Ann Rehabil Med.
2015 Apr;39(2):199-209. 10.5535/arm.2015.39.2.199.
Changes in Hyolaryngeal Movement and Swallowing Function After Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation in Patients With Dysphagia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Rehabilitation Institute of Neuromuscular Disease, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. srcho918@yuhs.ac
- 3Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- 4Department of Rehabilitation Medicine and Research Institute of Rehabilitation Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Brain Korea 21 PLUS Project for Medical Science, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Avison Biomedical Research Center, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2273041
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2015.39.2.199
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
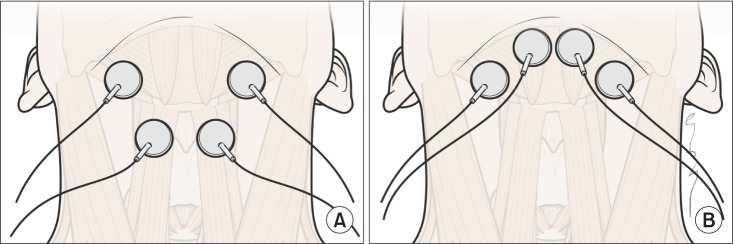
To investigate immediate changes in hyolaryngeal movement and swallowing function after a cycle of neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) on both submental and throat regions and submental placement alone in patients with dysphagia.
METHODS
Fifteen patients with dysphagia were recruited. First, videofluoroscopic swallowing study (VFSS) was performed before NMES. All patients thereafter received a cycle of NMES by 2 methods of electrode placement: 1) both submental and throat regions and 2) submental placement alone concomitant with VFSS. The Penetration-Aspiration Score (PAS) and the NIH-Swallowing Safety Scale (NIH-SSS) were measured for swallowing function.
RESULTS
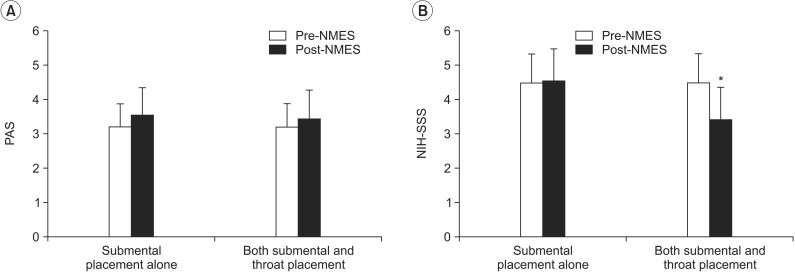
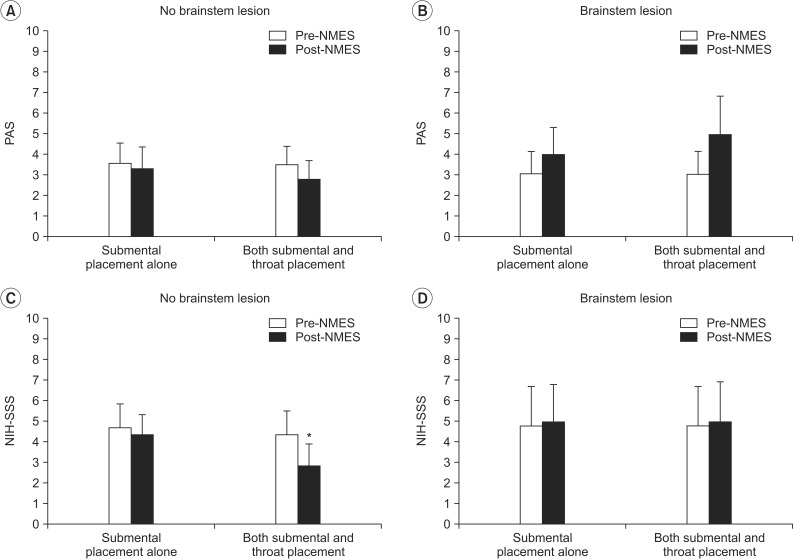
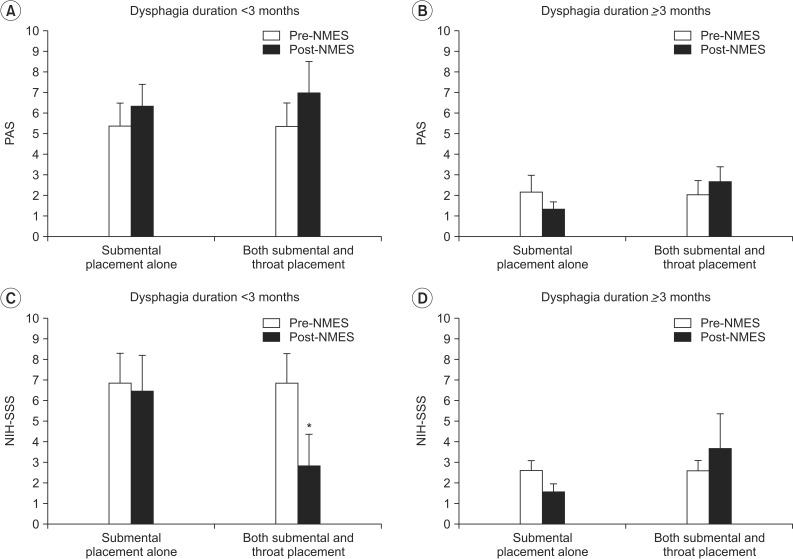
During swallowing, hyolaryngeal descent significantly occurred by NMES on both submental and throat regions, and anterior displacement of hyolaryngeal complex was significant on submental placement alone. NMES on submental placement alone did not change the PAS and NIH-SSS. However, NMES on both submental and throat regions significantly reduced the NIH-SSS, although it did not change the PAS. Patients with no brainstem lesion and with dysphagia duration of <3 months showed significantly improved the NIH-SSS.
CONCLUSION
Immediate hyolaryngeal movement was paradoxically depressed after NMES on both submental and throat regions with significant reductions in the NIH-SSS but not the PAS, suggesting improvement in pharyngeal peristalsis and cricopharyngeal functions at the esophageal entry rather than decreased aspiration and penetration. The results also suggested that patients with dysphagia should be carefully screened when determining motor-level NMES.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ertekin C, Aydogdu I. Neurophysiology of swallowing. Clin Neurophysiol. 2003; 114:2226–2244. PMID: 14652082.
Article2. Ludlow CL, Humbert I, Saxon K, Poletto C, Sonies B, Crujido L. Effects of surface electrical stimulation both at rest and during swallowing in chronic pharyngeal dysphagia. Dysphagia. 2007; 22:1–10. PMID: 16718620.
Article3. Park JW, Oh JC, Lee HJ, Park SJ, Yoon TS, Kwon BS. Effortful swallowing training coupled with electrical stimulation leads to an increase in hyoid elevation during swallowing. Dysphagia. 2009; 24:296–301. PMID: 19255707.
Article4. Shaw GY, Sechtem PR, Searl J, Keller K, Rawi TA, Dowdy E. Transcutaneous neuromuscular electrical stimulation (VitalStim) curative therapy for severe dysphagia: myth or reality? Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2007; 116:36–44. PMID: 17305276.
Article5. Blumenfeld L, Hahn Y, Lepage A, Leonard R, Belafsky PC. Transcutaneous electrical stimulation versus traditional dysphagia therapy: a nonconcurrent cohort study. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006; 135:754–757. PMID: 17071307.
Article6. Humbert IA, Poletto CJ, Saxon KG, Kearney PR, Crujido L, Wright-Harp W, et al. The effect of surface electrical stimulation on hyolaryngeal movement in normal individuals at rest and during swallowing. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2006; 101:1657–1663. PMID: 16873602.
Article7. Kiger M, Brown CS, Watkins L. Dysphagia management: an analysis of patient outcomes using VitalStim therapy compared to traditional swallow therapy. Dysphagia. 2006; 21:243–253. PMID: 17216386.
Article8. Bulow M, Speyer R, Baijens L, Woisard V, Ekberg O. Neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) in stroke patients with oral and pharyngeal dysfunction. Dysphagia. 2008; 23:302–309. PMID: 18437464.
Article9. Tan C, Liu Y, Li W, Liu J, Chen L. Transcutaneous neuromuscular electrical stimulation can improve swallowing function in patients with dysphagia caused by non-stroke diseases: a meta-analysis. J Oral Rehabil. 2013; 40:472–480. PMID: 23607530.
Article10. Carnaby-Mann GD, Crary MA. Examining the evidence on neuromuscular electrical stimulation for swallowing: a meta-analysis. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007; 133:564–571. PMID: 17576907.11. Palmer JB, Kuhlemeier KV, Tippett DC, Lynch C. A protocol for the videofluorographic swallowing study. Dysphagia. 1993; 8:209–214. PMID: 8359040.
Article12. Wijting Y, Freed ML. VitalStim therapy training manual. Hixson, TN: Chattanooga Group;2003. p. 103.13. Abramoff MD, Magalhaes PJ, Ram SJ. Image processing with ImageJ. Biophotonics Int. 2004; 11:36–43.14. Rosenbek JC, Robbins JA, Roecker EB, Coyle JL, Wood JL. A penetration-aspiration scale. Dysphagia. 1996; 11:93–98. PMID: 8721066.
Article15. Hamdy S, Rothwell JC, Aziz Q, Thompson DG. Organization and reorganization of human swallowing motor cortex: implications for recovery after stroke. Clin Sci (Lond). 2000; 99:151–157. PMID: 10918049.
Article16. Hamdy S, Rothwell JC. Gut feelings about recovery after stroke: the organization and reorganization of human swallowing motor cortex. Trends Neurosci. 1998; 21:278–282. PMID: 9683316.
Article17. Bath PM, Bath FJ, Smithard DG. Interventions for dysphagia in acute stroke. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000; (2):CD000323. PMID: 10796343.
Article18. Jacob P, Kahrilas PJ, Logemann JA, Shah V, Ha T. Upper esophageal sphincter opening and modulation during swallowing. Gastroenterology. 1989; 97:1469–1478. PMID: 2583413.
Article19. Ludlow CL. Electrical neuromuscular stimulation in dysphagia: current status. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010; 18:159–164. PMID: 20463480.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation for Dysphagia
- Effects of Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation in Combination with Saliva or Dry Swallowing in Stroke Patients with Dysphagia
- Clinical Application of FES for Swallowing: Intensity Levels and the Placement of Electrode
- Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation for Swallowing
- Effects of Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation on the Swallowing Function in a Child - A Case Report