Ann Dermatol.
2011 Feb;23(1):108-110. 10.5021/ad.2011.23.1.108.
Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis Caused by Diltiazem
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. dylee@skku.edu
- KMID: 2171967
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2011.23.1.108
Abstract
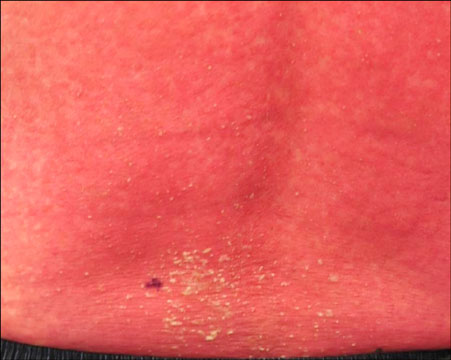
- Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis is clinically characterized by fever, pruritus and an acute pustular eruption. It can be described as having an abrupt onset and then spontaneous resolution occurs shortly after the start of symptoms, and there is usually only a single episode. Most cases have been triggered by the ingestion of drugs. Diltiazem hydrochloride is a calcium channel blocker that is commonly used for treating hypertension and angina. This drug was found to be the responsible agent in our current patient. There have been 9 such case reports in the English medical literature, yet this is the first such report in the Korean medical literature. We present the case of a 51-year-old male who experienced an acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis due to diltiazem hydrochloride and we review the relevant literature.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Roujeau JC, Bioulac-Sage P, Bourseau C, Guillaume JC, Bernard P, Lok C, et al. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis. Analysis of 63 cases. Arch Dermatol. 1991. 127:1333–1338.
Article2. Beylot C, Doutre MS, Beylot-Barry M. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 1996. 15:244–249.
Article3. Breathnach SM. Champion RH, Burton JL, Burns DA, Breathnach SM, editors. Drug reaction. Rook/Wilkinson/Ebling textbook of dermatology. 1998. 6th ed. Oxford: Blackwell Science;3349–3517.4. Sidoroff A, Dunant A, Viboud C, Halevy S, Bavinck JN, Naldi L, et al. Risk factors for acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP): results of a multinational case-control study (EuroSCAR). Br J Dermatol. 2007. 157:989–996.
Article5. Britschgi M, Steiner UC, Schmid S, Depta JP, Senti G, Bircher A, et al. T-cell involvement in drug-induced acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis. J Clin Invest. 2001. 107:1433–1441.
Article6. Britschgi M, Pichler WJ. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, a clue to neutrophil-mediated inflammatory processes orchestrated by T cells. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002. 2:325–331.
Article7. Beltraminelli HS, Lerch M, Arnold A, Bircher AJ, Haeusermann P. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis induced by the antifungal terbinafine: case report and review of the literature. Br J Dermatol. 2005. 152:780–783.
Article8. Moreau A, Dompmartin A, Castel B, Remond B, Leroy D. Drug-induced acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis with positive patch tests. Int J Dermatol. 1995. 34:263–266.
Article9. Stern R, Khalsa JH. Cutaneous adverse reactions associated with calcium channel blockers. Arch Intern Med. 1989. 149:829–832.
Article10. Lambert DG, Dalac S, Beer F, Chavannet P, Portier H. Acute generalized exanthematous pustular dermatitis induced by diltiazem. Br J Dermatol. 1988. 118:308–309.
Article11. Nishimura T, Yoshioka K, Katoh J, Mizuno N, Kono T, Tanii T, et al. Pustular drug eruption induced by diltiazem. Skin Res. 1991. 33:Suppl. 10. 251–254.12. Wittal RA, Fischer GO, Georgouras KE, Baird PJ. Skin reactions to diltiazem. Australas J Dermatol. 1992. 33:11–18.
Article13. Janier M, Gerault MH, Carlotti A, Vignon MD, Daniel F. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis due to diltiazem. Br J Dermatol. 1993. 129:354–355.
Article14. Wakelin SH, James MP. Diltiazem-induced acute generalised exanthematous pustulosis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1995. 20:341–344.
Article15. Jan V, Machet L, Gironet N, Martin L, Machet MC, Lorette G, et al. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis induced by diltiazem: value of patch testing. Dermatology. 1998. 197:274–275.16. Sousa-Basto A, Azenha A, Duarte ML, Pardal-Oliveira F. Generalized cutaneous reaction to diltiazem. Contact Dermatitis. 1993. 29:44–45.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis
- Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis with Hemodynamic Instability Induced by Ingestion of Lacquer Chicken
- A Case of Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis Possibly Induced by Ritodrine
- A Serial Occurrence of Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis in Childhood Siblings
- Two Cases of Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis