Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2015 Mar;19(2):167-175. 10.4196/kjpp.2015.19.2.167.
Effect of Stimulus Waveform of Biphasic Current Pulse on Retinal Ganglion Cell Responses in Retinal Degeneration (rd1) mice
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physiology, Chungbuk National University School of Medicine, Cheongju 362-763, Korea. ysgoo@chungbuk.ac.kr
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Chungbuk National University School of Medicine, Cheongju 362-763, Korea.
- 3Department of Information and Communication Engineering, Chungbuk National University College of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Cheongju 362-763, Korea.
- 4Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Ulsan, Ulsan 680-749, Korea.
- 5Devision of Neuroscience, Alfaisal University College of Medicine, Riyadh 11533, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
- KMID: 2285569
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2015.19.2.167
Abstract
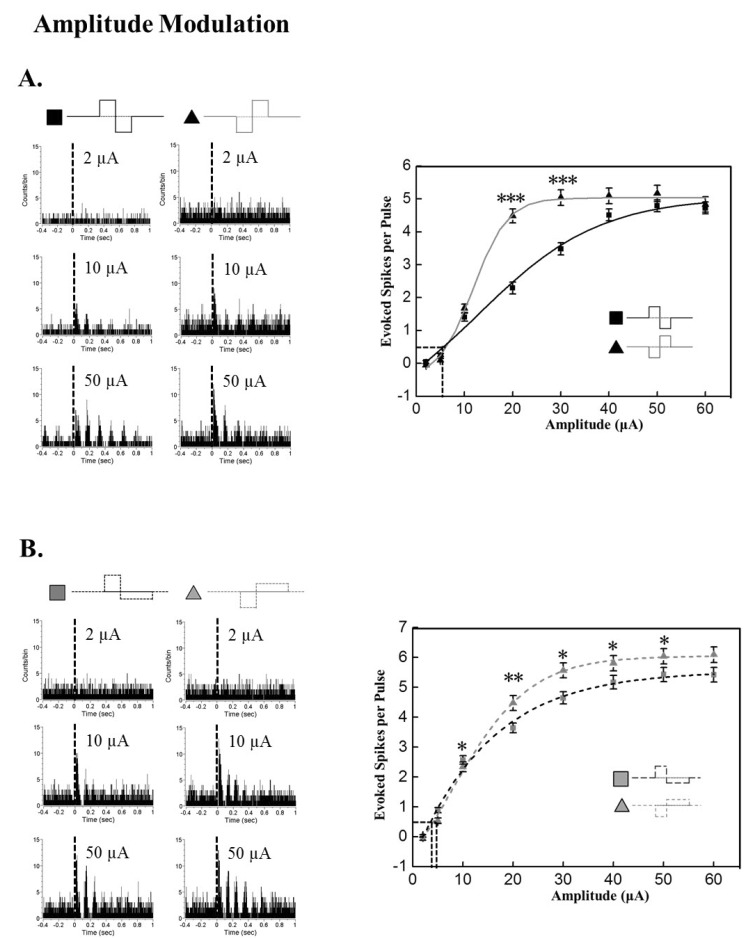
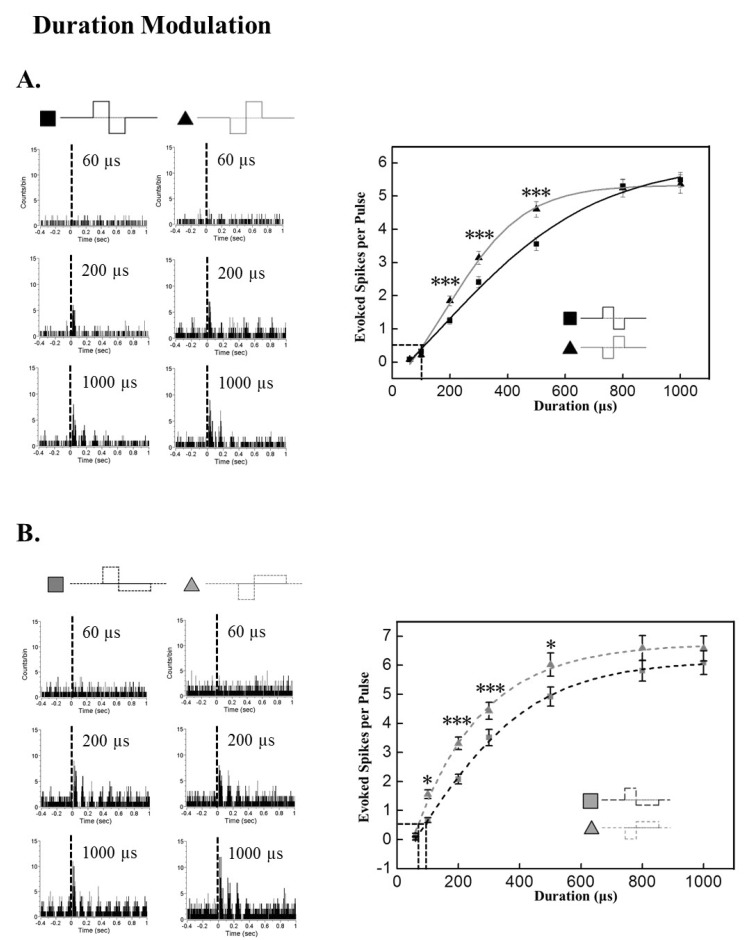
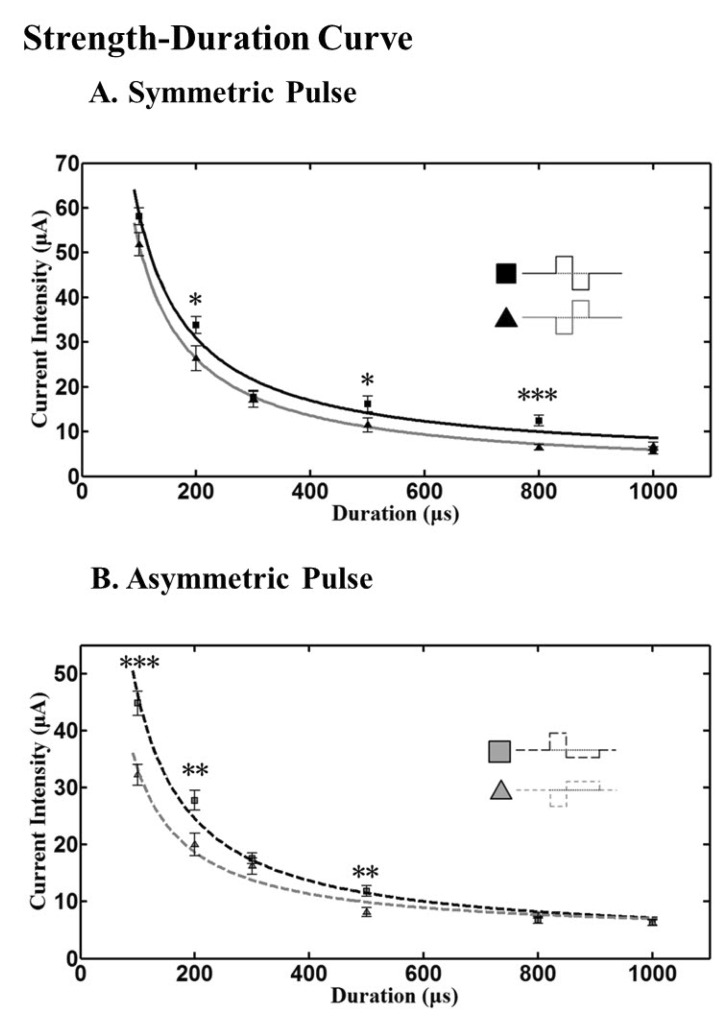
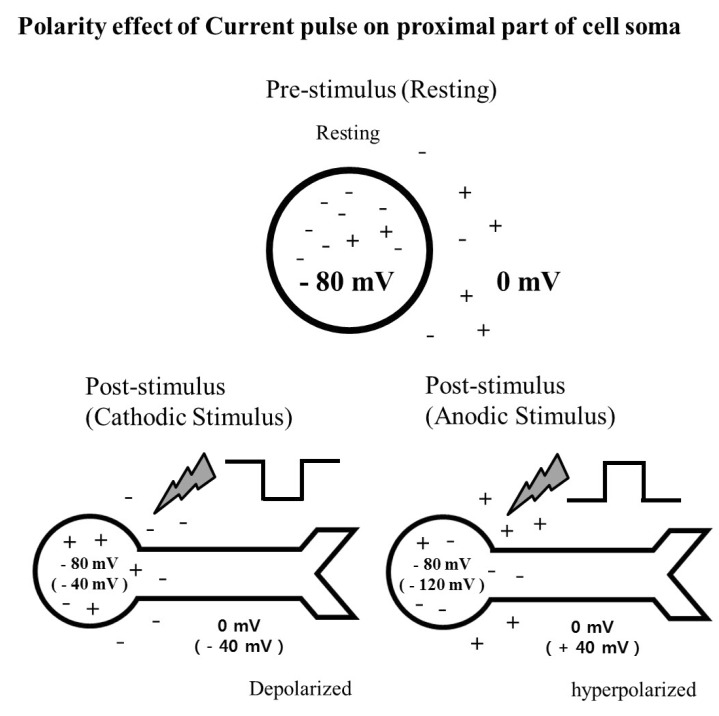
- A retinal prosthesis is being developed for the restoration of vision in patients with retinitis pigmentosa (RP) and age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Determining optimal electrical stimulation parameters for the prosthesis is one of the most important elements for the development of a viable retinal prosthesis. Here, we investigated the effects of different charge-balanced biphasic pulses with regard to their effectiveness in evoking retinal ganglion cell (RGC) responses. Retinal degeneration (rd1) mice were used (n=17). From the ex-vivo retinal preparation, retinal patches were placed ganglion cell layer down onto an 8x8 multielectrode array (MEA) and RGC responses were recorded while applying electrical stimuli. For asymmetric pulses, 1st phase of the pulse is the same with symmetric pulse but the amplitude of 2nd phase of the pulse is less than 10 microA and charge balanced condition is satisfied by lengthening the duration of the pulse. For intensities (or duration) modulation, duration (or amplitude) of the pulse was fixed to 500 micros (30 microA), changing the intensities (or duration) from 2 to 60 microA (60 to 1000 micros). RGCs were classified as response-positive when PSTH showed multiple (3~4) peaks within 400 ms post stimulus and the number of spikes was at least 30% more than that for the immediate pre-stimulus 400 ms period. RGC responses were well modulated both with anodic and cathodic phase-1st biphasic pulses. Cathodic phase-1st pulses produced significantly better modulation of RGC activity than anodic phase-1st pulses regardless of symmetry of the pulse.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
The advantage of topographic prominence-adopted filter for the detection of short-latency spikes of retinal ganglion cells
Jungryul Ahn, Myoung-Hwan Choi, Kwangsoo Kim, Solomon S. Senok, Dong-il Dan Cho, Kyo-in Koo, Yongsook Goo
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2017;21(5):555-563. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2017.21.5.555.Multiple consecutive-biphasic pulse stimulation improves spatially localized firing of retinal ganglion cells in the degenerate retina
Jungryul Ahn, Yongseok Yoo, Yong Sook Goo
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2023;27(6):541-553. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2023.27.6.541.
Reference
-
1. Arnold JJ, Heriot W. Age related macular degeneration. Clin Evid (Online). 2007; 2007:pii: 0701.2. Sieving PA, Caruso RC. Retinitis pigmentosa and related disorders. In : Yanoff M, Duker JS, editors. Ophthalmology. 3rd ed. Maryland Heights: Elsevier;2008. chap 6.10.3. Chader GJ, Weiland J, Humayun MS. Artificial vision: needs, functioning, and testing of a retinal electronic prosthesis. Prog Brain Res. 2009; 175:317–332. PMID: 19660665.
Article4. Rizzo JF 3rd. Update on retinal prosthetic research: the Boston Retinal Implant Project. J Neuroophthalmol. 2011; 31:160–168. PMID: 21593628.
Article5. Zrenner E, Bartz-Schmidt KU, Benav H, Besch D, Bruckmann A, Gabel VP, Gekeler F, Greppmaier U, Harscher A, Kibbel S, Koch J, Kusnyerik A, Peters T, Stingl K, Sachs H, Stett A, Szurman P, Wilhelm B, Wilke R. Subretinal electronic chips allow blind patients to read letters and combine them to words. Proc Biol Sci. 2011; 278:1489–1497. PMID: 21047851.
Article6. Tombran-Tink J, Barnstable CJ, Rizzo JF 3rd. Visual prosthesis and ophthalmic devices: new hope in sight. Totawa: Humana Press;2007.7. Grumet AE, Wyatt JL Jr, Rizzo JF 3rd. Multi-electrode stimulation and recording in the isolated retina. J Neurosci Methods. 2000; 101:31–42. PMID: 10967359.
Article8. Stett A, Barth W, Weiss S, Haemmerle H, Zrenner E. Electrical multisite stimulation of the isolated chicken retina. Vision Res. 2000; 40:1785–1795. PMID: 10814763.
Article9. Ye JH, Goo YS. The slow wave component of retinal activity in rd/rd mice recorded with a multi-electrode array. Physiol Meas. 2007; 28:1079–1088. PMID: 17827655.10. Ye JH, Ryu SB, Kim KH, Goo YS. Functional connectivity map of retinal ganglion cells for retinal prosthesis. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2008; 12:307–314. PMID: 19967072.
Article11. Goo YS, Ye JH, Lee S, Nam Y, Ryu SB, Kim KH. Retinal ganglion cell responses to voltage and current stimulation in wild-type and rd1 mouse retinas. J Neural Eng. 2011; 8:035003. PMID: 21593549.12. Goo YS, Ahn KN, Song YJ, Ahn SH, Han SK, Ryu SB, Kim KH. Spontaneous oscillatory rhythm in retinal activities of two retinal degeneration (rd1 and rd10) mice. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2011; 15:415–422. PMID: 22359480.13. Jae SA, Ahn KN, Kim JY, Seo JH, Kim HK, Goo YS. Electrophysiological and histologic evaluation of the time course of retinal degeneration in the rd10 mouse model of retinitis pigmentosa. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2013; 17:229–235. PMID: 23776400.14. Liu W, Vichienchom K, Clements M, DeMarco SC, Hughes C, McGucken E, Humayun MS, de Juan E, Weiland JD, Grenberg R. A neuro-stimulus chip with telemetry unit for retinal prosthetic device. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits. 2000; 35:1487–1497.
Article15. Brummer SB, Turner MJ. Electrical stimulation of the nervous system:the principle of safe charge injection with noble metal electrodes. Bioelectrochem Bioenerg. 1975; 2:13–25.16. Lilly JC, Hughes JR, Alvord EC Jr, Galkin TW. Brief, noninjurious electric waveform for stimulation of the brain. Science. 1955; 121:468–469. PMID: 14358670.
Article17. Mortimer JT, Shealy CN, Wheeler C. Experimental nondestructive electrical stimulation of the brain and spinal cord. J Neurosurg. 1970; 32:553–559. PMID: 5438095.
Article18. Mortimer JT, Kaufman D, Roessman U. Intramuscular electrical stimulation: tissue damage. Ann Biomed Eng. 1980; 8:235–244. PMID: 7224246.
Article19. Scheiner A, Mortimer JT, Roessmann U. Imbalanced biphasic electrical stimulation: muscle tissue damage. Ann Biomed Eng. 1990; 18:407–425. PMID: 2221508.
Article20. Shepherd RK, Javel E. Electrical stimulation of the auditory nerve: II. Effect of stimulus waveshape on single fibre response properties. Hear Res. 1999; 130:171–188. PMID: 10320107.
Article21. Merrill DR, Bikson M, Jefferys JG. Electrical stimulation of excitable tissue: design of efficacious and safe protocols. J Neurosci Methods. 2005; 141:171–198. PMID: 15661300.
Article22. Wagenaar DA, Pine J, Potter SM. Effective parameters for stimulation of dissociated cultures using multi-electrode arrays. J Neurosci Methods. 2004; 138:27–37. PMID: 15325108.
Article23. Farber DB, Flannery JG, Bowes-Rickman C. The rd mouse story: seventy years of research on an animal model of inherited retinal degeneration. Prog Ret Eye Res. 1994; 13:31–64.
Article24. McLaughlin ME, Sandberg MA, Berson EL, Dryja TP. Recessive mutations in the gene encoding the beta-subunit of rod phosphodiesterase in patients with retinitis pigmentosa. Nat Genet. 1993; 4:130–134. PMID: 8394174.25. McLaughlin ME, Ehrhart TL, Berson EL, Dryja TP. Mutation spectrum of the gene encoding the beta subunit of rod phosphodiesterase among patients with autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995; 92:3249–3253. PMID: 7724547.
Article26. Margolis DJ, Newkirk G, Euler T, Detwiler PB. Functional stability of retinal ganglion cells after degeneration-induced changes in synaptic input. J Neurosci. 2008; 28:6526–6536. PMID: 18562624.
Article27. Menzler J, Zeck G. Network oscillations in rod-degenerated mouse retinas. J Neurosci. 2011; 31:2280–2291. PMID: 21307264.
Article28. Nicolelis MAL. Methods for neural ensemble recordings. New York: CRC press;1999.29. Meister M, Berry MJ 2nd. The neural code of the retina. Neuron. 1999; 22:435–450. PMID: 10197525.
Article30. Jin GH, Cho HS, Lee TS, Goo YS. PCA-based waveform classification of rabbit retinal ganglion cell activity. Korean J Medical Physics. 2003; 14:211–217.31. Chapin JK, Nicolelis MA. Principal component analysis of neuronal ensemble activity reveals multidimensional somatosensory representations. J Neurosci Methods. 1999; 94:121–140. PMID: 10638820.
Article32. Jolliffe IT. Principal component analysis. New York: Springer-Verlag;2005.33. Holsheimer J, Demeulemeester H, Nuttin B, de Sutter P. Identification of the target neuronal elements in electrical deep brain stimulation. Eur J Neurosci. 2000; 12:4573–4577. PMID: 11122371.
Article34. Lapicque L. Recherches quantitatives sur l'excitation electrique des nerfs traites comme un polarization. J Physiol Paris. 1907; 9:620–635.35. Loeb GE, White MW, Jenkins WM. Biophysical considerations in electrical stimulation of the auditory nervous system. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983; 405:123–136. PMID: 6575638.
Article36. Ranck JB Jr. Which elements are excited in electrical stimulation of mammalian central nervous system: a review. Brain Res. 1975; 98:417–440. PMID: 1102064.
Article37. Fried SI, Lasker AC, Desai NJ, Eddington DK, Rizzo JF 3rd. Axonal sodium-channel bands shape the response to electric stimulation in retinal ganglion cells. J Neurophysiol. 2009; 101:1972–1987. PMID: 19193771.
Article38. Jensen RJ, Rizzo JF 3rd, Ziv OR, Grumet A, Wyatt J. Thresholds for activation of rabbit retinal ganglion cells with an ultrafine, extracellular microelectrode. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003; 44:3533–3543. PMID: 12882804.
Article39. Boinagrov D, Pangratz-Fuehrer S, Goetz G, Palanker D. Selectivity of direct and network-mediated stimulation of the retinal ganglion cells with epi-, sub- and intraretinal electrodes. J Neural Eng. 2014; 11:026008. PMID: 24608166.
Article40. Sekirnjak C, Hottowy P, Sher A, Dabrowski W, Litke AM, Chichilnisky EJ. Electrical stimulation of mammalian retinal ganglion cells with multielectrode arrays. J Neurophysiol. 2006; 95:3311–3327. PMID: 16436479.
Article41. Tehovnik EJ. Electrical stimulation of neural tissue to evoke behavioral responses. J Neurosci Methods. 1996; 65:1–17. PMID: 8815302.
Article42. Wollner DA, Catterall WA. Localization of sodium channels in axon hillocks and initial segments of retinal ganglion cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986; 83:8424–8428. PMID: 2430289.
Article43. Jimbo Y, Kawana A. Electrical stimulation and recording from cultured neurons using a planar electrode array. Bioelectrochem Bioenerg. 1992; 29:193–204.
Article44. Brown EA, Ross JD, Blum RA, Yoonkey Nam, Wheeler BC, Deweerth SP. Stimulus-artifact elimination in a multi-electrode system. IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst. 2008; 2:10–21. PMID: 23852629.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Multiple consecutive-biphasic pulse stimulation improves spatially localized firing of retinal ganglion cells in the degenerate retina
- Spontaneous Oscillatory Rhythm in Retinal Activities of Two Retinal Degeneration (rd1 and rd10) Mice
- Electrically-evoked Neural Activities of rd1 Mice Retinal Ganglion Cells by Repetitive Pulse Stimulation
- Comparison of Retinal Ganglion Cell Responses to Different Voltage Stimulation Parameters in Normal and rd1 Mouse Retina
- Comparison of Retinal Waveform between Normal and rd/rd Mouse