J Bone Metab.
2014 Aug;21(3):227-232. 10.11005/jbm.2014.21.3.227.
A Case of Cavernous Sinus Thrombophlebitis and Meningitis as a Complication in Osteopetrosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea. isnamgoong@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea.
- KMID: 2286294
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2014.21.3.227
Abstract
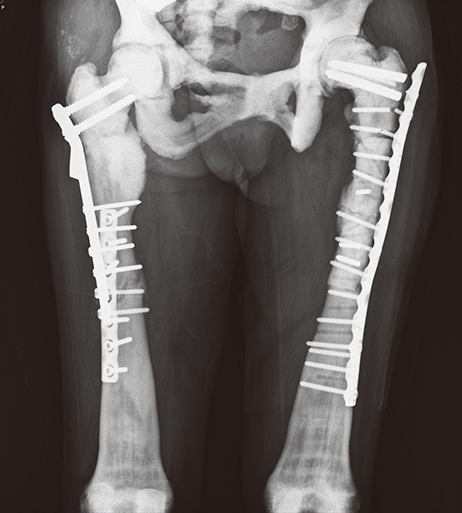
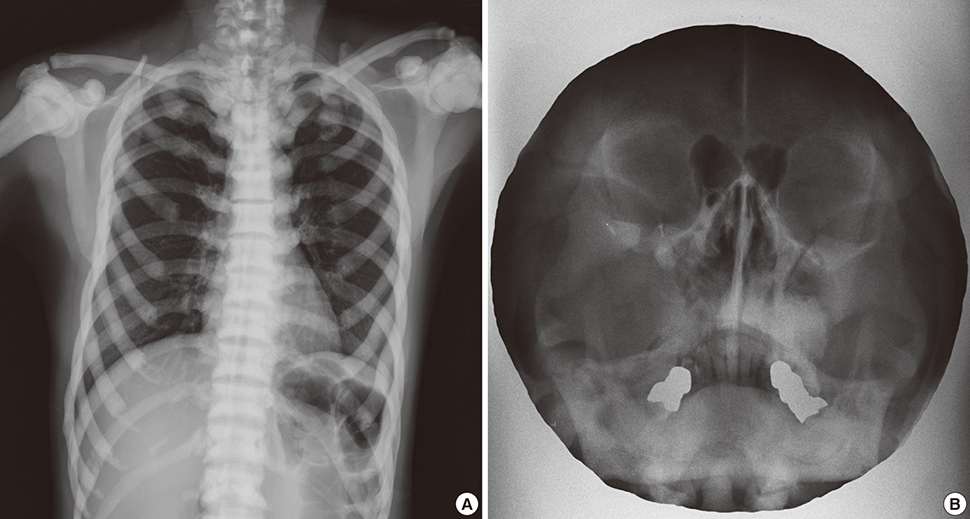
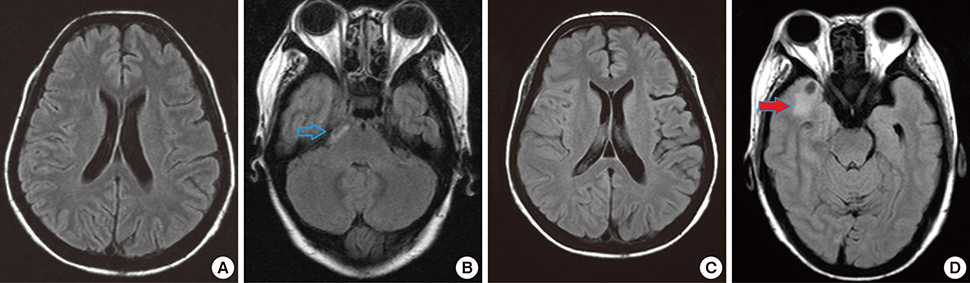
- Osteopetrosis is a rare genetic bone disease characterized by increased bone density but prone to breakage due to defective osteoclastic function. Among two primary types of autosomal dominant osteopetrosis (ADO), osteopetrosis type II is characterized by sclerosis of bones, predominantly involving the spine, the pelvis, and the skull base. Fragility of bones and dental abscess are leading complications. This report presents a case of osteopetrosis in a 52-years-old female, which was complicated by the development of cavernous sinus thrombophlebitis and meningitis. She was suffered from multiple fractures since one year ago. Laboratory data revealed elevated serum levels of tartrate resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) without carbonic anhydrase II DNA mutation. A thoracolumbar spine X-ray showed, typical findings of ADO type II (ADO II; Albers-Schonberg disease), prominent vertebral endplates so called the 'rugger jersey spine'. Her older sister also showed same typical spine appearance. We report a case of ADO II with cavernous sinus thrombophlebitis and meningitis that was successfully treated with long-term antibiotics with right sphenoidotomy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Lessons Learned from Long-Term Management of Hip Fracture in Patients with Osteopetrosis: A Report of Nine Hips in Five Patients
Jae-Young Lim, Boo Seop Kim, Byung-Ho Yoon, Jae Suk Chang, Chan-Ho Park, Kyung-Hoi Koo
J Bone Metab. 2019;26(3):201-206. doi: 10.11005/jbm.2019.26.3.201.
Reference
-
1. Del Fattore A, Cappariello A, Teti A. Genetics, pathogenesis and complications of osteopetrosis. Bone. 2008; 42:19–29.
Article2. Sobacchi C, Frattini A, Guerrini MM, et al. Osteoclast-poor human osteopetrosis due to mutations in the gene encoding RANKL. Nat Genet. 2007; 39:960–962.
Article3. Johnston CC Jr, Lavy N, Lord T, et al. Osteopetrosis. A clinical, genetic, metabolic, and morphologic study of the dominantly inherited, benign form. Medicine (Baltimore). 1968; 47:149–167.4. Bollerslev J, Andersen PE Jr. Radiological, biochemical and hereditary evidence of two types of autosomal dominant osteopetrosis. Bone. 1988; 9:7–13.
Article5. Bénichou OD, Laredo JD, de Vernejoul MC. Type II autosomal dominant osteopetrosis (Albers-Schonberg disease): clinical and radiological manifestations in 42 patients. Bone. 2000; 26:87–93.
Article6. Albers-Schönberg HE. Röntgenbilder einer seltenen knochenerkrankung. Munch Med Wochenschr. 1904; 51:365–368.7. Favus MJ, Vokes TJ. Chapter 355. Paget's disease and other dysplasias of bone. In : Longo DL, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, editors. Harrison's principles of internal medicine. 18th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill;2012.8. de Vernejoul MC, Schulz A, Kornak U. CLCN7-related osteopetrosis. 2007. cited by 2013 Jun 20. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1127/.9. Waguespack SG, Hui SL, White KE, et al. Measurement of tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase and the brain isoenzyme of creatine kinase accurately diagnoses type II autosomal dominant osteopetrosis but does not identify gene carriers. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002; 87:2212–2217.
Article10. Del Fattore A, Peruzzi B, Rucci N, et al. Clinical, genetic, and cellular analysis of 49 osteopetrotic patients: implications for diagnosis and treatment. J Med Genet. 2006; 43:315–325.
Article11. Whyte MP, Kempa LG, McAlister WH, et al. Elevated serum lactate dehydrogenase isoenzymes and aspartate transaminase distinguish Albers-Schonberg disease (Chloride Channel 7 Deficiency Osteopetrosis) among the sclerosing bone disorders. J Bone Miner Res. 2010; 25:2515–2526.
Article12. Campos-Xavier AB, Saraiva JM, Ribeiro LM, et al. Chloride channel 7 (CLCN7) gene mutations in intermediate autosomal recessive osteopetrosis. Hum Genet. 2003; 112:186–189.
Article13. Mandell GL, Bennett JE, Dolin R. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's principles and practices of infectious diseases. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Churchill Livingstone;2005.14. Clarke M, Enuh H, Saverimuttu J, et al. Streptococcus group C meningitis with cavernous sinus thrombosis. Infect Drug Resist. 2013; 6:79–81.15. Cannon ML, Antonio BL, McCloskey JJ, et al. Cavernous sinus thrombosis complicating sinusitis. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2004; 5:86–88.
Article16. Roos KL, Tyler KL. Chapter 381. Meningitis, encephalitis, brain abscess, and empyema. In : Longo DL, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, editors. Harrison's principles of internal medicine. 18th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill;2012.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Cavernous Sinus Thrombophlebitis Secondary toAcute Isolated Sphenoid Sinusitis
- Oculomotor and Abducens Nerve Palsy Complicated by Cavernous Sinus Thrombophlebitis Resulting from Acute Sinusitis
- Lateral Sinus Thrombophlebitis Caused by Isolated Sphenoid Sinusitis
- Fulminant Superior Ophthalmic Vein and Cavernous Sinus Thrombophlebitis with Intracranial Extensions: Case Reports
- A Case of Cavernous Sinus Thrombophlebitis and Abducence Nerve Palsy Secondary to Petrositis