J Adv Prosthodont.
2013 May;5(2):104-109. 10.4047/jap.2013.5.2.104.
Effect of silane activation on shear bond strength of fiber-reinforced composite post to resin cement
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Prosthodontics, Department of Dentistry, College of Medicine, University of Ulsan, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea. chahyunsuk@hanmail.net
- 2Division of Oral and maxillofacial Surgery, Department of Dentistry, College of Medicine, University of Ulsan, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
- 3Department of Dentistry, Seoul National University Boramae Hospital, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
- KMID: 2284748
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2013.5.2.104
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Among the surface treatment methods suggested to enhance the adhesion of resin cement to fiber-reinforced composite posts, conflicting results have been obtained with silanization. In this study, the effects of silanization, heat activation after silanization, on the bond strength between fiber-reinforced composite post and resin cement were determined.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
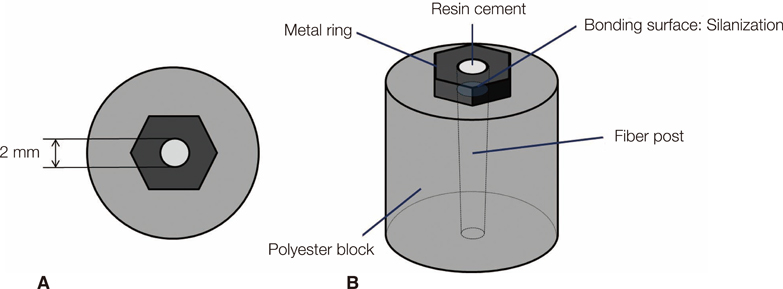
Six groups (n=7) were established to evaluate two types of fiber post (FRC Postec Plus, D.T. Light Post) and three surface treatments (no treatment; air drying; drying at 38degrees C). Every specimen were bonded with dual-curing resin cement (Variolink N) and stored in distilled water for 24 hours at 37degrees C. Shear-bond strength (MPa) between the fiber post and the resin cement were measured using universal testing device. The data were analyzed with 1-way ANOVA and by multiple comparisons according to Tukey's HSD (alpha=0.05). The effect of surface treatment, fiber post type, and the interactions between these two factors were analyzed using 2-way ANOVA and independent sample T-tests.
RESULTS
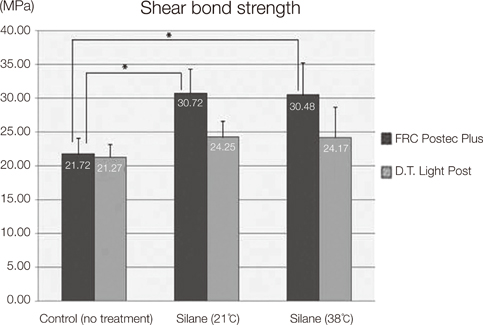
Silanization of the FRC Postec Plus significantly increased bond strength compared with the respective non-treated control, whereas no effect was determined for the D.T. Light Post. Heat drying the silane coupling agent on to the fiber-reinforced post did not significantly improve bond strength compared to air-syringe drying.
CONCLUSION
The bond strength between the fiber-reinforced post and the resin cement was significantly increased with silanization in regards to the FRC Postec Plus post. Bond strength was not significantly improved by heat activation of the silane coupling agent.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Aksornmuang J, Foxton RM, Nakajima M, Tagami J. Microtensile bond strength of a dual-cure resin core material to glass and quartz fibre posts. J Dent. 2004; 32:443–450.2. Aksornmuang J, Nakajima M, Foxton RM, Panyayong W, Tagami J. Regional bond strengths and failure analysis of fiber posts bonded to root canal dentin. Oper Dent. 2008; 33:636–643.3. Ferrari M, Cagidiaco MC, Goracci C, Vichi A, Mason PN, Radovic I, Tay F. Long-term retrospective study of the clinical performance of fiber posts. Am J Dent. 2007; 20:287–291.4. Monticelli F, Osorio R, Sadek FT, Radovic I, Toledano M, Ferrari M. Surface treatments for improving bond strength to prefabricated fiber posts: a literature review. Oper Dent. 2008; 33:346–355.5. Albashaireh ZS, Ghazal M, Kern M. Effects of endodontic post surface treatment, dentin conditioning, and artificial aging on the retention of glass fiber-reinforced composite resin posts. J Prosthet Dent. 2010; 103:31–39.6. Balbosh A, Kern M. Effect of surface treatment on retention of glass-fiber endodontic posts. J Prosthet Dent. 2006; 95:218–223.7. Choi Y, Pae A, Park EJ, Wright RF. The effect of surface treatment of fiber-reinforced posts on adhesion of a resin-based luting agent. J Prosthet Dent. 2010; 103:362–368.8. Yenisey M, Kulunk S. Effects of chemical surface treatments of quartz and glass fiber posts on the retention of a composite resin. J Prosthet Dent. 2008; 99:38–45.9. Mazzitelli C, Ferrari M, Toledano M, Osorio E, Monticelli F, Osorio R. Surface roughness analysis of fiber post conditioning processes. J Dent Res. 2008; 87:186–190.10. de Sousa Menezes M, Queiroz EC, Soares PV, Faria-e-Silva AL, Soares CJ, Martins LR. Fiber post etching with hydrogen peroxide: effect of concentration and application time. J Endod. 2011; 37:398–402.11. Barghi N, Berry T, Chung K. Effects of timing and heat treatment of silanated porcelain on the bond strength. J Oral Rehabil. 2000; 27:407–412.12. Shen C, Oh WS, Williams JR. Effect of post-silanization drying on the bond strength of composite to ceramic. J Prosthet Dent. 2004; 91:453–458.13. Perdigao J, Gomes G, Lee IK. The effect of silane on the bond strengths of fiber posts. Dent Mater. 2006; 22:752–758.14. Bitter K, Noetzel J, Neumann K, Kielbassa AM. Effect of silanization on bond strengths of fiber posts to various resin cements. Quintessence Int. 2007; 38:121–128.15. Mosharraf R, Baghaei Yazdi N. Comparative evaluation of effects of different surface treatment methods on bond strength between fiber post and composite core. J Adv Prosthodont. 2012; 4:103–108.16. Goracci C, Raffaelli O, Monticelli F, Balleri B, Bertilli E, Ferrari M. The adhesion between prefabricated FRC posts and composite resin cores: microtensile bond strength with and without post-silanization. Dent Mater. 2005; 21:437–444.17. Monticelli F, Toledano M, Osorio R, Ferrari M. Effect of temperature on the silane coupling agents when bonding core resin to quartz fiber posts. Dent Mater. 2006; 22:1024–1028.18. Goracci C, Ferrari M. Current perspectives on post systems: a literature review. Aust Dent J. 2011; 56:Suppl 1. 77–83.19. de la Fuente JL, Madruga EL. Solvent effects on the free-radical copolymerization of butyl acrylate with methyl methacrylate. Macromol Chem Phys. 1999; 200:1639–1643.20. Barghi N. To silanate or not to silanate: making a clinical decision. Compend Contin Educ Dent. 2000; 21:659–662.21. Novais VR, Simamotos Junior PC, Rontani RM, Correr-Sobrinho L, Soares CJ. Bond strength between fiber posts and composite resin core: influence of temperature on silane coupling agents. Braz Dent J. 2012; 23:8–14.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of hydrogen peroxide pretreatment and heat activation of silane on the shear bond strength of fiber-reinforced composite posts to resin cement
- Bond strength of self-adhesive resin cements to composite submitted to different surface pretreatments
- The shear bond strength of two adhesives bonded to composite resin and glass ionomer cement restorations
- Influence of adhesive application on shear bond strength of the resin cement to indirect resin composite
- A shear bond strength of resin cements bonded to pressable porcelain with various surface treatments