Korean J Obstet Gynecol.
2010 May;53(5):401-409. 10.5468/kjog.2010.53.5.401.
Measurement of apoptosis using M30 in culture media of cell lines treated with anti-cancer agents
- Affiliations
-
- 1Clinical Research Laboratory, St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, The Catholic University of Korea School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. nowonhkt@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2273871
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5468/kjog.2010.53.5.401
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
We investigated a possible use of the induced apoptosis as a biomarker in the cells and their media treated with commonly used anti-cancer agents in gynecologic malignancies.
METHODS
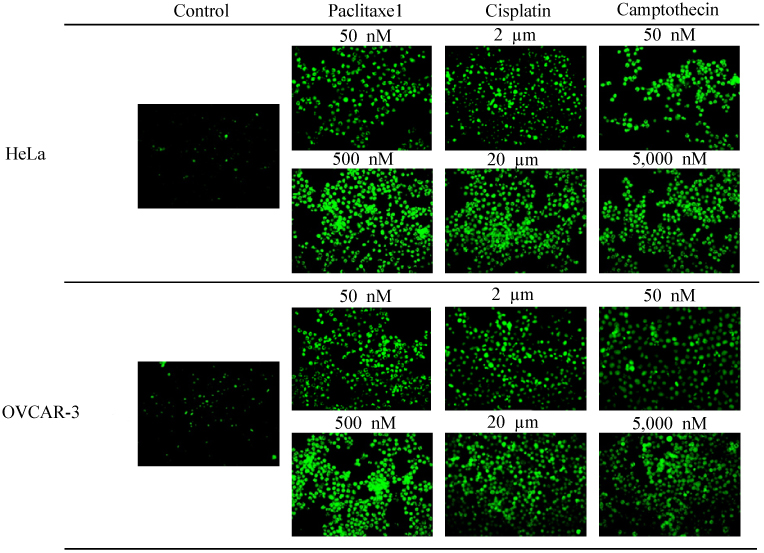
After treatments with low and high concentrations of paclitaxel, cisplatin, and camptothecin in HeLa and OVCAR-3 cells, the levels of M30 antigen were detected in the cells and their media by immunofluorescence staining and ELISA methods, respectively.
RESULTS
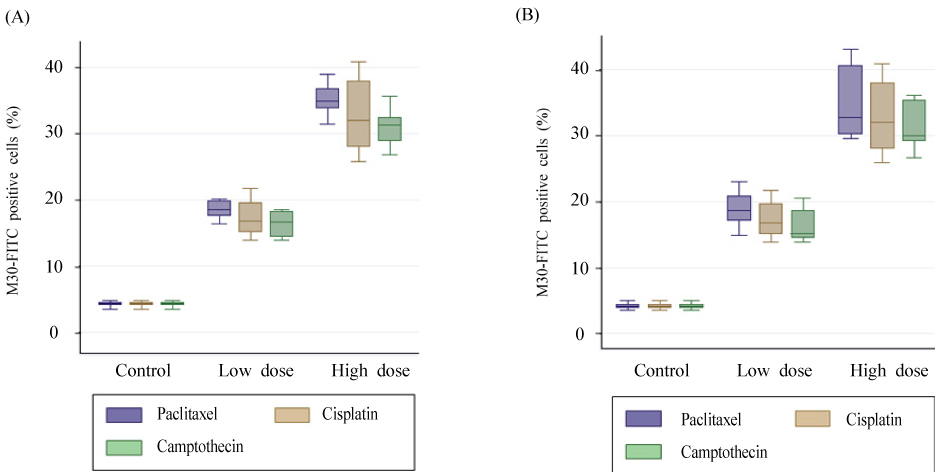
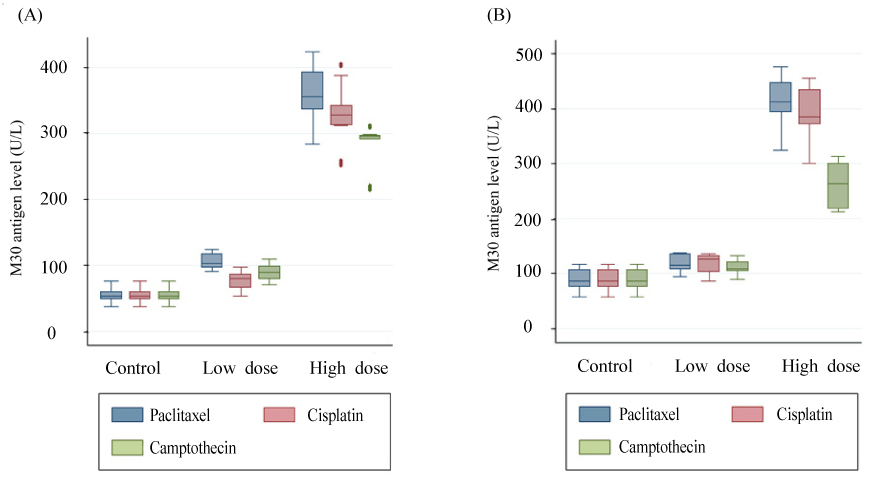
The percentages of M30-fluoresein isothiocyanate (FITC) positive cells in HeLa and OVCAR-3 cells treated with paclitaxel, cisplatin, and camptothecin were 4.3% vs 18.1% vs 34.87% and 4.07% vs 18.6% vs 32.63%, 4.3% vs 17.87% vs 32.38% and 4.07% vs 16.83% vs 32%, and 4.3% vs 16.75% vs 31.3% and 4.07% vs 15.18% vs 29.9% in control, low dose, and hight dose groups, respectively (P<0.001). M30 antigen levels (U/L) measured in culture media of HeLa and OVCAR-3 cells treated with paclitaxel, cisplatin, and camptothecin were 53.03 vs 101.53 vs 355.59 and 86 vs 114.41 vs 412.04, 53.03 vs 79.84 vs 327.64 and 86 vs 125.44 vs 385.09, and 53.03 vs 88.41 vs 295.005 and 86 vs 108.42 vs 263.1 in control, low dose, and hight dose groups, respectively (P<0.001).
CONCLUSION
Our results obtained in this preclinical study suggests that measurement of the levels of M30 antigen may help to predict the clinical responses and to select the effective anti-cancer agents in clinical settings, rapidly and quantitatively.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ricci MS, Zong WX. Chemotherapeutic approaches for targeting cell death pathways. Oncologist. 2006. 11:342–357.2. Viktorsson K, Lewensohn R, Zhivotovsky B. Apoptotic pathways and therapy resistance in human malignancies. Adv Cancer Res. 2005. 94:143–196.3. Demiray M, Ulukaya EE, Arslan M, Gokgoz S, Saraydaroglu O, Ercan I, et al. Response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer could be predictable by measuring a novel serum apoptosis product, caspase-cleaved cytokeratin 18: a prospective pilot study. Cancer Invest. 2006. 24:669–676.4. Hägg M, Bivén K, Ueno T, Rydlander L, Björklund P, Wiman KG, et al. A novel high-through-put assay for screening of pro-apoptotic drugs. Invest New Drugs. 2002. 20:253–259.5. Schutte B, Henfling M, Kölgen W, Bouman M, Meex S, Leers MP, et al. Keratin 8/18 breakdown and reorganization during apoptosis. Exp Cell Res. 2004. 297:11–26.6. Leers MP, Kölgen W, Björklund V, Bergman T, Tribbick G, Persson B, et al. Immunocytochemical detection and mapping of a cytokeratin 18 neo-epitope exposed during early apoptosis. J Pathol. 1999. 187:567–572.7. Kramer G, Erdal H, Mertens HJ, Nap M, Mauermann J, Steiner G, et al. Differentiation between cell death modes using measurements of different soluble forms of extracellular cytokeratin 18. Cancer Res. 2004. 64:1751–1756.8. Ueno T, Toi M, Bivén K, Bando H, Ogawa T, Linder S. Measurement of an apoptotic product in the sera of breast cancer patients. Eur J Cancer. 2003. 39:769–774.9. Kramer G, Schwarz S, Hagg M, Havelka AM, Linder S. Docetaxel induces apoptosis in hormone refractory prostate carcinomas during multiple treatment cycles. Br J Cancer. 2006. 94:1592–1598.10. Holubec H, Payne CM, Bernstein H, Dvorakova K, Bernstein C, Waltmire CN, et al. Assessment of apoptosis by immunohistochemical markers compared to cellular morphology in ex vivo-stressed colonic mucosa. J Histochem Cytochem. 2005. 53:229–235.11. Ulukaya E, Yilmaztepe A, Akgoz S, Linder S, Karadag M. The levels of caspase-cleaved cytokeratin 18 are elevated in serum from patients with lung cancer and helpful to predict the survival. Lung Cancer. 2007. 56:399–404.12. Wang D, Lippard SJ. Cellular processing of platinum anticancer drugs. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005. 4:307–320.13. Wang TH, Wang HS, Soong YK. Paclitaxel-induced cell death: where the cell cycle and apoptosis come together. Cancer. 2000. 88:2619–2628.14. Majno G, Joris I. Apoptosis, oncosis, and necrosis. An overview of cell death. Am J Pathol. 1995. 146:3–15.15. Untch M, Ditsch N, Hermelink K. Immunotherapy: new options in breast cancer treatment. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2003. 3:403–408.16. Ueno T, Toi M, Linder S. Detection of epithelial cell death in the body by cytokeratin 18 measurement. Biomed Pharmacother. 2005. 59:Suppl 2. S359–S362.17. Olofsson MH, Ueno T, Pan Y, Xu R, Cai F, van der Kuip H, et al. Cytokeratin-18 is a useful serum biomarker for early determination of response of breast carcinomas to chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2007. 13:3198–3206.18. Stearns V, Singh B, Tsangaris T, Crawford JG, Novielli A, Ellis MJ, et al. A prospective randomized pilot study to evaluate predictors of response in serial core biopsies to single agent neoadjuvant doxorubicin or paclitaxel for patients with locally advanced breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2003. 9:124–133.19. Morse DL, Gray H, Payne CM, Gillies RJ. Docetaxel induces cell death through mitotic catastrophe in human breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2005. 4:1495–1504.20. Woods CM, Zhu J, McQueney PA, Bollag D, Lazarides E. Taxol-induced mitotic block triggers rapid onset of a p53-independent apoptotic pathway. Mol Med. 1995. 1:506–526.21. Mosesso P, Pichierri P, Franchitto A, Palitti F. Evidence that camptothecin-induced aberrations in the G2phase of cell cycle of Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell lines is associated with transcription. Mutat Res. 2000. 452:189–195.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Detection of chemosensitivity using K18-Asp(396) (M30) antibody in HeLa and OVCAR-3 cell lines treated with anticancer agents
- Toxicity of Bile Acids on Colon Cancer Cell Lines
- The Expression of Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF), IGF- Binding Protein (IGFBP) and the Role of IGFBP-3 in the Korean Gastric Cancer Cell Lines
- Induction of Apoptosis and Inhibition of Cellular Proliferation in Aspirin-treated SNU-668 Human Gastric Adenocarcinoma Cell Lines
- The Effect of Serum Concentrations of the Culture Media on the in vitro Secretion of Free beta-subunit of Human Chorionic Gonadotropin by Ovarian Cancer Cells