Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2015 Mar;19(2):99-104. 10.4196/kjpp.2015.19.2.99.
Prediction of Pharmacokinetics and Penetration of Moxifloxacin in Human with Intra-Abdominal Infection Based on Extrapolated PBPK Model
- Affiliations
-
- 1Tianjin First Central Hospital, Tianjin 300192, China. zlq0713@aliyun.com
- 2Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300070, China.
- 3The 153 Central Hospital of the Chinese People's Liberation Army, Henan 450000, China.
- KMID: 2285560
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2015.19.2.99
Abstract
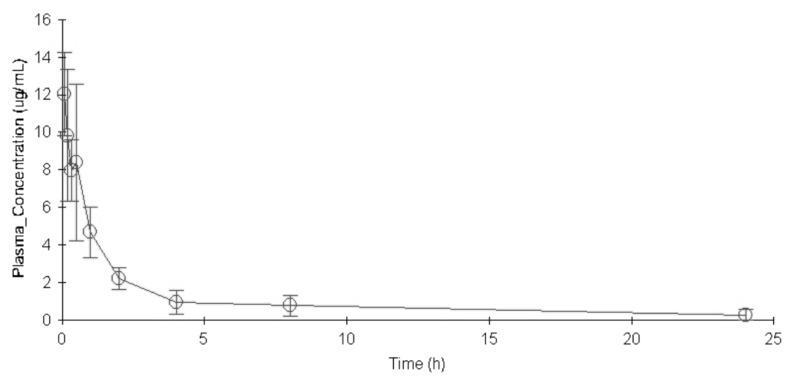
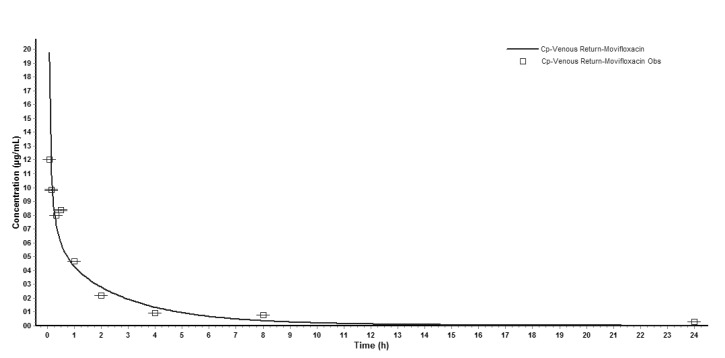
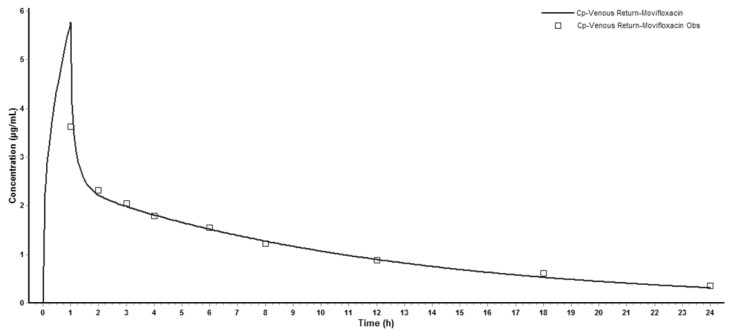
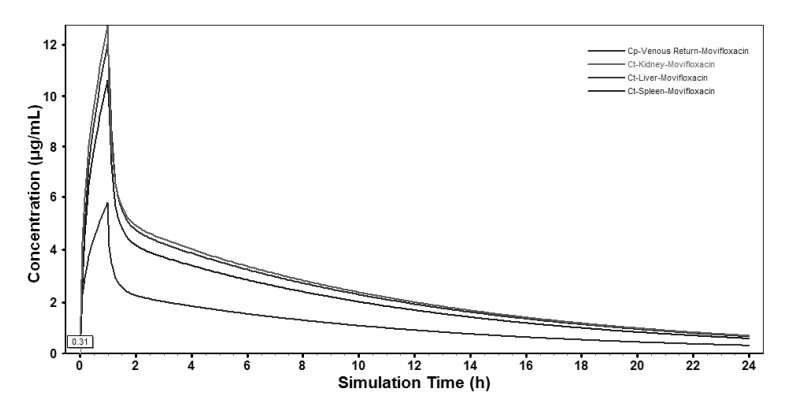
- The aim of this study is to develop a physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) model in intraabdominal infected rats, and extrapolate it to human to predict moxifloxacin pharmacokinetics profiles in various tissues in intra-abdominal infected human. 12 male rats with intra- abdominal infections, induced by Escherichia coli, received a single dose of 40 mg/kg body weight of moxifloxacin. Blood plasma was collected at 5, 10, 20, 30, 60, 120, 240, 480, 1440 min after drug injection. A PBPK model was developed in rats and extrapolated to human using GastroPlus software. The predictions were assessed by comparing predictions and observations. In the plasma concentration versus time profile of moxifloxcinin rats, Cmax was 11.151 microg/mL at 5 min after the intravenous injection and t1/2 was 2.936 h. Plasma concentration and kinetics in human were predicted and compared with observed datas. Moxifloxacin penetrated and accumulated with high concentrations in redmarrow, lung, skin, heart, liver, kidney, spleen, muscle tissues in human with intra-abdominal infection. The predicted tissue to plasma concentration ratios in abdominal viscera were between 1.1 and 2.2. When rat plasma concentrations were known, extrapolation of a PBPK model was a method to predict drug pharmacokinetics and penetration in human. Moxifloxacin has a good penetration into liver, kidney, spleen, as well as other tissues in intra-abdominal infected human. Close monitoring are necessary when using moxifloxacin due to its high concentration distribution. This pathological model extrapolation may provide reference to the PK/PD study of antibacterial agents.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Singh R, Ledesma KR, Chang KT, Hou JG, Prince RA, Tam VH. Pharmacodynamics of moxifloxacin against a high inoculum of Escherichia coli in an in vitro infection model. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2009; 64:556–562. PMID: 19589810.2. Kern A, Kanhai W, Frohde R, et al. BAY 12-8039, a new 8-methoxy-quinolone: metabolism in rat, monkey and man [abstract no. F23]. In : 36th Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy; 1996 Sep 15-18; New Orleans, Louisiana. p. 103.3. Edginton AN, Ahr G, Willmann S, Stass H. Defining the role of macrophages in local moxifloxacin tissue concentrations using biopsy data and whole-body physiologically based pharmacokinetic modelling. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2009; 48:181–187. PMID: 19385711.
Article4. Yoshida K, Okimoto N, Kishimoto M, Fukano H, Hara H, Yoneyama H, Moriya O, Kawanishi M, Kimura M, Matsushima T, Niki Y. Efficacy and safety of moxifloxacin for community-acquired bacterial pneumonia based on pharmacokinetic analysis. J Infect Chemother. 2011; 17:678–685. PMID: 21847518.
Article5. Ober MC, Hoppe-Tichy T, Köninger J, Schunter O, Sonntag HG, Weigand MA, Encke J, Gutt C, Swoboda S. Tissue penetration of moxifloxacin into human gallbladder wall in patients with biliary tract infections. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2009; 64:1091–1095. PMID: 19734170.
Article6. Majcher-Peszynska J, Sass M, Schipper S, Czaika V, Gussmann A, Lobmann R, Mundkowski RG, Luebbert C, Kujath P, Ruf BR, Koch H, Schareck W, Klar E, Drewelow B. Moxifloxacin-DFI Study Group. Pharmacokinetics and penetration of moxifloxacin into infected diabetic foot tissue in a large diabetic patient cohort. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2011; 67:135–142. PMID: 20871984.
Article7. Kees MG, Weber S, Kees F, Horbach T. Pharmacokinetics of moxifloxacin in plasma and tissue of morbidly obese patients. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011; 66:2330–2335. PMID: 21729931.
Article8. Stass H, Kubitza D, Halabi A, Delesen H. Pharmacokinetics of moxifloxacin, a novel 8-methoxy-quinolone, in patients with renal dysfunction. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2002; 53:232–237. PMID: 11874385.
Article9. Barth J, Jäger D, Mundkowski R, Drewelow B, Welte T, Burkhardt O. Single- and multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of intravenous moxifloxacin in patients with severe hepatic impairment. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2008; 62:575–578. PMID: 18515790.
Article10. Pletz MW, Bloos F, Burkhardt O, Brunkhorst FM, Bode-Böger SM, Martens-Lobenhoffer J, Greer MW, Stass H, Welte T. Pharmacokinetics of moxifloxacin in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock. Intensive Care Med. 2010; 36:979–983. PMID: 20336279.
Article11. Stass H, Rink AD, Delesen H, Kubitza D, Vestweber KH. Pharmacokinetics and peritoneal penetration of moxifloxacin in peritonitis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2006; 58:693–696. PMID: 16895940.
Article12. Rink AD, Stass H, Delesen H, Kubitza D, Vestweber KH. Pharmacokinetics and tissue penetration of moxifloxacin in intervention therapy for intra-abdominal abscess. Clin Drug Investig. 2008; 28:71–79.13. Campbell A. Development of PBPK model of molinate and molinate sulfoxide in rats and humans. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2009; 53:195–204. PMID: 19545510.
Article14. Wenli Y, Naiqiang C, Qiang F, Donghua L. Immune imbalance of rats with severe abdominal infection. Chin J Surg Integr Tradit West Med. 2011; 17:276–279.15. Poirier A, Funk C, Scherrmann JM, Lavé T. Mechanistic modeling of hepatic transport from cells to whole body: application to napsagatran and fexofenadine. Mol Pharm. 2009; 6:1716–1733. PMID: 19739673.
Article16. Rodgers T, Leahy D, Rowland M. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling 1: predicting the tissue distribution of moderate-to-strong bases. J Pharm Sci. 2005; 94:1259–1276. PMID: 15858854.
Article17. Rodgers T, Rowland M. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modelling 2: predicting the tissue distribution of acids, very weak bases, neutrals and zwitterions. J Pharm Sci. 2006; 95:1238–1257. PMID: 16639716.
Article18. Mannhold R, Poda GI, Ostermann C, Tetko IV. Calculation of molecular lipophilicity: State-of-the-art and comparison of log P methods on more than 96,000 compounds. J Pharm Sci. 2009; 98:861–893. PMID: 18683876.19. De Buck SS, Sinha VK, Fenu LA, Gilissen RA, Mackie CE, Nijsen MJ. The prediction of drug metabolism, tissue distribution, and bioavailability of 50 structurally diverse compounds in rat using mechanism-based absorption, distribution, and metabolism prediction tools. Drug Metab Dispos. 2007; 35:649–659. PMID: 17267621.
Article20. Lee AC, Crippen GM. Predicting pKa. J Chem Inf Model. 2009; 49:2013–2033. PMID: 19702243.
Article21. Senggunprai L, Yoshinari K, Yamazoe Y. Selective role of sulfotransferase 2A1 (SULT2A1) in the N-sulfoconjugation of quinolone drugs in humans. Drug Metab Dispos. 2009; 37:1711–1717. PMID: 19420132.22. Lemaire S, Tulkens PM, Van Bambeke F. Contrasting effects of acidic pH on the extracellular and intracellular activities of the anti-gram-positive fluoroquinolones moxifloxacin and delafloxacin against Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011; 55:649–658. PMID: 21135179.23. Beyer R, Pestova E, Millichap JJ, Stosor V, Noskin GA, Peterson LR. A convenient assay for estimating the possible involvement of efflux of fluoroquinolones by Streptococcus pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus: evidence for diminished moxifloxacin, sparfloxacin, and trovafloxacin efflux. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2000; 44:798–801. PMID: 10681364.24. MacGowan AP. Moxifloxacin (Bay 12-8039): a new methoxy quinolone antibacterial. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 1999; 8:181–199.
Article25. Wise R. A review of the clinical pharmacology of moxifloxacin, a new 8-methoxyquinolone, and its potential relation to therapeutic efficacy. Clin Drug Investig. 1999; 17:365–387.26. Li GF, Wang K, Chen R, Zhao HR, Yang J, Zheng QS. Simulation of the pharmacokinetics of bisoprolol in healthy adults and patients with impaired renal function using whole-body physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012; 33:1359–1371. PMID: 23085739.
Article27. Jones HM, Parrott N, Jorga K, Lavé T. A novel strategy for physiologically based predictions of human pharmacokinetics. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2006; 45:511–542. PMID: 16640456.
Article28. Eichler HG, Müller M. Drug distribution. The forgotten relative in clinical pharmacokinetics. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1998; 34:95–99. PMID: 9515183.29. Siefert HM, Kohlsdorfer C, Steinke W, Witt A. Pharmacokinetics of the 8-methoxyquinolone, moxifloxacin: tissue distribution in male rats. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1999; 43(Suppl B):61–67. PMID: 10382877.30. Stass H. Distribution and Tissue Penetration of Moxifloxacin. Drugs. 1999; 58(2):Suppl. 229–230.
Article31. Stass H, Kubitza D, Aydeniz B, Wallwiener D, Halabi A, Gleiter C. Penetration and accumulation of moxifloxacin in uterine tissue. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2008; 102:132–136. PMID: 18501909.
Article32. Edmiston CE, Krepel CJ, Seabrook GR, Somberg LR, Nakeeb A, Cambria RA, Towne JB. In vitro activities of moxifloxacin against 900 aerobic and anaerobic surgical isolates from patients with intra-abdominal and diabetic foot infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004; 48:1012–1016. PMID: 14982797.33. Schaumann R, Goldstein EJ, Forberg J, Rodloff AC. Activity of moxifloxacin against Bacteroides fragilis and Escherichia coli in an in vitro pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model employing pure and mixed cultures. J Med Microbiol. 2005; 54:749–753. PMID: 16014428.34. Singh VP, Singh N, Jaggi AS. A review on renal toxicity profile of common abusive drugs. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2013; 17:347–357. PMID: 23946695.
Article35. Randhawa PK, Singh K, Singh N, Jaggi AS. A review on chemical-induced inflammatory bowel disease models in rodents. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2014; 18:279–288. PMID: 25177159.
Article36. Watson KJ, Gorczyca WP, Umland J, Zhang Y, Chen X, Sun SZ, Fermini B, Holbrook M, Van Der Graaf PH. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modelling of the effect of Moxifloxacin on QTc prolongation in telemetered cynomolgus monkeys. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2011; 63:304–313. PMID: 21419854.
Article37. Moxifloxacin. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2008; 88:127–131. PMID: 18486050.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Compatibility Study between Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) and Compartmental PK Model Using Lumping Method: Application to the Voriconazole Case
- Prediction of pharmacokinetics and drug-drug interaction potential using physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling approach: A case study of caffeine and ciprofloxacin
- Qualification and application of liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-offlight mass spectrometric method for the determination of carisbamate in rat plasma and prediction of its human pharmacokinetics using physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling
- Predicting human pharmacokinetics from preclinical data: volume of distribution
- Physiologically-based pharmacokinetic modeling of nafamostat to support dose selection for treatment of pediatric patients with COVID-19