Ewha Med J.
2012 Sep;35(2):95-101. 10.12771/emj.2012.35.2.95.
Polymorphism of M341I in the Type A Human Natriuretic Peptide Receptor Gene in Essential Hypertension in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Eone Reference Laboratory, Seoul, Korea. secho0824@gmail.com
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Seoul Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2283999
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12771/emj.2012.35.2.95
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
There are 3 subtypes of natriuretic peptide (NP) receptors: type A natriuretic peptide receptor (NPRA), NPRB, and NPRC. The NPRA gene polymorphism, consisting of substition of methionine (ATG) to isoleucine (ATC) at nucleotide 1023 (M341I) of exon 3 was revealed to be associated with increased risk for essential hypertension (EH) in Japanese people. The purpose of this study is to investigate association between EH and the M341I polymorphism in the NPRA gene in Korea.
METHODS
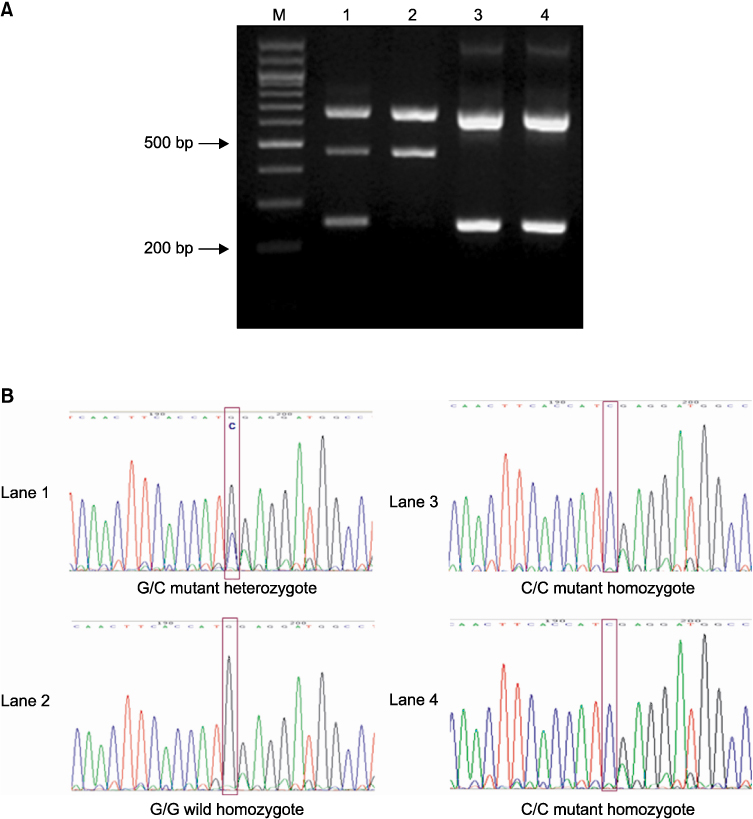
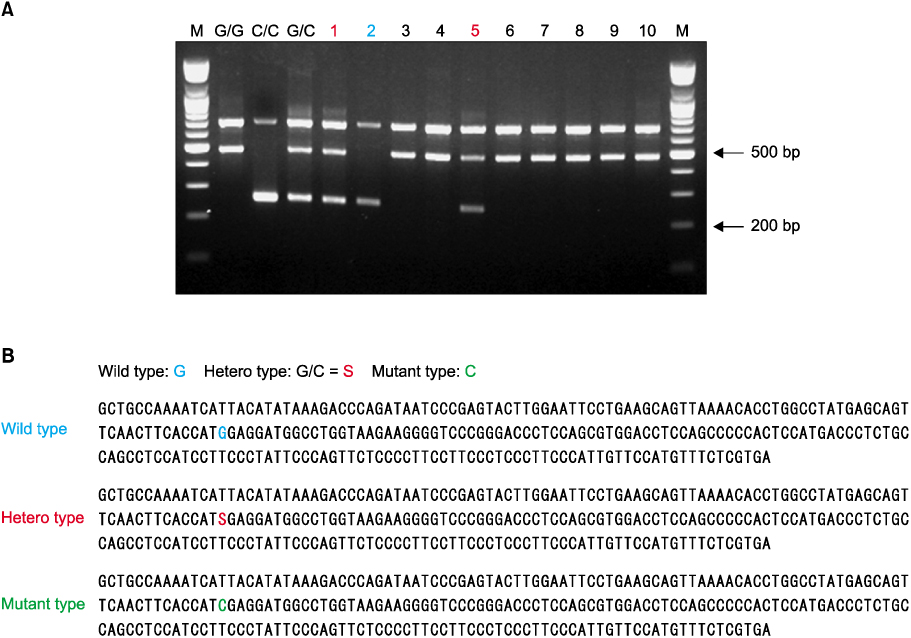
Eighty patients in whom type B natriuretic peptide (BNP) was measured were enrolled in this study. 66 patients had EH and 14 patients did not. The polymorphism of M341I was evaluated by multiplex genotyping polymerase chain reaction and by sequencing analysis.
RESULTS
The overall distribution of alleles was not significantly different between the control and EH groups. However, the C/C homozygous genotype was found only in the EH group. In the EH group, patient carrying the C/C homozygous genotype had the trend of having higher systolic and diastolic BP levels regardless of the previous treatment, even though other laboratory markers including BNP levels had no significant differences according to the genotypes.
CONCLUSION
This would be meaningful for the first identification of the M341I polymorphism in the NPRA gene and for the first suggestion of association of the EH with it in Korea.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fuller F, Porter JG, Arfsten AE, Miller J, Schilling JW, Scarborough RM, et al. Atrial natriuretic peptide clearance receptor: complete sequence and functional expression of cDNA clones. J Biol Chem. 1988. 263:9395–9401.2. Maack T, Camargo MJ, Kleinert HD, Laragh JH, Atlas SA. Atrial natriuretic factor: structure and functional properties. Kidney Int. 1985. 27:607–615.3. Yuen PS, Garbers DL. Guanylyl cyclase-linked receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1992. 15:193–225.4. Meloche S, McNicoll N, Liu B, Ong H, De Léan A. Atrial natriuretic factor R1 receptor from bovine adrenal zona glomerulosa: purification, characterization, and modulation by amiloride. Biochemistry. 1988. 27:8151–8158.5. Schenk DB, Phelps MN, Porter JG, Fuller F, Cordell B, Lewicki JA. Purification and subunit composition of atrial natriuretic peptide receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987. 84:1521–1525.6. Bennett BD, Bennett GL, Vitangcol RV, Jewett JR, Burnier J, Henzel W, et al. Extracellular domain-IgG fusion proteins for three human natriuretic peptide receptors: hormone pharmacology and application to solid phase screening of synthetic peptide antisera. J Biol Chem. 1991. 266:23060–23067.7. Nakayama T, Soma M, Takahashi Y, Rehemudula D, Kanmatsuse K, Furuya K. Functional deletion mutation of the 5'-flanking region of type A human natriuretic peptide receptor gene and its association with essential hypertension and left ventricular hypertrophy in the Japanese. Circ Res. 2000. 86:841–845.8. Thompson DK, Garbers DL. Dominant negative mutations of the guanylyl cyclase-A receptor: extracellular domain deletion and catalytic domain point mutations. J Biol Chem. 1995. 270:425–430.9. Nakayama T, Soma M, Mizutani Y, Xinjuan X, Honye J, Kaneko Y, et al. A novel missense mutation of exon 3 in the type A human natriuretic peptide receptor gene: possible association with essential hypertension. Hypertens Res. 2002. 25:395–401.10. Nakayama T, Soma M, Saito S, Honye J, Sato M, Aoi N, et al. Missense mutation of exon 3 in the type A human natriuretic peptide receptor gene is associated with myocardial infarction. Med Sci Monit. 2003. 9:CR505–CR510.11. Lucarelli K, Iacoviello M, Dessì-Fulgheri P, Sarzani R, Romito R, Sorrentino S, et al. Natriuretic peptides and essential arterial hypertension. Ital Heart J Suppl. 2002. 3:1085–1091.12. Knowles JW, Erickson LM, Guy VK, Sigel CS, Wilder JC, Maeda N. Common variations in noncoding regions of the human natriuretic peptide receptor A gene have quantitative effects. Hum Genet. 2003. 112:62–70.13. Nakayama T. The genetic contribution of the natriuretic peptide system to cardiovascular diseases. Endocr J. 2005. 52:11–21.14. Palmer BR, Frampton CM, Richards AM, Cameron VA, Nakayama T. Absence of a NPR-A gene functional deletion allele in a postmyocardial infarction cohort from New Zealand. Circ Res. 2004. 94:e86.15. Takahashi Y, Nakayama T, Soma M, Izumi Y, Kanmatsuse K. Organization of the human natriuretic peptide receptor A gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998. 246:736–739.16. Nakayama T, Soma M, Takahashi Y, Rehemudula D, Sato M, Uwabo J, et al. Nucleotide sequence of the 5'-flanking region of the type A human natriuretic peptide receptor gene and association analysis using a novel microsatellite in essential hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 1999. 12:1144–1148.17. Rubattu S, Bigatti G, Evangelista A, Lanzani C, Stanzione R, Zagato L, et al. Association of atrial natriuretic peptide and type a natriuretic peptide receptor gene polymorphisms with left ventricular mass in human essential hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006. 48:499–505.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Role of C-type Natriuretic Peptide in Linear Growth
- Fok I and Bsm I gene polymorphism of vitamin D receptor and essential hypertension: a mechanistic link
- Biomarkers in Heart Failure: Focus on B-type Natriuretic Peptide
- Investigation of the Association between Normal-tension Glaucoma and Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Natriuretic Peptide Gene
- Bio-Molecular Markers for Cardiovascular Disease: Significance of Natriuretic Peptides and Adrenomedullin