Blood Res.
2013 Mar;48(1):40-45. 10.5045/br.2013.48.1.40.
The prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in iron-deficient and normal children under the age of 24 months
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, CHA University School of Medicine, CHA Bundang Medical Center, Seongnam, Korea. mkkim929@gmail.com
- KMID: 2270725
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/br.2013.48.1.40
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Iron and vitamin D deficiencies cause a variety of health issues in children, which might have long-lasting effects even in asymptomatic cases. The present study sought to elucidate the potential association between iron status and serum vitamin D levels in infants.
METHODS
We evaluated 102 infants aged 3-24 months who visited the CHA Bundang Medical Center from August 2010 to July 2011. Questionnaire and laboratory data were collected. The infants were classified into iron deficiency anemia (IDA), iron deficiency (ID), and normal groups according to hemoglobin (Hb) and ferritin levels. They were then classified into vitamin D deficiency (VDD), vitamin D insufficiency (VDI), and vitamin D sufficiency (VDS) groups according to 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] levels.
RESULTS
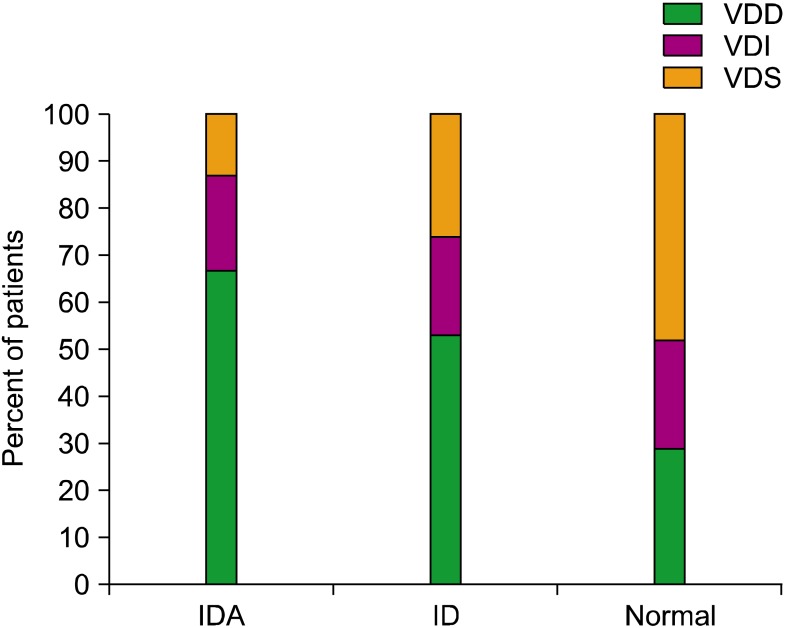
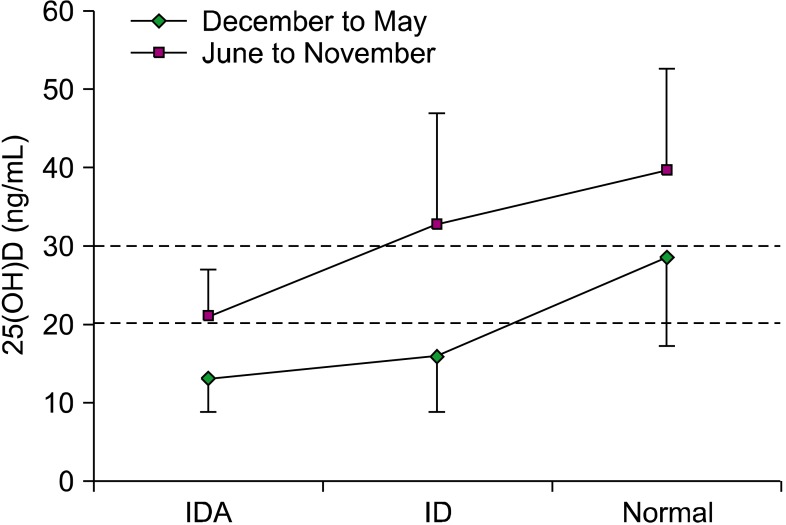
VDD was present in 67% of IDA, 53% of ID, and 29% of normal subjects. The proportion of breastfed infants was the highest in the IDA (97%) and VDD (96%) groups. The odds ratio for the likelihood of iron-deficient infants to have subnormal vitamin D levels was 4.115. There was a significant correlation between Hb and 25(OH)D levels. Plasma 25(OH)D levels were lower in the winter/spring. Body mass index values were higher in the IDA/ID groups. Iron, age, and season were predictors of 25(OH)D levels.
CONCLUSION
The prevalence of iron and vitamin D deficiency was high in breastfed infants. There was also a significant association between Hb and 25(OH)D levels in infants. Since all breastfed infants should receive vitamin D supplementation, there should also be concern about concurrent deficiencies in infants with IDA.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Retinol, α-tocopherol, and selected minerals in breast milk of lactating women with full-term infants in South Korea
Hyesook Kim, Byung-Mun Jung, Bum-Noh Lee, Yun-Je Kim, Ji A Jung, Namsoo Chang
Nutr Res Pract. 2017;11(1):64-69. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2017.11.1.64.
Reference
-
1. Christian P, Tielsch JM. Evidence for multiple micronutrient effects based on randomized controlled trials and meta-analyses in developing countries. J Nutr. 2012; 142:173S–177S. PMID: 22157540.
Article2. Suskind DL. Nutritional deficiencies during normal growth. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2009; 56:1035–1053. PMID: 19931062.
Article3. Domellof M, Cohen RJ, Dewey KG, Hernell O, Rivera LL, Lonnerdal B. Iron supplementation of breast-fed Honduran and Swedish infants from 4 to 9 months of age. J Pediatr. 2001; 138:679–687. PMID: 11343043.4. Beard JL. Iron biology in immune function, muscle metabolism and neuronal functioning. J Nutr. 2001; 131:568S–579S. PMID: 11160590.
Article5. Aggett PJ, Agostoni C, Axelsson I, et al. Iron metabolism and requirements in early childhood: do we know enough?: a commentary by the ESPGHAN Committee on Nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2002; 34:337–345. PMID: 11930085.
Article6. Munoz P, Humeres A. Iron deficiency on neuronal function. Biometals. 2012; 25:825–835. PMID: 22639188.
Article7. Balasubramanian S. Vitamin D deficiency in breastfed infants & the need for routine vitamin D supplementation. Indian J Med Res. 2011; 133:250–252. PMID: 21441676.8. Arabi A, El Rassi R, El-Hajj Fuleihan G. Hypovitaminosis D in developing countries-prevalence, risk factors and outcomes. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2010; 6:550–561. PMID: 20852586.
Article9. McGillivray G, Skull SA, Davie G, et al. High prevalence of asymptomatic vitamin D and iron deficiency in East African immigrant children and adolescents living in a temperate climate. Arch Dis Child. 2007; 92:1088–1093. PMID: 17768148.
Article10. Wagner CL, Greer FR. Prevention of rickets and vitamin D deficiency in infants, children, and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2008; 122:1142–1152. PMID: 18977996.
Article11. Misra M, Pacaud D, Petryk A, Collett-Solberg PF, Kappy M. Vitamin D deficiency in children and its management: review of current knowledge and recommendations. Pediatrics. 2008; 122:398–417. PMID: 18676559.
Article13. Prentice A, Goldberg GR, Schoenmakers I. Vitamin D across the lifecycle: physiology and biomarkers. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008; 88:500S–506S. PMID: 18689390.
Article14. Danescu LG, Levy S, Levy J. Vitamin D and diabetes mellitus. Endocrine. 2009; 35:11–17. PMID: 18979202.
Article15. Dube K, Schwartz J, Mueller MJ, Kalhoff H, Kersting M. Iron intake and iron status in breastfed infants during the first year of life. Clin Nutr. 2010; 29:773–778. PMID: 20627488.
Article16. Huang SC, Yang YJ, Cheng CN, Chen JS, Lin CH. The etiology and treatment outcome of iron deficiency and iron deficiency anemia in children. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2010; 32:282–285. PMID: 20404750.
Article17. Huh SY, Gordon CM. Vitamin D deficiency in children and adolescents: epidemiology, impact and treatment. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2008; 9:161–170. PMID: 18175220.
Article18. Lozoff B, Jimenez E, Wolf AW. Long-term developmental outcome of infants with iron deficiency. N Engl J Med. 1991; 325:687–694. PMID: 1870641.
Article19. Grindulis H, Scott PH, Belton NR, Wharton BA. Combined deficiency of iron and vitamin D in Asian toddlers. Arch Dis Child. 1986; 61:843–848. PMID: 3767413.
Article20. Yoon JH, Park CS, Seo JY, Choi YS, Ahn YM. Clinical characteristics and prevalence of vitamin D insufficiency in children less than two years of age. Korean J Pediatr. 2011; 54:298–303. PMID: 22025923.
Article21. Yoon JW, Kim SW, Yoo EG, Kim MK. Prevalence and risk factors for vitamin D deficiency in children with iron deficiency anemia. Korean J Pediatr. 2012; 55:206–211. PMID: 22745645.
Article22. Moon JS. Nutritional management of breastfeeding infants for the prevention of common nutrient deficiencies and excesses. Korean J Pediatr. 2011; 54:282–286. PMID: 22025920.
Article23. Katsumata S, Katsumata-Tsuboi R, Uehara M, Suzuki K. Severe iron deficiency decreases both bone formation and bone resorption in rats. J Nutr. 2009; 139:238–243. PMID: 19106323.
Article24. Diaz-Castro J, Lopez-Frias MR, Campos MS, et al. Severe nutritional iron-deficiency anaemia has a negative effect on some bone turnover biomarkers in rats. Eur J Nutr. 2012; 51:241–247. PMID: 21647667.
Article25. Taylor JA, Geyer LJ, Feldman KW. Use of supplemental vitamin d among infants breastfed for prolonged periods. Pediatrics. 2010; 125:105–111. PMID: 19948571.
Article26. Holick MF, Binkley NC, Bischoff-Ferrari HA, et al. Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011; 96:1911–1930. PMID: 21646368.
Article27. Specker BL. Do North American women need supplemental vitamin D during pregnancy or lactation? Am J Clin Nutr. 1994; 59:484S–490S. PMID: 8304286.
Article28. Jain V, Gupta N, Kalaivani M, Jain A, Sinha A, Agarwal R. Vitamin D deficiency in healthy breastfed term infants at 3 months & their mothers in India: seasonal variation & determinants. Indian J Med Res. 2011; 133:267–273. PMID: 21441679.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical characteristics and prevalence of vitamin D insufficiency in children less than two years of age
- Prevalence and risk factors for vitamin D deficiency in children with iron deficiency anemia
- Iron Deficiency and Feeding Practices in Infants and Young Children
- Iron Deficiency is Not Associated with Increased Blood Cadmium in Infants
- Clinical characteristics of vitamin D deficiency rickets in infants and preschool children