Clinicopathologic Manifestations of 36 Korean Patients with Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis: A Case Series and Review of the Literature
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. yymmpark6301@hotmail.com
- KMID: 2265386
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2010.22.2.163
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
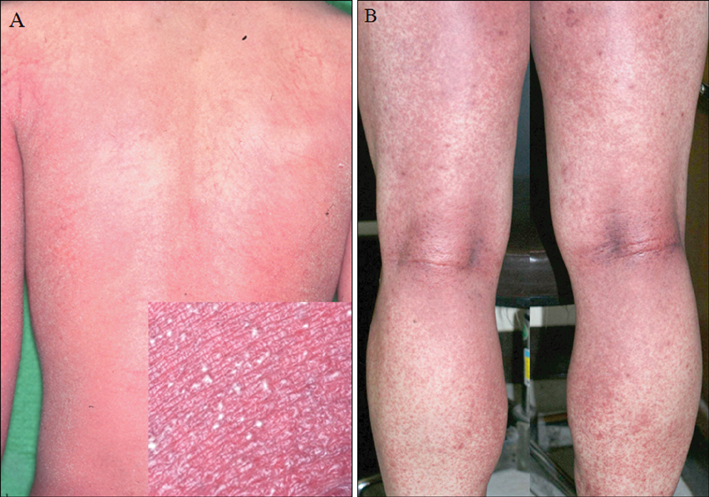
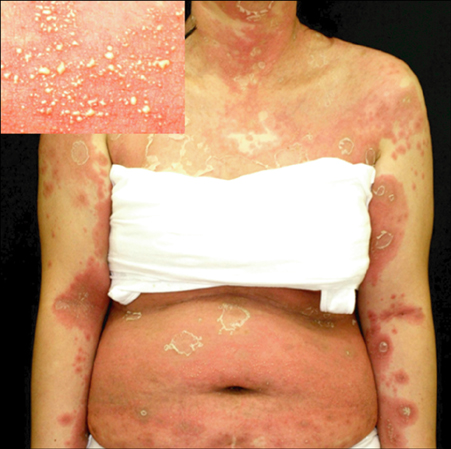
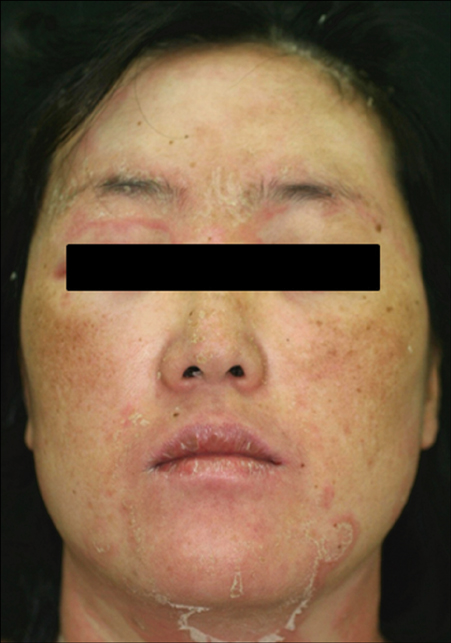
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) is a rare and severe subtype of drug eruption, characterized by acute, extensive, non-follicular, sterile pustules on an erythematous background, accompanied by fever and leukocytosis.
OBJECTIVE
The purpose of this study was to characterize AGEP in Korean patients in terms of clinical, laboratory, and pathologic findings.
METHODS
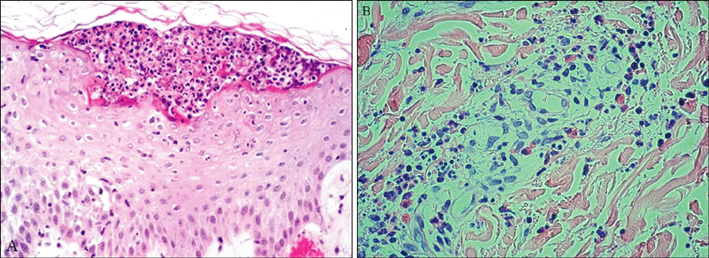
Thirty-six patients (M:F=17:19) with AGEP were identified from an extensive review of medical records over a 15 year period. All patient cases were confirmed by biopsy and fulfilled the diagnostic criteria. RESULTS: The patient ages ranged from 4~80 years (37.6+/-19.4). The incubation period was 1~23 days. The duration of disease was 5~14 days. Neutrophilia (36/36), high CRP (14/36), and eosinophilia (30/36) were common laboratory findings. A history of drug administration existed in 23 of 36 patients; herbal medications, lacquers and radiocontrast media were the unique causative drugs. Spongioform subcorneal or intraepidermal pustules in the epidermis was observed in all patients. Thirty-six patients were subdivided into 2 groups: group A (n=23) was strongly associated with known agents; and group B (n=13) had no identified causative agents. There was no significant difference between the 2 groups.
CONCLUSION
Our results demonstrate the characteristic features of AGEP in Korean patients as follows: lower identification of causative agents; herbal medications, lacquers, and radiocontrast media were the main causative agents; and no significant differences existed between the 2 groups.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 7 articles
-
A Case of Celecoxib Induced Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis
Hyun-Tae Shin, Se-Won Park, Kyung-Tae Lee, Hae-Young Park, Ji-Hye Park, Dong-Youn Lee, Joo-Heung Lee, Jun-Mo Yang, Eil-Soo Lee
Ann Dermatol. 2011;23(Suppl 3):S380-S382. doi: 10.5021/ad.2011.23.S3.S380.Generalized Pustulosis Diagnosed as Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis: Tzanck Smear and Pathological Evaluation of the Pustule Roof Can Provide Evidence for Early Diagnosis
Soo Min Kim, Yee Jeong Kim, Nam Joon Cho
Ann Dermatol. 2015;27(5):616-617. doi: 10.5021/ad.2015.27.5.616.Immunohistochemical Comparison of IL-36 and the IL-23/Th17 Axis of Generalized Pustular Psoriasis and Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis
Hyo Sang Song, Sang Jin Kim, Tae-In Park, Yong Hyun Jang, Eun-So Lee
Ann Dermatol. 2016;28(4):451-456. doi: 10.5021/ad.2016.28.4.451.Piperacillin/Tazobactam-Associated Hypersensitivity Syndrome with Overlapping Features of Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis and Drug-Related Rash with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms Syndrome
Tae In Kim, Ki Heon Jeong, Min Kyung Shin, Nack In Kim
Ann Dermatol. 2016;28(1):98-101. doi: 10.5021/ad.2016.28.1.98.Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis due to hydroxychloroquine in a rheumatoid arthritis patient
Hye Jin Lim, Ji Hye Jung, Min Jeoung Kim, Jeoung Min Kim, Hye Ran Kang, Yoon Kyung Song, Jin Wuk Hur, Sang-Hoon Kim, Eun Kyung Kim
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2013;1(2):176-178. doi: 10.4168/aard.2013.1.2.176.Adverse drug reactions after taking the extract of Cudrania tricuspidata
Beom Seok Koh, Hye Jung Park, Sung Ryeol Kim, Il Joo Moon, Dong Woo Leem, Kyung Hee Park, Jae-Hyun Lee, Jung-Won Park
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2014;2(5):387-390. doi: 10.4168/aard.2014.2.5.387.Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions: A Single-Center Retrospective Study of 173 Patients in China
Zhongyi Xu, Jie Shen, Yiwen Yang, Ruoyue Yuan, Leihong Flora Xiang, Chengfeng Zhang
Ann Dermatol. 2019;31(5):545-554. doi: 10.5021/ad.2019.31.5.545.
Reference
-
1. Baker H, Ryan TJ. Generalized pustular psoriasis. A clinical and epidemiological study of 104 cases. Br J Dermatol. 1968. 80:771–793.2. Beylot C, Bioulac P, Doutre MS. Acute generalized exanthematic pustuloses (four cases). Ann Dermatol Venereol. 1980. 107:37–48.3. Roujeau JC, Bioulac-Sage P, Bourseau C, Guillaume JC, Bernard P, Lok C, et al. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis. Analysis of 63 cases. Arch Dermatol. 1991. 127:1333–1338.
Article4. Chang SL, Huang YH, Yang CH, Hu S, Hong HS. Clinical manifestations and characteristics of patients with acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis in Asia. Acta Derm Venereol. 2008. 88:363–365.5. Rouchouse B, Bonnefoy M, Pallot B, Jacquelin L, Dimoux-Dime G, Claudy AL. Acute generalized exanthematous pustular dermatitis and viral infection. Dermatologica. 1986. 173:180–184.
Article6. Davidovici BB, Pavel D, Cagnano E, Rozenman D, Halevy S. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis following a spider bite: report of 3 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006. 55:525–529.
Article7. Sidoroff A, Dunant A, Viboud C, Halevy S, Bavinck JN, Naldi L, et al. Risk factors for acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP)-results of a multinational case-control study (EuroSCAR). Br J Dermatol. 2007. 157:989–996.
Article8. Kim SJ, Lee SH, Ahn SK, Lee WS, Lee BJ. Clinicopathologic study of pustular drug eruption. Korean J Dermatol. 1994. 32:554–561.9. Lim JY, Jang HS, Oh CK, Kwon KS, Kim MB. Clinicopathologic study of generalized pustular psoriasis and acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis. Korean J Dermatol. 2002. 40:244–252.10. Saper RB, Kales SN, Paquin J, Burns MJ, Eisenberg DM, Davis RB, et al. Heavy metal content of ayurvedic herbal medicine products. JAMA. 2004. 292:2868–2873.
Article11. Bogusz MJ, al Tufail M, Hassan H. How natural are 'natural herbal remedies'? A Saudi perspective. Adverse Drug React Toxicol Rev. 2002. 21:219–229.12. Park YM, Park JG, Kang H, Houh D, Byun DG, Kim JW. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis induced by ingestion of lacquer chicken. Br J Dermatol. 2000. 143:230–232.
Article13. Foti C, Bonamonte D, Conserva A, Antelmi AR, Antonaci CE, Angelini G. Occupational allergic contact dermatitis to a non-ionic iodinated contrast medium containing iomeprol. Contact Dermatitis. 2008. 59:252–253.
Article14. Atasoy M, Erdem T, Sari RA. A case of acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) possibly induced by iohexol. J Dermatol. 2003. 30:723–726.
Article15. Peterson A, Katzberg RW, Fung MA, Wootton-Gorges SL, Dager W. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis as a delayed dermatotoxic reaction to IV-administered nonionic contrast media. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006. 187:W198–W201.
Article16. Belgodere X, Wolkenstein P, Pastor MJ. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis induced by iopamidol. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2004. 131:831–832.17. Hammerbeck AA, Daniels NH, Callen JP. Ioversol-induced acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: a case report. Arch Dermatol. 2009. 145:683–687.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis with Hemodynamic Instability Induced by Ingestion of Lacquer Chicken
- A Case of Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis Possibly Induced by Ritodrine
- Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis Caused by Diltiazem
- Two Cases of Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis
- Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis