J Clin Neurol.
2012 Dec;8(4):301-304. 10.3988/jcn.2012.8.4.301.
Association between the G252A Tumor Necrosis Factor-beta Gene Polymorphism and Medication-Overuse Headache
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathophysiology, Showa University School of Pharmacy, Tokyo, Japan. masakazu@pharm.showa-u.ac.jp
- 2Department of Neurology, Showa University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan.
- 3Center of Pharmaceutical Education, Showa University School of Pharmacy, Tokyo, Japan.
- KMID: 2287582
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2012.8.4.301
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
Migraine patients are particularly prone to the complication of medication-overuse headache (MOH). Although it has been shown that A allele carriers for the tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-beta gene G252A polymorphism are at high risk of the development of migraine without aura, the relationship between the TNF-beta gene G252A polymorphism and MOH is unknown. We investigated whether the TNF-beta gene G252A polymorphism is involved in the aggravation of migraine by overuse of medications.
METHODS
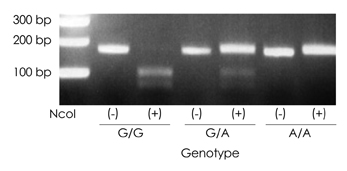
Forty-seven migraine patients (6 males and 41 females; age 36.4+/-10.3 years, mean+/-SD) and 22 MOH patients (1 male and 21 females; age 39.6+/-9.9 years) who had migraine were included in this study. The genotype for the TNF-beta gene G252A polymorphism was determined by polymerase-chain-reaction restriction-fragment-length polymorphism analysis.
RESULTS
The distribution of TNF-beta gene G252A genotype frequency differed significantly between migraine and MOH patients (p=0.013). The G/G genotype was carried by 23% of the migraine patients but it was absent in MOH patients.
CONCLUSIONS
G/G genotype carriers appear to be less susceptible to the aggravation of migraine by overuse of medications. The G252A TNF-beta gene polymorphism may be one of the factors contributing to the complications of MOH in patients with migraine.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Migraine Susceptibility Genes in Han Chinese of Fujian Province
Qi-fang Lin, Zi-chun Chen, Xian-guo Fu, Jing Yang, Luo-yuan Cao, Long-teng Yao, Yong-tong Xin, Gen-bin Huang
J Clin Neurol. 2017;13(1):71-76. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2017.13.1.71.
Reference
-
1. Sakai F, Igarashi H. Prevalence of migraine in Japan: a nationwide survey. Cephalalgia. 1997. 17:15–22.2. Bahra A, Walsh M, Menon S, Goadsby PJ. Does chronic daily headache arise de novo in association with regular use of analgesics? Headache. 2003. 43:179–190.
Article3. Headache Classification Committee. Olesen J, Bousser MG, Diener HC, Dodick D, First M, et al. New appendix criteria open for a broader concept of chronic migraine. Cephalalgia. 2006. 26:742–746.
Article4. Imai N, Kitamura E, Konishi T, Suzuki Y, Serizawa M, Okabe T. Clinical features of probable medication-overuse headache: a retrospective study in Japan. Cephalalgia. 2007. 27:1020–1023.
Article5. Kanki R, Nagaseki Y, Sakai F. Medication-overuse headache in Japan. Cephalalgia. 2008. 28:1227–1228.
Article6. Kaji Y, Hirata K. Characteristics of mood disorders in Japanese patients with medication-overuse headache. Intern Med. 2009. 48:981–986.
Article7. Lee JY, Kim M. Current issues in migraine genetics. J Clin Neurol. 2005. 1:8–13.
Article8. Waeber C, Moskowitz MA. Migraine as an inflammatory disorder. Neurology. 2005. 64:S9–S15.
Article9. Perini F, D'Andrea G, Galloni E, Pignatelli F, Billo G, Alba S, et al. Plasma cytokine levels in migraineurs and controls. Headache. 2005. 45:926–931.
Article10. Trabace S, Brioli G, Lulli P, Morellini M, Giacovazzo M, Cicciarelli G, et al. Tumor necrosis factor gene polymorphism in migraine. Headache. 2002. 42:341–345.
Article11. Asuni C, Stochino ME, Cherchi A, Manchia M, Congiu D, Manconi F, et al. Migraine and tumour necrosis factor gene polymorphism. An association study in a Sardinian sample. J Neurol. 2009. 256:194–197.
Article12. Headache Classification Subcommittee of the International Headache Society. The International Classification of Headache Disorders: 2nd edition. Cephalalgia. 2004. 24:Suppl 1. 9–160.13. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-IV-TR. 2000. 4th ed, text revision. Washington, D.C.: American Psychiatric Association.14. Grimble RF, Howell WM, O'Reilly G, Turner SJ, Markovic O, Hirrell S, et al. The ability of fish oil to suppress tumor necrosis factor α production by peripheral blood mononuclear cells in healthy men is associated with polymorphisms in genes that influence tumor necrosis factor α production. Am J Clin Nutr. 2002. 76:454–459.
Article15. Abraham LJ, French MA, Dawkins RL. Polymorphic MHC ancestral haplotypes affect the activity of tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993. 92:14–18.
Article16. Messer G, Spengler U, Jung MC, Honold G, Blömer K, Pape GR, et al. Polymorphic structure of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) locus: an NcoI polymorphism in the first intron of the human TNF-β gene correlates with a variant amino acid in position 26 and a reduced level of TNF-β production. J Exp Med. 1991. 173:209–219.
Article17. Hagiwara N, Kitazono T, Kamouchi M, Kuroda J, Ago T, Hata J, et al. Polymorphisms in the lymphotoxin alpha gene and the risk of ischemic stroke in the Japanese population. The Fukuoka Stroke Registry and the Hisayama Study. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2008. 25:417–422.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The evolving classifications and epidemiological challenges surrounding chronic migraine and medication overuse headache: a review
- TNF-alpha and TNF-beta Polymorphisms are Associated with Susceptibility to Osteoarthritis in a Korean Population
- Possible Association between -G308A Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha Gene Polymorphism and Major Depressive Disorder
- Medication-overuse Headache: Diagnostic Criteria, Epidemiology, and Treatment
- Comprehensive approach for the treatment of medication-overuse headache