Ann Dermatol.
2010 May;22(2):149-155. 10.5021/ad.2010.22.2.149.
Epidemiologic Study of Malassezia Yeasts in Seborrheic Dermatitis Patients by the Analysis of 26S rDNA PCR-RFLP
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. 20070178@kuh.ac.kr
- KMID: 2265384
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2010.22.2.149
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
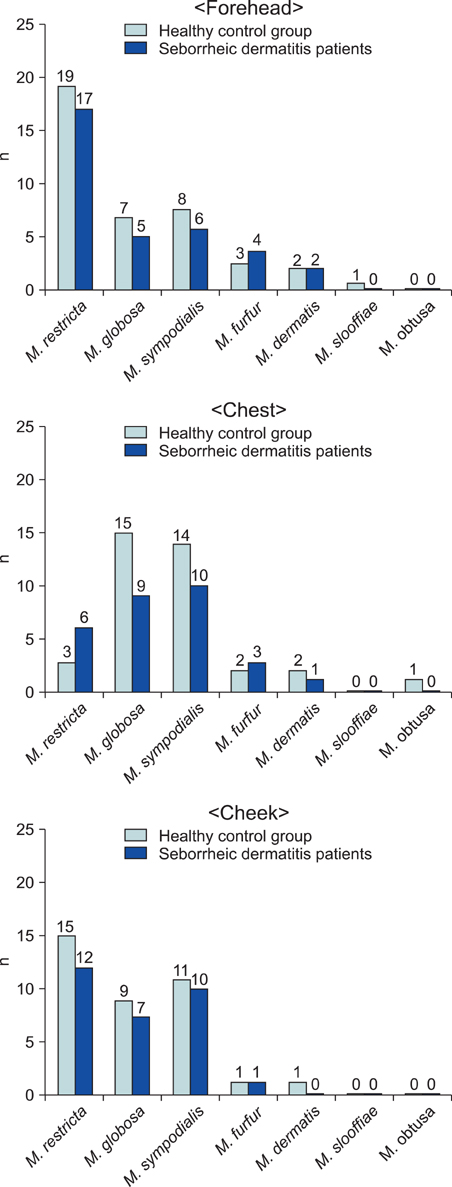
This case-control study concerns a molecular biological method based on the data gathered from a group of Korean subjects to examine the distribution of Malassezia yeasts in seborrheic dermatitis (SD) patients. Cultures for Malassezia yeasts were taken from the foreheads, cheeks and chests of 60 patients with SD and in 60 healthy controls of equivalent age.
OBJECTIVE
The purpose of this study is to identify the relationship between certain species of Malassezia and SD. This was done by analyzing the differences in the distribution of Malassezia species in terms of age and body parts of the host with healthy controls.
METHODS
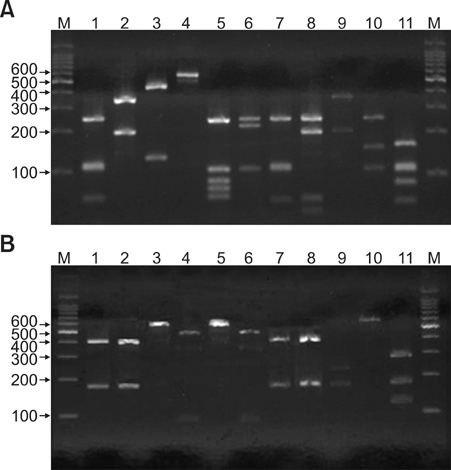
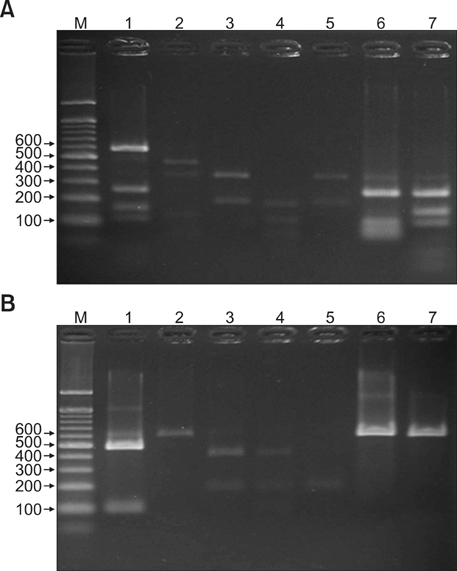
26S rDNA PCR-RFLP, a fast and accurate molecular biological method, was used to overcome the limits of morphological and biochemical methods. RESULTS: The positive Malassezia culture rate was 51.7% in patients with SD, which was lower than that of healthy adults (63.9%). M. restricta was dominant in patients with SD (19.5%). Likewise, M. restricta was identified as a common species (20.5%) in healthy controls. In the ages 31~40, M. restricta was found to be the most common species (31.6%) among SD patients.
CONCLUSION
According to the results of the study, the most frequently isolated species was M. restricta (19.5%) in patients with SD. There was no statistically significant difference in the distribution of Malassezia species between the SD patients and healthy control groups.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Progress in Malassezia Research in Korea
Soo Young Kim, Yang Won Lee, Yong Beom Choe, Kyu Joong Ahn
Ann Dermatol. 2015;27(6):647-657. doi: 10.5021/ad.2015.27.6.647.Efficacy and Safety of Cream Containing Climbazole/Piroctone Olamine for Facial Seborrheic Dermatitis: A Single-Center, Open-Label Split-Face Clinical Study
Hae Jeong Youn, Soo Young Kim, Minji Park, Won Hee Jung, Yang Won Lee, Yong Beom Choe, Kyu Joong Ahn
Ann Dermatol. 2016;28(6):733-739. doi: 10.5021/ad.2016.28.6.733.
Reference
-
1. Gerd P, Thomas J. Wolff K, Goldsmith LA, Katz SI, Gilchrest BA, Paller AS, Leffell DJ, editors. Seborrheic dermatitis. Fitzpatrick's dermatology in general medicine. 2008. 7th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill;1822–1830.2. Comert A, Bekiroglu N, Gurbuz O, Ergun T. Efficacy of oral fluconazole in the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis: a placebo-controlled study. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2007. 8:235–238.3. Miranda KC, de Araujo CR, Costa CR, Passos XS, de Fatima Lisboa Fernandes O, do Rosario Rodrigues Silva M. Antifungal activities of azole agents against the Malassezia species. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2007. 29:281–284.
Article4. Drouhet E, Dompmartin D, Papachristou-Moraiti A, Ravisse P. Experimental dermatitis caused by Pityrosporum ovale and (or) Pityrosporum orbiculare in the guinea pig and the mouse. Sabouraudia. 1980. 18:149–156.5. Williamson P, Kligman AM. A new method for the quantitative investigation of cutaneous bacteria. J Invest Dermatol. 1965. 45:498–503.
Article6. Leeming JP, Notman FH, Holland KT. The distribution and ecology of Malassezia furfur and cutaneous bacteria on human skin. J Appl Bacteriol. 1989. 67:47–52.
Article7. Jang SJ, Choi YB, Ahn KJ. Malassezia species cultured from the lesions of Malassezia folliculitis. Korean J Med Mycol. 2003. 8:55–62.8. Leeming JP, Notman FH. Improved methods for isolation and enumeration of Malassezia furfur from human skin. J Clin Microbiol. 1987. 25:2017–2019.
Article9. Mirhendi H, Makimura K, Zomorodian K, Yamada T, Sugita T, Yamaguchi H. A simple PCR-RFLP method for identification and differentiation of 11 Malassezia species. J Microbiol Methods. 2005. 61:281–284.
Article10. Kim SM, Lim SH, Jung BR, Lee YW, Choe YB, Ahn KJ. The application of colony PCR in the molecular biological analysis of Malassezia yeasts. Korean J Med Mycol. 2007. 12:180–188.11. Ahn KJ. Taxonomy of the genus Malassezia. Korean J Med Mycol. 1998. 3:81–88.12. Lee YW, Lim SH, Ahn KJ. The application of 26S rDNA PCR-RFLP in the identification and classification of Malassezia yeast. Korean J Med Mycol. 2006. 11:141–153.13. Choe YB, Jang SJ, Yim SM, Ahn KJ. The quantitative study on the distribution of Malassezia yeasts on the normal skin of the young adults. Korean J Med Mycol. 2004. 9:174–181.14. Baillon EH. Traité de botanique médicale cryptogamique, suivi du tableau du droguier de la Faculté de médecine de Paris. 1889. Paris: Doin.15. Gueho E, Simmons RB, Pruitt WR, Meyer SA, Ahearn DG. Association of Malassezia pachydermatis with systemic infections of humans. J Clin Microbiol. 1987. 25:1789–1790.
Article16. Ashbee HR, Ingham E, Holland KT, Cunliffe WJ. The carriage of Malassezia furfur serovars A, B and C in patients with pityriasis versicolor, seborrhoeic dermatitis and controls. Br J Dermatol. 1993. 129:533–540.
Article17. Mayser P, Haze P, Papavassilis C, Pickel M, Gruender K, Gueho E. Differentiation of Malassezia species: selectivity of cremophor EL, castor oil and ricinoleic acid for M. furfur. Br J Dermatol. 1997. 137:208–213.
Article18. Crespo Erchiga V, Ojeda Martos A, Vera Casano A, Crespo Erchiga A, Sanchez Fajardo F. Malassezia globosa as the causative agent of pityriasis versicolor. Br J Dermatol. 2000. 143:799–803.
Article19. Ashbee HR. Recent developments in the immunology and biology of Malassezia species. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2006. 47:14–23.20. Gueho E, Midgley G, Guillot J. The genus Malassezia with description of four new species. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1996. 69:337–355.
Article21. Sugita T, Takashima M, Shinoda T, Suto H, Unno T, Tsuboi R, et al. New yeast species, Malassezia dermatis, isolated from patients with atopic dermatitis. J Clin Microbiol. 2002. 40:1363–1367.
Article22. Sugita T, Takashima M, Kodama M, Tsuboi R, Nishikawa A. Description of a new yeast species, Malassezia japonica, and its detection in patients with atopic dermatitis and healthy subjects. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. 41:4695–4699.
Article23. Sugita T, Tajima M, Takashima M, Amaya M, Saito M, Tsuboi R, et al. A new yeast, Malassezia yamatoensis, isolated from a patient with seborrheic dermatitis, and its distribution in patients and healthy subjects. Microbiol Immunol. 2004. 48:579–583.
Article24. Hirai A, Kano R, Makimura K, Duarte ER, Hamdan JS, Lachance MA, et al. Malassezia nana sp. nov., a novel lipid-dependent yeast species isolated from animals. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2004. 54:623–627.
Article25. Cabanes FJ, Theelen B, Castella G, Boekhout T. Two new lipid-dependent Malassezia species from domestic animals. FEMS Yeast Res. 2007. 7:1064–1076.26. Nakabayashi A, Sei Y, Guillot J. Identification of Malassezia species isolated from patients with seborrhoeic dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, pityriasis versicolor and normal subjects. Med Mycol. 2000. 38:337–341.
Article27. Ahn KJ. Malassezia species cultured from the lesions of pityriasis versicolor. Korean J Dermatol. 1997. 35:736–743.28. Ginarte M, Fabeiro JM, Toribio J. Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis (Gougerot-Carteaud) successfully treated with tacalcitol. J Dermatolog Treat. 2002. 13:27–30.
Article29. Yesudian P, Kamalam S, Razack A. Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis (Gougerot-Carteaud). An abnormal host reaction to Malassezzia furfur. Acta Derm Venereol. 1973. 53:381–384.30. Chowdhary A, Randhawa HS, Sharma S, Brandt ME, Kumar S. Malassezia furfur in a case of onychomycosis: colonizer or etiologic agent? Med Mycol. 2005. 43:87–90.
Article31. Gupta AK, Batra R, Bluhm R, Boekhout T, Dawson TL Jr. Skin diseases associated with Malassezia species. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004. 51:785–798.
Article32. Curvale-Fauchet N, Botterel F, Legrand P, Guillot J, Bretagne S. Frequency of intravascular catheter colonization by Malassezia spp. in adult patients. Mycoses. 2004. 47:491–494.
Article33. Devlin RK. Invasive fungal infections caused by Candida and Malassezia species in the neonatal intensive care unit. Adv Neonatal Care. 2006. 6:68–77.
Article34. Tajima M, Sugita T, Nishikawa A, Tsuboi R. Molecular analysis of Malassezia microflora in seborrheic dermatitis patients: comparison with other diseases and healthy subjects. J Invest Dermatol. 2008. 128:345–351.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Application of 26S rDNA PCR-RFLP in the Identification and Classification of Malassezia Yeast
- Comparison of Nested PCR and RFLP for Identification and Classification of Malassezia Yeasts from Healthy Human Skin
- Epidemiologic Study of Malassezia Yeasts in Patients with Malassezia Folliculitis by 26S rDNA PCR-RFLP Analysis
- Epidemiologic Study of Malassezia Yeasts in Acne Patients by Analysis of 26S rDNA PCR-RFLP
- Distribution of Malassezia Species on the Scalp in Korean Seborrheic Dermatitis Patients