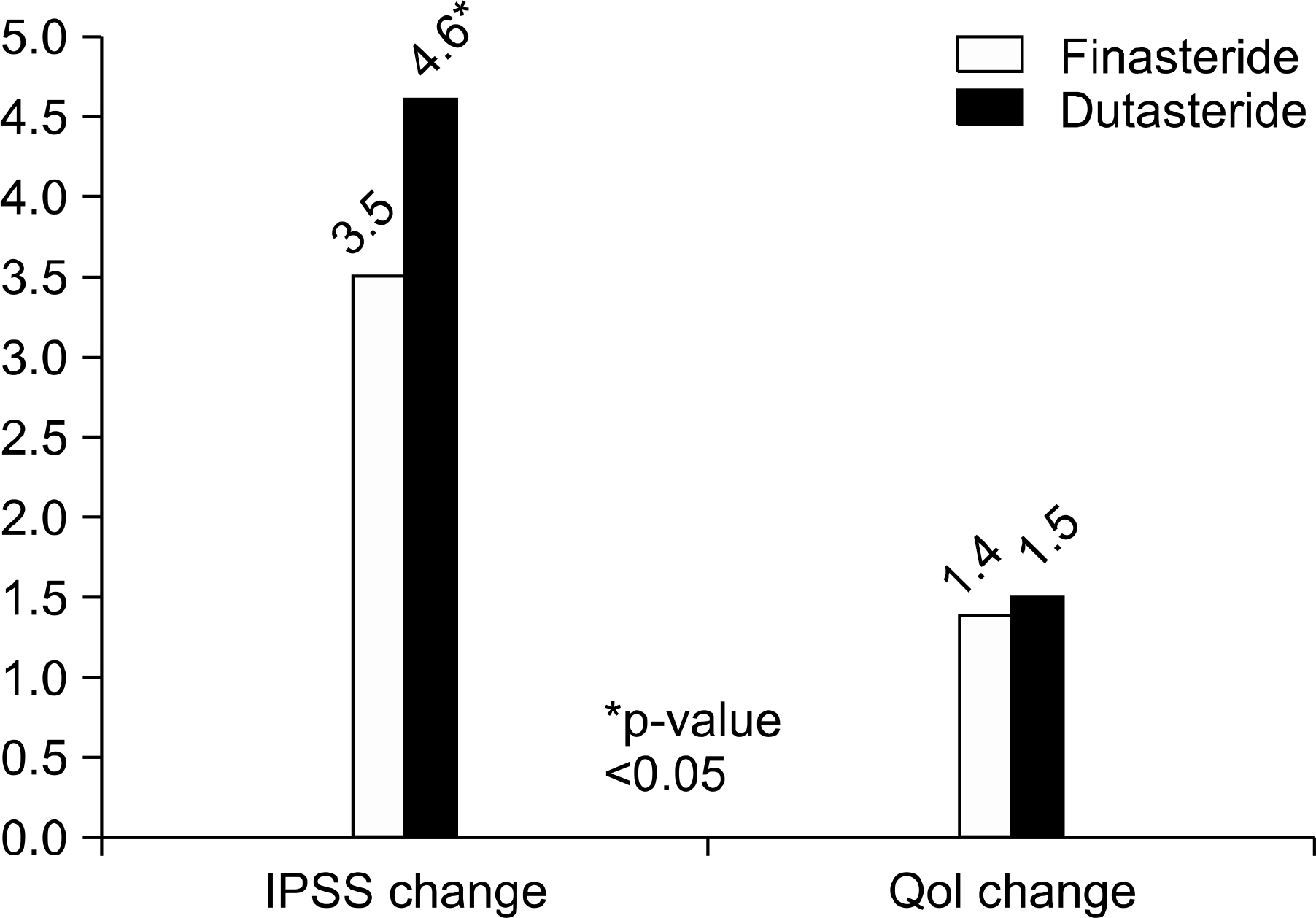
The F group (n=129) and D group (n=225) showed no differences in baseline characteristics for age, TPV, IPSS, QoL scores, or PSA. After medication, decreases in TPV were relatively higher in the D group than the F group (28.2% vs 20.5%). In addition, the decrease in PSA (43.6% vs 39.2%) and IPSS score (4.6 vs 3.5) were also higher in the D group. There were no significant differences in QoL score, Qmax, PVR change, or side effects between the two groups.
CONCLUSIONS
Dutasteride showed greater efficacy in reduction of TPV and PSA and in symptomatic improvement by IPSS score than finasteride. More large scale studies about the differences on clinical efficacy of finasteride and dutasteride are needed.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). McConnell JD, Bruskewitz R, Walsh P, Andriole G, Lieber M, Holtgrewe HL, et al. The effect of finasteride on the risk of acute urinary retention and the need for surgical treatment among men with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Finasteride Long-Term Efficacy and Safety Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1998; 338:557–63.2). Emberton M, Cornel EB, Bassi PF, Fourcade RO, Gómez JM, Castro R. Benign prostatic hyperplasia as a progressive disease: a guide to the risk factors and options for medical management. Int J Clin Pract. 2008; 62:1076–86.
Article3). Roehrborn CG, Boyle P, Nickel JC, Hoefner K, Andriole G. ARIA3001 ARIA3002 and ARIA3003 Study Investigators. Efficacy and safety of a dual inhibitor of 5-alpha-reductase types 1 and 2 (dutasteride) in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology. 2002; 60:434–41.
Article4). Kim CI, Chang HS, Kim BK, Park CH. Longterm results of medical treatment in benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology. 2006; 68:1015–9.
Article5). Nickel JC. Comparison of clinical trials with finasteride and dutasteride. Rev Urol. 2004; 6(Suppl 9):S31-9.6). Jacobsen SJ, Jacobson DJ, Girman CJ, Roberts RO, Rhodes T, Guess HA, et al. Natural history of prostatism: risk factors for acute urinary retention. J Urol. 1997; 158:481–7.
Article7). Carson C 3rd, Rittmaster R. The role of dihydrotestosterone in benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology. 2003; 61(4 Suppl 1):2–7.
Article8). IehléC. Délos S, Guirou O, Tate R, Raynaud JP, Martin PM. Human prostatic steroid 5 alpha-reductase isoforms-a comparative study of selective inhibitors. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1995; 54:273–9.9). Clark RV, Hermann DJ, Cunningham GR, Wilson TH, Morrill BB, Hobbs S. Marked suppression of dihydrotestosterone in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia by dutasteride, a dual 5alpha-reductase inhibitor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004; 89:2179–84.10). Gravas S, Oelke M. Current status of 5alpha-reductase inhibitors in the management of lower urinary tract symptoms and BPH. World J Urol. 2010; 28:9–15.11). McConnell JD, Roehrborn CG, Bautista OM, Andriole GL Jr, Dixon CM, Kusek JW, et al. Medical Therapy of Prostatic Symptoms (MTOPS) Research Group. The longterm effect of doxazosin, finasteride, and combination therapy on the clinical progression of benign prostatic hyperplasia. N Engl J Med. 2003; 349:2387–98.
Article12). Andriole GL, Bostwick DG, Brawley OW, Gomella LG, Marberger M, Montorsi F, et al. REDUCE Study Group. Effect of dutasteride on the risk of prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010; 362:1192–202.
Article13). Choi YH, Cho SY, Cho IR. The different reduction rate of prostate-specific antigen in dutasteride and finasteride. Korean J Urol. 2010; 51:704–8.
Article14). Nickel JC, Gilling P, Tammela TL, Morrill B, Wilson TH, Rittmaster RS. Comparison of dutasteride and finasteride for treating benign prostatic hyperplasia: the Enlarged Prostate International Comparator Study (EPICS). BJU Int. 2011; 108:388–94.
Article15). Choi H, Chang YS, Kim JB, Kang SH, Park HS, Lee JG. Analysis of initial baseline clinical parameters and treatment strategy associated with medication failure in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia in Korea. Int Neurourol J. 2010; 14:261–6.
Article16). Hagerty JA, Ginsberg PC, Metro MJ, Harkaway RC. A prospective, comparative study of the onset of symptomatic benefit of dutasteride versus finasteride in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia in clinical practice. J Urol. 2004; 171:356–9.17). Andriole GL, Kirby R. Safety and tolerability of the dual 5alpha-reductase inhibitor dutasteride in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Eur Urol. 2003; 44:82–8.18). Barkin J. Review of dutasteride/tamsulosin fixed-dose combination for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia: efficacy, safety, and patient acceptability. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2011; 5:483–90.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Different Reduction Rate of Prostate-Specific Antigen in Dutasteride and Finasteride
- A Case of Combination Therapy with Finasteride and Low Dose Dutasteride in the Treatment of Androgenetic Alopecia
- Retrospective Pharmacotherapeutic Evaluation of Dutasteride not Approved by US FDA for Androgenetic Alopecia in Korea
- Persistent Erectile Dysfunction after Discontinuation of 5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitor Therapy in Rats Depending on the Duration of Treatment
- The Effect of 5-alpha Reductase Inhibitors on the Efficacy of Photoselective Vaporization of the Prostate with 120 W GreenLight HPS Laser