Diabetes Metab J.
2011 Dec;35(6):580-586. 10.4093/dmj.2011.35.6.580.
Effect on Glycemic, Blood Pressure, and Lipid Control according to Education Types
- Affiliations
-
- 1Diabetes Center, Department of Internal Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. cydoctor@chol.com
- KMID: 2280725
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.6.580
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Diabetes self-management education and reinforcement are important for effective management of the disease. We investigated the effectiveness of interactive small-group education on glycemic, blood pressure, and lipid levels.
METHODS
For this study, 207 type 2 diabetes patients with suboptimal glycemic control (HbA1c levels >6.5%) were enrolled. The conventional education group received an existing education program from April to November in 2006, and the interactive education group received a new small-group education program from December 2006 to July 2007. The two groups were comparatively analyzed for changes in blood sugar, glycated hemoglobin, lipid, and blood pressure at baseline, 3, 6, and 12 months and the proportion of patients achieving target goals at 12 months.
RESULTS
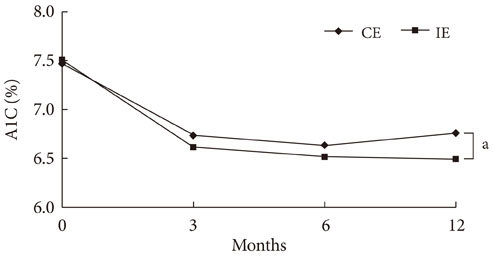
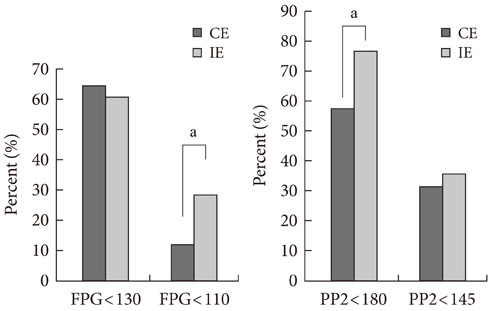
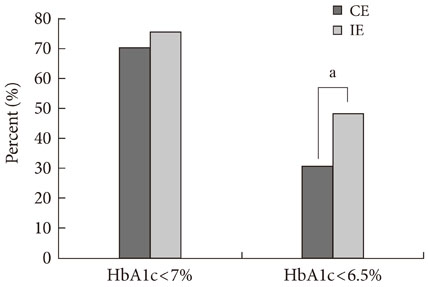
After 12 months of follow-up, HbA1c levels in the interactive education group were significantly lower than in the conventional education group (6.7% vs. 6.4%, P<0.001). Fasting and 2 hour postprandial glucose concentrations, total cholesterol, and low density lipoprotein cholesterol were significantly lower in the interactive education group than in the conventional education group. The proportion of patients that achieved target goals was significantly higher in the interactive education group.
CONCLUSION
The small-group educational method improved and re-established the existing group educational method. This finding suggests that the importance of education appears to be related to the method by which it is received rather than the education itself. Thus, the use of small-group educational methods to supplement existing educational methods established for diverse age levels should be considered in the future.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
The Effectiveness of Multidisciplinary Team-Based Education in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes
Jong Ho Kim, Yun Jeong Nam, Won Jin Kim, Kyung Ah Lee, A Ran Baek, Jung Nam Park, Jin Mi Kim, Seo Young Oh, Eun Heui Kim, Min Jin Lee, Yun Kyung Jeon, Bo Hyun Kim, In Joo Kim, Yong Ki Kim, Sang Soo Kim
J Korean Diabetes. 2018;19(2):119-133. doi: 10.4093/jkd.2018.19.2.119.Diabetes Camp as Continuing Education for Diabetes Self-Management in Middle-Aged and Elderly People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
So Young Park, Sun Young Kim, Hye Mi Lee, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hyeon Kim, Moon-Kyu Lee, Kang-Hee Sim, Sang-Man Jin
Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(2):99-112. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2017.41.2.99.
Reference
-
1. International Diabetes Federation. Diabetes atlas. 2003. 2nd ed. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation;17–71.2. WHO Study Group on Prevention of Diabetes Mellitus. Prevention of diabetes mellitus: report of a WHO Study Group. 1994. Geneva: World Health Organization.3. The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulindependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993. 329:977–986.4. UK Prospective Diabetes Study Group. Tight blood pressure control and risk of macrovascular and microvascular complications in type 2 diabetes: UKPDS 38. BMJ. 1998. 317:703–713.5. Cho NH. Diabetes epidemiology in Korean. J Korean Diabetes Assoc. 2001. 25:1–10.6. Sarkadi A, Rosenqvist U. Study circles at the pharmacy: a new model for diabetes education in groups. Patient Educ Couns. 1999. 37:89–96.7. Orchard TJ, Temprosa M, Goldberg R, Haffner S, Ratner R, Marcovina S, Fowler S. Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. The effect of metformin and intensive lifestyle intervention on the metabolic syndrome: the Diabetes Prevention Program randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2005. 142:611–619.8. Norris SL. Health-related quality of life among adults with diabetes. Curr Diab Rep. 2005. 5:124–130.9. Keers JC, Groen H, Sluiter WJ, Bouma J, Links TP. Cost and benefits of a multidisciplinary intensive diabetes education programme. J Eval Clin Pract. 2005. 11:293–303.10. Tang TS, Gillard ML, Funnell MM, Nwankwo R, Parker E, Spurlock D, Anderson RM. Developing a new generation of ongoing: diabetes self-management support interventions--a preliminary report. Diabetes Educ. 2005. 31:91–97.11. Funnell MM, Nwankwo R, Gillard ML, Anderson RM, Tang TS. Implementing an empowerment-based diabetes self-management education program. Diabetes Educ. 2005. 31:5355–56. 6112. Hong MH, Gu MJ, Lee JR, Kim SA, Sim KH, Jang SH, Yoo JW, Gu MO, Kang YG, Park BS, Ro SS, Song BR, Eum JH. A study on effects and their continuity of the self regulation education program in patients with type 2 diabetes. Korean Clin Diabetes. 2009. 10:187–195.13. Chang KS, Lee K, Lim HS. Glycemic control and health behaviors through diabetes mellitus education in a clinic. J Korean Diabetes Assoc. 2006. 30:73–81.14. Song MS, Song KH, Ko SH, Ahn YB, Kim JS, Shin JH, Cho YK, Yoon KH, Cha BY, Son HY, Lee DH. The long-term effect of a structured diabetes education program for uncontrolled type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: a 4-year follow-up. J Korean Diabetes Assoc. 2005. 29:140–150.15. Task Force Team of Korean Diabetes Association. Treatment guideline for diabetes. 2007. 1st ed. Seoul: Korean Diabetes Association.16. Nathan DM, Buse JB, Davidson MB, Heine RJ, Holman RR, Sherwin R, Zinman B. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: a consensus algorithm for the initiation and adjustment of therapy: a consensus statement from the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2006. 29:1963–1972.17. International Diabetes Federation. Global guideline for type 2 diabetes. 2005. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation.18. Kim JH, Chang SA. Effect of diabetes education program on glycemic control and self management for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Korean Diabetes J. 2009. 33:518–525.19. Davidson MB. How our current medical care system fails people with diabetes: lack of timely, appropriate clinical decisions. Diabetes Care. 2009. 32:370–372.20. Lee YS. The current status of type 2 diabetes management at a university hospital. Korean Diabetes J. 2009. 33:241–250.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Chronic Disease Management Based on Clinics for Blood Pressure or Glycemic Control in Patients with Hypertension or Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- The Non-glycemic Effects of SGLT2 Inhibitor
- Effects of Low Glycemic Index Nutrition Education on the Blood Glucose Control in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Knowledge and Learning Needs Related to Coronary Artery Disease in Diabetic Patient by Glycemic Control
- Factors Influencing Glycemic Control by gender in Workers with Diabetes Mellitus