Diabetes Metab J.
2011 Apr;35(2):159-165. 10.4093/dmj.2011.35.2.159.
Predictive Clinical Parameters for the Therapeutic Efficacy of Sitagliptin in Korean Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. acw@yuhs.ac
- 2Severance Institute for Vascular and Metabolic Research, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2281714
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.2.159
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Sitagliptin is a highly selective dipeptidyl peptide-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor that increases blood levels of active glucagon-like peptide (GLP)-1 and glucose-dependent insulinotrophic polypeptide (GIP), resulting in increased insulin secretion. While studies conducted in other countries have indicated the efficacy and safety of using sitagliptin to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), its predictors of effects to sitagliptin are not well understood. Therefore, we evaluated the predictive clinical parameters for the therapeutic benefits of sitagliptin when added to an ongoing metformin or sulfonylurea therapy in Korean T2DM subjects.
METHODS
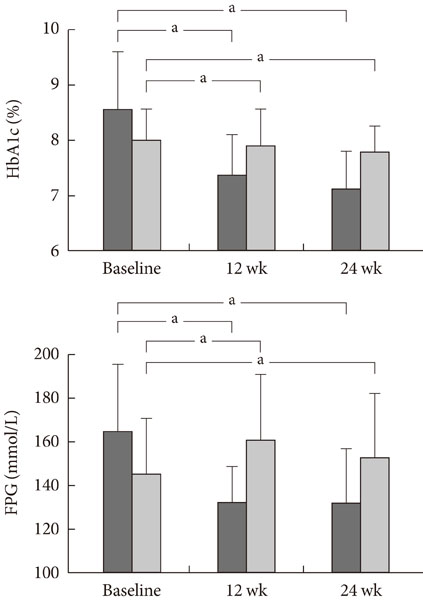
We obtained data from 251 Korean T2DM subjects who had recently started taking sitagliptin as add-on therapy. Exclusion criteria included any insulin use. Changes in HbA1c (DeltaHbA1c) and fasting plasma glucose (DeltaFPG) were assessed by comparing baseline levels prior to sitagliptin administration to levels 12 and 24 weeks after treatment. Responders were defined as subjects who experienced decrease from baseline of >10% in DeltaHbA1c or >20% in DeltaFPG levels at 24 weeks.
RESULTS
We classified 81% of the subjects (204 out of 251) as responders. The responder group had a lower mean body mass index (23.70+/-2.40 vs. 26.00+/-2.26, P< or =0.01) and were younger (58.83+/-11.57 years vs. 62.87+/-12.09 years, P=0.03) than the non-responder group.
CONCLUSION
In Korean T2DM subjects, sitagliptin responders had lower body mass index and were younger compared to non-responders.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Factors Influencing Glycemic Control Response of Sitagliptin
Gun Woo Kim, Jae Hyun Kim, Mi Young Lee, Jang Yel Shin, Young Goo Shin, Eun Ho Ha, Choon Hee Chung
J Korean Diabetes. 2013;14(4):206-211. doi: 10.4093/jkd.2013.14.4.206.Predictive Factors for the Therapeutic Response to Concomitant Treatment with DPP-4 Inhibitors in Type 2 Diabetes with Short-Term Follow-Up
Jong-Ha Baek, Bo Ra Kim, Jeong Woo Hong, Soo Kyoung Kim, Jung Hwa Jung, Jaehoon Jung, Jong Ryeal Hahm
Kosin Med J. 2016;31(2):146-156. doi: 10.7180/kmj.2016.31.2.146.
Reference
-
1. Lee CH, Chang WJ, Chung HH, Kim HJ, Park SH, Moon JS, Lee JE, Yoon JS, Chun KA, Won KC, Cho IH, Lee HW. The combination of fasting plasma glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin as a predictor for type 2 diabetes in Korean adults. Korean Diabetes J. 2009. 33:306–314.2. The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT) Research Group. Effect of intensive diabetes management on macrovascular events and risk factors in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. Am J Cardiol. 1995. 75:894–903.3. The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993. 329:977–986.4. Stratton IM, Adler AI, Neil HA, Matthews DR, Manley SE, Cull CA, Hadden D, Turner RC, Holman RR. Association of glycaemia with macrovascular and microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 35): prospective observational study. BMJ. 2000. 321:405–412.5. Bonora E, Muggeo M. Postprandial blood glucose as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease in type II diabetes: the epidemiological evidence. Diabetologia. 2001. 44:2107–2114.6. UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet. 1998. 352:837–853.7. Yoon KH, Ko SH, Lee JM, Kim SR, Seo SH, Kang MI, Cha BY, Lee KW, Son HY, Kang SK, Kim YG, Moon IS, Lee MD, Kim DK, Lee KY, Kang CS, Kim BK. Quantification of the pancreatic beta-cell mass in normal and type 2 diabetic subjects in Korea. J Korean Diabetes Assoc. 2000. 24:524–532.8. Choi SH, Hur KY, Kim DJ, Ahn CW, Kang ES, Cha BS, Lim SK, Huh KB, Lee HC. Staged diabetes management according to individual patient insulin resistance and beta-cell function ameliorates glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2008. 69:549–555.9. Nauck MA, Meininger G, Sheng D, Terranella L, Stein PP. Sitagliptin Study 024 Group. Efficacy and safety of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, sitagliptin, compared with the sulfonylurea, glipizide, in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin alone: a randomized, double-blind, non-inferiority trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2007. 9:194–205.10. Aschner P, Kipnes MS, Lunceford JK, Sanchez M, Mickel C, Williams-Herman DE. Sitagliptin Study 021 Group. Effect of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor sitagliptin as monotherapy on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2006. 29:2632–2637.11. Kim JH, Lee MS. Incretin-based combination therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Korean Med Assoc. 2009. 52:1030–1036.12. Lim S, Kim DJ, Jeong IK, Son HS, Chung CH, Koh G, Lee DH, Won KC, Park JH, Park TS, Ahn J, Kim J, Park KG, Ko SH, Ahn YB, Lee I. A nationwide survey about the current status of glycemic control and complications in diabetic patients in 2006: The Committee of the Korean Diabetes Association on the Epidemiology of Diabetes Mellitus. Korean Diabetes J. 2009. 33:48–57.13. Hemkens LG, Grouven U, Bender R, Gunster C, Gutschmidt S, Selke GW, Sawicki PT. Risk of malignancies in patients with diabetes treated with human insulin or insulin analogues: a cohort study. Diabetologia. 2009. 52:1732–1744.14. Dejgaard A, Lynggaard H, Rastam J, Krogsgaard Thomsen M. No evidence of increased risk of malignancies in patients with diabetes treated with insulin detemir: a meta-analysis. Diabetologia. 2009. 52:2507–2512.15. Ehninger G, Schmidt AH. Putting insulin glargine and malignancies into perspective. Oncologist. 2009. 14:1169–1174.16. Raz I, Hanefeld M, Xu L, Caria C, Williams-Herman D, Khatami H. Sitagliptin Study 023 Group. Efficacy and safety of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor sitagliptin as monotherapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 2006. 49:2564–2571.17. Charbonnel B, Karasik A, Liu J, Wu M, Meininger G. Sitagliptin Study 020 Group. Efficacy and safety of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor sitagliptin added to ongoing metformin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin alone. Diabetes Care. 2006. 29:2638–2643.18. Rosenstock J, Brazg R, Andryuk PJ, Lu K, Stein P. Sitagliptin Study 019 Group. Efficacy and safety of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor sitagliptin added to ongoing pioglitazone therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes: a 24-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study. Clin Ther. 2006. 28:1556–1568.19. Riche DM, East HE, Riche KD. Impact of sitagliptin on markers of beta-cell function: a meta-analysis. Am J Med Sci. 2009. 337:321–328.20. Mu J, Woods J, Zhou YP, Roy RS, Li Z, Zycband E, Feng Y, Zhu L, Li C, Howard AD, Moller DE, Thornberry NA, Zhang BB. Chronic inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 with a sitagliptin analog preserves pancreatic beta-cell mass and function in a rodent model of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2006. 55:1695–1704.21. Ristic S, Byiers S, Foley J, Holmes D. Improved glycaemic control with dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibition in patients with type 2 diabetes: vildagliptin (LAF237) dose response. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2005. 7:692–698.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Letter: Predictive Clinical Parameters for the Therapeutic Efficacy of Sitagliptin in Korean Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J 2011;35:159-65)
- Response: Predictive Clinical Parameters for the Therapeutic Efficacy of Sitagliptin in Korean Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J 2011;35:159-65)
- Effects of Sitagliptin on Insulin and Glucagon Levels in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Efficacy of Sitagliptin When Added to Ongoing Therapy in Korean Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Two-Year Therapeutic Efficacy and Safety of Initial Triple Combination of Metformin, Sitagliptin, and Empagliflozin in Drug-Naïve Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients (Diabetes Metab J 2024;48:253-64)