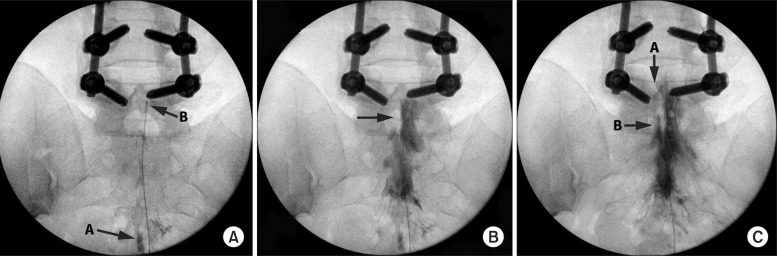
Epidural Lysis of Adhesions
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Critical Care Medicine, Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, USA.
- 2Department of Anesthesiology, Walter Reed National Military Medical Center, Bethesda, USA.
- 3Department of Anesthesiology, Neurology, Psychiatry & Orthopaedics and Rehabilitation, University of Florida, Gainesville, USA.
- 4Department of Anesthesiology and Critical Care Medicine and Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation, Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, and Walter Reed National Military Medical Center, Baltimore, USA. scohen40@jhmi.edu
- KMID: 2278196
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2014.27.1.3
Abstract
- As our population ages and the rate of spine surgery continues to rise, the use epidural lysis of adhesions (LOA) has emerged as a popular treatment to treat spinal stenosis and failed back surgery syndrome. There is moderate evidence that percutaneous LOA is more effective than conventional ESI for both failed back surgery syndrome, spinal stenosis, and lumbar radiculopathy. For cervical HNP, cervical stenosis and mechanical pain not associated with nerve root involvement, the evidence is anecdotal. The benefits of LOA stem from a combination of factors to include the high volumes administered and the use of hypertonic saline. Hyaluronidase has been shown in most, but not all studies to improve treatment outcomes. Although infrequent, complications are more likely to occur after epidural LOA than after conventional epidural steroid injections.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 7 articles
-
Percutaneous Adhesiolysis Versus Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injection for the Treatment of Chronic Radicular Pain Caused by Lumbar Foraminal Spinal Stenosis: A Retrospective Comparative Study
Yongbum Park, Woo Yong Lee, Jae Ki Ahn, Hee-Seung Nam, Ki Hoon Lee
Ann Rehabil Med. 2015;39(6):941-949. doi: 10.5535/arm.2015.39.6.941.Effectiveness of continuous hypertonic saline infusion with an automated infusion pump for decompressive neuroplasty: a randomized clinical trial
Ho-Jin Lee, Jaewoo Lee, Yeon wook Park, Ho Young Gil, Eunjoo Choi, Francis Sahngun Nahm, Pyung Bok Lee
Korean J Pain. 2019;32(3):196-205. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2019.32.3.196.Epidural Steroid Injection: A Need for a New Clinical Practice Guideline
Jeong Gill Leem
Korean J Pain. 2014;27(3):197-199. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2014.27.3.197.Acute Motor Weakness of Opposite Lower Extremity after Percutaneous Epidural Neuroplasty
Yong Seok Lim, Ki Tea Jung, Cheon Hee Park, Sang Woo Wee, Sung Sik Sin, Joon Kim
Korean J Pain. 2015;28(2):144-147. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2015.28.2.144.The outcome of epiduroscopy treatment in patients with chronic low back pain and radicular pain, operated or non-operated for lumbar disc herniation: a retrospective study in 88 patients
Derya Burcu Hazer, Arsal Acarbaş, Hans Eric Rosberg
Korean J Pain. 2018;31(2):109-115. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2018.31.2.109.Percutaneous epidural balloon neuroplasty: a narrative review of current evidence
Doo-Hwan Kim, Jin-Woo Shin, Seong-Soo Choi
Anesth Pain Med. 2022;17(4):361-370. doi: 10.17085/apm.22237.Involvement of the spinal γ-aminobutyric acid receptor in the analgesic effects of intrathecally injected hypertonic saline in spinal nerve-ligated rats
Myong-Hwan Karm, Hyun-Jung Kwon, Euiyong Shin, Honggyoon Bae, Young Ki Kim, Seong-Soo Choi
Korean J Pain. 2023;36(4):441-449. doi: 10.3344/kjp.23162.
Reference
-
1. Nallegowda M, Chiravuri S. Re: Radcliff K, Kepler C, Hilibrand A, et al. Epidural steroid injections are associated with less improvement in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis: a subgroup analysis of the spine patient outcomes research trial. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38:279-91. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013; 38:1521. PMID: 23900112.2. Cohen SP, Bicket MC, Jamison D, Wilkinson I, Rathmell JP. Epidural steroids: a comprehensive, evidence-based review. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2013; 38:175–200. PMID: 23598728.3. Pinto RZ, Maher CG, Ferreira ML, Hancock M, Oliveira VC, McLachlan AJ, et al. Epidural corticosteroid injections in the management of sciatica: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2012; 157:865–877. PMID: 23362516.
Article4. Manchikanti L, Pampati V, Falco FJ, Hirsch JA. Growth of spinal interventional pain management techniques: analysis of utilization trends and Medicare expenditures 2000 to 2008. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013; 38:157–168. PMID: 22781007.5. Chan CW, Peng P. Failed back surgery syndrome. Pain Med. 2011; 12:577–606. PMID: 21463472.
Article6. Lieberman IH. Disc bulge bubble: spine economics 101. Spine J. 2004; 4:609–613. PMID: 15541690.
Article7. Wang MC, Kreuter W, Wolfla CE, Maiman DJ, Deyo RA. Trends and variations in cervical spine surgery in the United States: Medicare beneficiaries, 1992 to 2005. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009; 34:955–961. PMID: 19352223.8. Verbiest H. Pathomorphologic aspects of developmental lumbar stenosis. Orthop Clin North Am. 1975; 6:177–196. PMID: 1113966.
Article9. Bolender NF, Schönström NS, Spengler DM. Role of computed tomography and myelography in the diagnosis of central spinal stenosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1985; 67:240–246. PMID: 3968115.
Article10. Verbiest H. The significance and principles of computerized axial tomography in idiopathic developmental stenosis of the bony lumbar vertebral canal. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1979; 4:369–378. PMID: 483044.
Article11. De Villiers PD, Booysen EL. Fibrous spinal stenosis. A report on 850 myelograms with a water-soluble contrast medium. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976; (115):140–144. PMID: 1253477.12. Roberson GH, Llewellyn HJ, Taveras JM. The narrow lumbar spinal canal syndrome. Radiology. 1973; 107:89–97. PMID: 4689450.
Article13. Fanuele JC, Birkmeyer NJ, Abdu WA, Tosteson TD, Weinstein JN. The impact of spinal problems on the health status of patients: have we underestimated the effect? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000; 25:1509–1514. PMID: 10851099.14. Kalichman L, Cole R, Kim DH, Li L, Suri P, Guermazi A, et al. Spinal stenosis prevalence and association with symptoms: the Framingham Study. Spine J. 2009; 9:545–550. PMID: 19398386.
Article15. Racz GB, Holubec JT. Lysis of adhesions in the epidural space. In : Racz GB, editor. Techniques of neurolysis. Boston (MA): Kluwer Academic;1989. p. 57–72.16. Racz GB, Heavner JE, Diede JH. Lysis of epidural adhesions utilizing the epidural approach. In : Waldman SD, Winnie AP, editors. Interventional pain management. Philadelphia (PA): WB Saunders;1996. p. 339–351.17. Manchikanti L, Pakanati RR, Bakhit CE, Pampati V. Role of adhesiolysis and hypertonic saline neurolysis in management of low back pain: evaluation of modification of the Racz protocol. Pain Dig. 1999; 9:91–96.18. Kuslich SD, Ulstrom CL, Michael CJ. The tissue origin of low back pain and sciatica: a report of pain response to tissue stimulation during operations on the lumbar spine using local anesthesia. Orthop Clin North Am. 1991; 22:181–187. PMID: 1826546.19. Ross JS, Robertson JT, Frederickson RC, Petrie JL, Obuchowski N, Modic MT, et al. ADCON-L European Study Group. Association between peridural scar and recurrent radicular pain after lumbar discectomy: magnetic resonance evaluation. Neurosurgery. 1996; 38:855–861. PMID: 8692415.
Article20. Maroon JC, Abla A, Bost J. Association between peridural scar and persistent low back pain after lumbar discectomy. Neurol Res. 1999; 21(Suppl 1):S43–S46. PMID: 10214571.
Article21. Almeida DB, Prandini MN, Awamura Y, Vitola ML, Simião MP, Milano JB, et al. Outcome following lumbar disc surgery: the role of fibrosis. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2008; 150:1167–1176. PMID: 18936878.
Article22. Rönnberg K, Lind B, Zoega B, Gadeholt-Göthlin G, Halldin K, Gellerstedt M, et al. Peridural scar and its relation to clinical outcome: a randomised study on surgically treated lumbar disc herniation patients. Eur Spine J. 2008; 17:1714–1720. PMID: 18946688.
Article23. Jarvik JG, Deyo RA. Diagnostic evaluation of low back pain with emphasis on imaging. Ann Intern Med. 2002; 137:586–597. PMID: 12353946.
Article24. Rabinovitch DL, Peliowski A, Furlan AD. Influence of lumbar epidural injection volume on pain relief for radicular leg pain and/or low back pain. Spine J. 2009; 9:509–517. PMID: 19398387.
Article25. Trescot AM, Chopra P, Abdi S, Datta S, Schultz DM. Systematic review of effectiveness and complications of adhesiolysis in the management of chronic spinal pain: an update. Pain Physician. 2007; 10:129–146. PMID: 17256027.26. Chopra P, Smith HS, Deer TR, Bowman RC. Role of adhesiolysis in the management of chronic spinal pain: a systematic review of effectiveness and complications. Pain Physician. 2005; 8:87–100. PMID: 16850047.27. Racz GB, Heavner JE, Trescot A. Percutaneous lysis of epidural adhesions--evidence for safety and efficacy. Pain Pract. 2008; 8:277–286. PMID: 18503627.
Article28. Epter RS, Helm S 2nd, Hayek SM, Benyamin RM, Smith HS, Abdi S. Systematic review of percutaneous adhesiolysis and management of chronic low back pain in post lumbar surgery syndrome. Pain Physician. 2009; 12:361–378. PMID: 19305485.29. Belozer M, Wang G. Epidural adhesiolysis for the treatment of back pain: health technology assessment. Olympia (WA): Washington State Department of Labor & Industries;2004.30. Helm Ii S, Benyamin RM, Chopra P, Deer TR, Justiz R. Percutaneous adhesiolysis in the management of chronic low back pain in post lumbar surgery syndrome and spinal stenosis: a systematic review. Pain Physician. 2012; 15:E435–E462. PMID: 22828693.31. Hegmann KT. American College of Occupational and Environmental Medicine. Occupational medicine practice guidelines: evaluation and management of common health problems and functional recovery in workers. 3rd ed. Elk Grove Village (IL): American College of Occupational and Environmental Medicine;2011.32. Tran de QH, Duong S, Finlayson RJ. Lumbar spinal stenosis: a brief review of the nonsurgical management. Can J Anaesth. 2010; 57:694–703. PMID: 20428988.
Article33. Chou R, Huffman LH. Guideline for the evaluation and management of low back pain: evidence review. Glenview (IL): American Pain Society;2009.34. Manchikanti L, Datta S, Gupta S, Munglani R, Bryce DA, Ward SP, et al. A critical review of the American Pain Society clinical practice guidelines for interventional techniques: part 2. Therapeutic interventions. Pain Physician. 2010; 13:E215–E264. PMID: 20648212.35. Manchikanti L, Singh V, Derby R, Helm S 2nd, Trescot AM, Staats PS, et al. Review of occupational medicine practice guidelines for interventional pain management and potential implications. Pain Physician. 2008; 11:271–289. PMID: 18523500.36. Chou R, Manchikanti L. American Pain Society (APS) low back pain guidelines: A pro/con debate. In : Presented at the American Academy of Pain Medicine's 27th Annual Meeting; 2011 Mar 24-7; National Harbor (MD). Chicago (IL): American Pain Society;2011.37. American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Chronic Pain Management. American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine. Practice guidelines for chronic pain management: an updated report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Chronic Pain Management and the American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine. Anesthesiology. 2010; 112:810–833. PMID: 20124882.38. Heavner JE, Racz GB, Raj P. Percutaneous epidural neuroplasty: prospective evaluation of 0.9% NaCl versus 10% NaCl with or without hyaluronidase. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 1999; 24:202–207. PMID: 10338168.
Article39. Manchikanti L, Rivera JJ, Pampati V, Damron KS, McManus CD, Brandon DE, et al. One day lumbar epidural adhesiolysis and hypertonic saline neurolysis in treatment of chronic low back pain: a randomized, double-blind trial. Pain Physician. 2004; 7:177–186. PMID: 16868590.40. Veihelmann A, Devens C, Trouillier H, Birkenmaier C, Gerdesmeyer L, Refior HJ. Epidural neuroplasty versus physiotherapy to relieve pain in patients with sciatica: a prospective randomized blinded clinical trial. J Orthop Sci. 2006; 11:365–369. PMID: 16897200.
Article41. Gerdesmeyer L, Wagenpfeil S, Birkenmaier C, Veihelmann A, Hauschild M, Wagner K, et al. Percutaneous epidural lysis of adhesions in chronic lumbar radicular pain: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Pain Physician. 2013; 16:185–196. PMID: 23703406.42. Manchikanti L, Singh V, Cash KA, Pampati V, Datta S. A comparative effectiveness evaluation of percutaneous adhesiolysis and epidural steroid injections in managing lumbar post surgery syndrome: a randomized, equivalence controlled trial. Pain Physician. 2009; 12:E355–E368. PMID: 19935992.43. Manchikanti L, Cash KA, McManus CD, Pampati V, Singh V, Benyamin R. The preliminary results of a comparative effectiveness evaluation of adhesiolysis and caudal epidural injections in managing chronic low back pain secondary to spinal stenosis: a randomized, equivalence controlled trial. Pain Physician. 2009; 12:E341–E354. PMID: 19935991.44. Manchikanti L, Cash KA, McManus CD, Pampati V, Fellows B. Results of 2-year follow-up of a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial of fluoroscopic caudal epidural injections in central spinal stenosis. Pain Physician. 2012; 15:371–384. PMID: 22996849.45. Park CH, Lee SH, Jung JY. Dural sac cross-sectional area does not correlate with efficacy of percutaneous adhesiolysis in single level lumbar spinal stenosis. Pain Physician. 2011; 14:377–382. PMID: 21785481.46. Manchikanti L, Pampati V, Bakhit CE, Pakanati RR. Non-endoscopic and endoscopic adhesiolysis in post-lumbar laminectomy syndrome: a one-year outcome study and cost effectiveness analysis. Pain Physician. 1999; 2:52–58. PMID: 16906216.47. Gerdesmeyer L, Lampe R, Veihelmann A, Burgkart R, Göbel M, Gollwitzer H, et al. Chronic radiculopathy. Use of minimally invasive percutaneous epidural neurolysis according to Racz. Schmerz. 2005; 19:285–295. PMID: 15549419.48. Brouwers PJ, Kottink EJ, Simon MA, Prevo RL. A cervical anterior spinal artery syndrome after diagnostic blockade of the right C6-nerve root. Pain. 2001; 91:397–399. PMID: 11275398.
Article49. Rozin L, Rozin R, Koehler SA, Shakir A, Ladham S, Barmada M, et al. Death during transforaminal epidural steroid nerve root block (C7) due to perforation of the left vertebral artery. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 2003; 24:351–355. PMID: 14634474.
Article50. Asano M, Akatsuka M, Uda R, Son H, Nagano Y, Tatsumi T. Suspected migration of cervical epidural catheter into the brainstem after a difficult catheter insertion. J Anesth. 2013; [in press].
Article51. Park CH, Lee SH, Lee SC. Preliminary results of the clinical effectiveness of percutaneous adhesiolysis using a Racz catheter in the management of chronic pain due to cervical central stenosis. Pain Physician. 2013; 16:353–358. PMID: 23877451.52. Park EJ, Park SY, Lee SJ, Kim NS, Koh do Y. Clinical outcomes of epidural neuroplasty for cervical disc herniation. J Korean Med Sci. 2013; 28:461–465. PMID: 23487574.
Article53. Bosscher HA, Heavner JE. Incidence and severity of epidural fibrosis after back surgery: an endoscopic study. Pain Pract. 2010; 10:18–24. PMID: 19735365.
Article54. Bosscher HA, Heavner JE. Diagnosis of the vertebral level from which low back or leg pain originates. A comparison of clinical evaluation, MRI and epiduroscopy. Pain Pract. 2012; 12:506–512. PMID: 22429715.
Article55. Manchikanti L, Boswell MV, Rivera JJ, Pampati VS, Damron KS, McManus CD, et al. [ISRCTN 16558617] A randomized, controlled trial of spinal endoscopic adhesiolysis in chronic refractory low back and lower extremity pain. BMC Anesthesiol. 2005; 5:10. PMID: 16000173.56. Dashfield AK, Taylor MB, Cleaver JS, Farrow D. Comparison of caudal steroid epidural with targeted steroid placement during spinal endoscopy for chronic sciatica: a prospective, randomized, double-blind trial. Br J Anaesth. 2005; 94:514–519. PMID: 15695544.
Article57. Richardson J, McGurgan P, Cheema S, Prasad R, Gupta S. Spinal endoscopy in chronic low back pain with radiculopathy. A prospective case series. Anaesthesia. 2001; 56:454–460. PMID: 11350333.
Article58. Geurts JW, Kallewaard JW, Richardson J, Groen GJ. Targeted methylprednisolone acetate/hyaluronidase/clonidine injection after diagnostic epiduroscopy for chronic sciatica: a prospective, 1-year follow-up study. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2002; 27:343–352. PMID: 12132057.
Article59. Igarashi T, Hirabayashi Y, Seo N, Saitoh K, Fukuda H, Suzuki H. Lysis of adhesions and epidural injection of steroid/local anaesthetic during epiduroscopy potentially alleviate low back and leg pain in elderly patients with lumbar spinal stenosis. Br J Anaesth. 2004; 93:181–187. PMID: 15194631.
Article60. Sakai T, Aoki H, Hojo M, Takada M, Murata H, Sumikawa K. Adhesiolysis and targeted steroid/local anesthetic injection during epiduroscopy alleviates pain and reduces sensory nerve dysfunction in patients with chronic sciatica. J Anesth. 2008; 22:242–247. PMID: 18685930.
Article61. Avellanal M, Diaz-Reganon G. Interlaminar approach for epiduroscopy in patients with failed back surgery syndrome. Br J Anaesth. 2008; 101:244–249. PMID: 18552347.
Article62. Hsu E, Atanelov L, Plunkett AR, Chai N, Chen Y, Cohen SP. Epidural lysis of adhesions for failed back surgery syndrome and spinal stenosis: factors associated with treatment outcome. Anesth Analg. 2014; 118:215–224. PMID: 24356168.
Article63. Harris I, Mulford J, Solomon M, van Gelder JM, Young J. Association between compensation status and outcome after surgery: a meta-analysis. JAMA. 2005; 293:1644–1652. PMID: 15811984.
Article64. Lee JH, Lee SH. Clinical effectiveness of percutaneous adhesiolysis and predictive factors of treatment efficacy in patients with lumbosacral spinal stenosis. Pain Med. 2013; [in press].
Article65. Lee JH, Lee SH. Clinical effectiveness of percutaneous adhesiolysis using Navicath for the management of chronic pain due to lumbosacral disc herniation. Pain Physician. 2012; 15:213–221. PMID: 22622905.66. Yousef AA, EL-Deen AS, Al-Deeb AE. The role of adding hyaluronidase to fluoroscopically guided caudal steroid and hypertonic saline injection in patients with failed back surgery syndrome: a prospective, double-blinded, randomized study. Pain Pract. 2010; 10:548–553. PMID: 20412501.
Article67. Kim SB, Lee KW, Lee JH, Kim MA, An BW. The effect of hyaluronidase in interlaminar lumbar epidural injection for failed back surgery syndrome. Ann Rehabil Med. 2012; 36:466–473. PMID: 22977771.
Article68. Kim SB, Lee KW, Lee JH, Kim MA, Kim BH. The additional effect of hyaluronidase in lumbar interlaminar epidural injection. Ann Rehabil Med. 2011; 35:405–411. PMID: 22506151.
Article69. Wong GK, Arab AA, Chew SC, Naser B, Crawford MW. Major complications related to epidural analgesia in children: a 15-year audit of 3,152 epidurals. Can J Anaesth. 2013; 60:355–363. PMID: 23296493.
Article70. Manchikanti L, Malla Y, Wargo BW, Cash KA, Pampati V, Fellows B. A prospective evaluation of complications of 10,000 fluoroscopically directed epidural injections. Pain Physician. 2012; 15:131–140. PMID: 22430650.71. Talu GK, Erdine S. Complications of epidural neuroplasty: a retrospective evaluation. Neuromodulation. 2003; 6:237–247. PMID: 22151070.
Article72. Wagner KJ, Sprenger T, Pecho C, Kochs EF, Tölle TR, Berthele A, et al. Risks and complications of epidural neurolysis -- a review with case report. Anasthesiol Intensivmed Notfallmed Schmerzther. 2006; 41:213–222. PMID: 16636945.73. Perkins WJ, Davis DH, Huntoon MA, Horlocker TT. A retained Racz catheter fragment after epidural neurolysis: implications during magnetic resonance imaging. Anesth Analg. 2003; 96:1717–1719. PMID: 12761003.
Article74. Ho KY, Manghnani P. Acute monoplegia after lysis of epidural adhesions: a case report. Pain Pract. 2008; 8:404–407. PMID: 18721177.
Article75. Justiz R, Taylor V, Day M. Neurogenic bladder: a complication after endoscopic adhesiolysis with return of bladder function while using nitrofurantoin. Anesth Analg. 2010; 110:1496–1498. PMID: 20304983.76. Birkenmaier C, Redeker J, Sievers B, Melcher C, Jansson V, Mayer-Wagner S. An evaluation of medications commonly used for epidural neurolysis procedures in a human fibroblast cell culture model. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2011; 36:140–144. PMID: 21270726.
Article