Ann Dermatol.
2012 Nov;24(4):413-419. 10.5021/ad.2012.24.4.413.
Analysis of Colonization and Genotyping of the Exotoxins of Staphylococcus aureus in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- 2Department of Dermatology, Gil Medical Center, Gachon University of Medicine and Science, Incheon, Korea. dmjj1@gilhospital.com
- 3Department of Microbiology, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2266035
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2012.24.4.413
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The skin of atopic dermatitis (AD) patients has a high susceptibility to Staphylococcus aureus colonization, and the toxins produced by S. aureus may aggravate AD by acting as superantigens.
OBJECTIVE
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the relationship of the skin barrier function, colonization of S. aureus, and the clinical severity of AD. We also examined the predominant toxin genes produced in Korean AD patients.
METHODS
Thirty-nine patients with AD were evaluated for clinical severity and skin barrier function by using Severity Scoring of Atopic Dermatitis (SCORAD) index and transepidermal water loss (TEWL). S. aureus was isolated from the forearm, popliteal fossa, and anterior nares of AD patients (n=39) and age-matched controls (n=40); the toxin genes were analyzed by performing multiplex polymerase chain reaction.
RESULTS
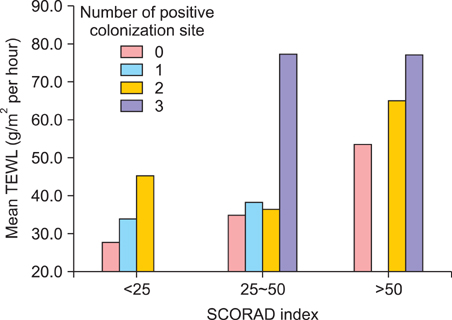
TEWL showed a statistically significant correlation with clinical severity in patients with AD (p<0.05). TEWL was correlated with the number of S. aureus colonization sites and the presence of nasal colonization, but these results were not statistically significant. S. aureus strains were isolated in 64.1% of the 39 AD patients. The SCORAD index and AD severity were strongly correlated with the number of colonization sites. The predominant toxin gene found in AD patients was staphylococcal enterotoxin a (sea) only, which was produced in 52.6% of patients. The toxin genes sea and toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 (tsst-1) were found together in 42.1%, while tsst-1 only was found in 5.3% of the patients.
CONCLUSION
S. aureus strains were isolated in 64.1% of the 39 AD patients. Skin barrier function, as measured by TEWL, revealed a statistically significant correlation with clinical severity in AD patients. The SCORAD index and severity of AD was strongly correlated with the number of colonization. The most common toxin gene was sea in the Korean AD patients and this gene might have an important role in the pathogenesis of AD.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Prevalence of atopic dermatitis and its associated factors for elementary school children in Gyeonggi-do province
Eunji Kim, Soohyun Ri, Sung Chul Seo, Ji Tae Choung, Young Yoo
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2016;4(5):346-353. doi: 10.4168/aard.2016.4.5.346.
Reference
-
1. Laughter D, Istvan JA, Tofte SJ, Hanifin JM. The prevalence of atopic dermatitis in Oregon schoolchildren. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000. 43:649–655.
Article2. Weidinger S, Illig T, Baurecht H, Irvine AD, Rodriguez E, Diaz-Lacava A, et al. Loss-of-function variations within the filaggrin gene predispose for atopic dermatitis with allergic sensitizations. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006. 118:214–219.
Article3. Nomura T, Sandilands A, Akiyama M, Liao H, Evans AT, Sakai K, et al. Unique mutations in the filaggrin gene in Japanese patients with ichthyosis vulgaris and atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007. 119:434–440.
Article4. Gupta J, Grube E, Ericksen MB, Stevenson MD, Lucky AW, Sheth AP, et al. Intrinsically defective skin barrier function in children with atopic dermatitis correlates with disease severity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008. 121:725–730.
Article5. Kim DW, Park JY, Na GY, Lee SJ, Lee WJ. Correlation of clinical features and skin barrier function in adolescent and adult patients with atopic dermatitis. Int J Dermatol. 2006. 45:698–701.
Article6. Sung HC, Jung HD, Park KD, Lee WJ, Lee SJ, Kim DW. A quantitative culture study of Staphylococcus aureus in adolescent and adult patients with atopic dermatitis using the contact-plate sampling technique. Korean J Dermatol. 2007. 45:673–679.7. Lebon A, Labout JA, Verbrugh HA, Jaddoe VW, Hofman A, van Wamel WJ, et al. Role of Staphylococcus aureus nasal colonization in atopic dermatitis in infants: the Generation R Study. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2009. 163:745–749.8. Park YL, Kim HD, Kim KH, Kim MN, Kim JW, Ro YS, et al. Report from ADRG: a study on the diagnostic criteria of Korean atopic dermatitis. Korean J Dermatol. 2006. 44:659–663.9. Roll A, Cozzio A, Fischer B, Schmid-Grendelmeier P. Microbial colonization and atopic dermatitis. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004. 4:373–378.
Article10. Breuer K, Kapp A, Werfel T. Bacterial infections and atopic dermatitis. Allergy. 2001. 56:1034–1041.
Article11. Breuer K, HAussler S, Kapp A, Werfel T. Staphylococcus aureus: colonizing features and influence of an antibacterial treatment in adults with atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. 2002. 147:55–61.
Article12. Tomi NS, Kränke B, Aberer E. Staphylococcal toxins in patients with psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, and erythroderma, and in healthy control subjects. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005. 53:67–72.
Article13. Bunikowski R, Mielke ME, Skarabis H, Worm M, Anagnostopoulos I, Kolde G, et al. Evidence for a disease-promoting effect of Staphylococcus aureus-derived exotoxins in atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000. 105:814–819.
Article14. Kim DW, Park JY, Park KD, Kim TH, Lee WJ, Lee SJ, et al. Are there predominant strains and toxins of Staphylococcus aureus in atopic dermatitis patients? Genotypic characterization and toxin determination of S. aureus isolated in adolescent and adult patients with atopic dermatitis. J Dermatol. 2009. 36:75–81.
Article15. Yagi S, Wakaki N, Ikeda N, Takagi Y, Uchida H, Kato Y, et al. Presence of staphylococcal exfoliative toxin A in sera of patients with atopic dermatitis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2004. 34:984–993.
Article16. Zouharova M, Rysanek D. Multiplex PCR and RPLA Identification of Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxigenic strains from bulk tank milk. Zoonoses Public Health. 2008. 55:313–319.
Article17. Yim YS, Park CW, Lee CH, Song WK. A study on the evaluation of the staphylococcal exotoxins and staphylococcal enterotoxin a-specific ige antibody in childhood atopic dermatitis. Korean J Dermatol. 2002. 40:607–615.18. Leung DY, Harbeck R, Bina P, Reiser RF, Yang E, Norris DA, et al. Presence of IgE antibodies to staphylococcal exotoxins on the skin of patients with atopic dermatitis. Evidence for a new group of allergens. J Clin Invest. 1993. 92:1374–1380.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effect of Skin-colonizing Staphylococcus aureus and Its Exotoxins on Childhood Atopic Dermatitis
- A Study on the Evaluation of the Staphylococcal Exotoxins and Staphylococcal Enterotoxin A-specific IgE Antibody in Childhood Atopic Dermatitis
- The association between Staphylococcus aureus colonization and food sensitization in children with atopic dermatitis
- A Comparison Study of the Staphylococcal Exotoxins and Staphylococcal Enterotoxin A-specific IgE Antibody between Childhood and Adulthood Atopic Dermatitis
- Colonization of Staphylococcus aureus and sensitivity to antibiotics in children with atopic dermatitis