Ann Dermatol.
2012 Aug;24(3):287-294. 10.5021/ad.2012.24.3.287.
Molecular Phylogenetics of Exophiala Species Isolated from Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Gyeongju, Korea. smg@dongguk.ac.kr
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Gyeongju, Korea.
- 3Department of Dermatology, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2265301
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2012.24.3.287
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Recently, identification of fungi have been supplemented by molecular tools, such as ribosomal internal transcribed spacer (ITS) sequence analysis. According to these tools, morphological Exophiala species was newly introduced or redefined.
OBJECTIVE
This study was designed to investigate the phylogenetics based on ribosomal ITS sequence analysis from clinical Exophiala species isolated in Korea.
METHODS
The strains of Exophiala species were 4 clinical isolates of phaeohyphomycosis agents kept in the department of dermatology, Dongguk University Medical Center(DUMC), Gyeongju, Korea. The DNAs of total 5 strains of Exophiala species were extracted by bead-beating method. Polymerase chain reaction of ITS region using the primer pairs ITS1-ITS4, was done and phylogenetic tree contributed from sequences of ITS region from 5 Korean isolates including E. dermatitidis CBS 109154 and comparative related strains deposited in GenBank.
RESULTS
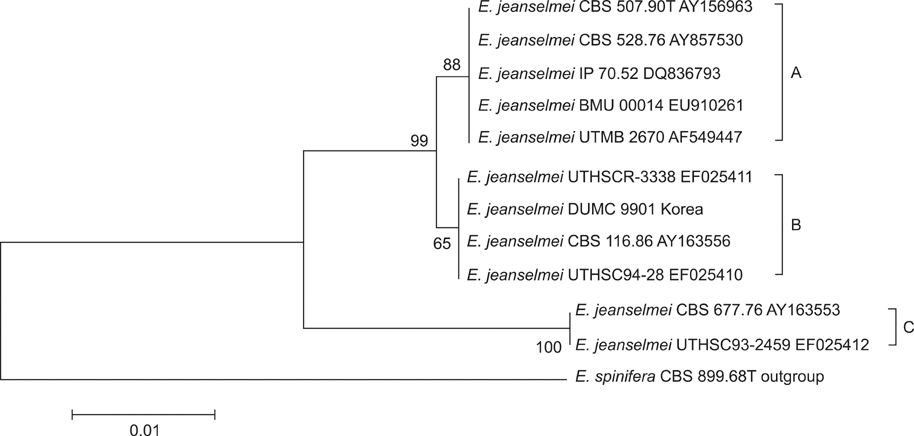
The strains of Exophiala species were 3 strains of E. dermatitidis, 1 strain of E. jeanselmei and 1 strain of Exophiala new species. Among the 3 subtypes (type A, B, C) of E. jeanselmei, E. jeanselmei DUMC 9901 belonged to type B. Of the 2 main types of E. dermatitidis (type A, B) and 3 subtypes of E. dermatitidis type A (A0, A1 and A2), two strains (E. dermatitidis CBS 709.95, E. dermatitidis CBS 109154) belonged to A0 subtypes, 1 strain (E. dermatitidis DUMC 9902) A1 subtype, respectively.
CONCLUSION
Phylogenetic analysis of ITS region sequence provided useful information not only for new species identification but for the subtyping and origin of Exophiala species.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Case of Phaeohyphomycosis on the Wrist: Identification of Exophiala spinifera in Korea
Weon Ju Lee, Dong Hyuk Eun, Yong Hyun Jang, Seok-Jong Lee, Yong Jun Bang, Jae Bok Jun
Ann Dermatol. 2018;30(2):232-233. doi: 10.5021/ad.2018.30.2.232.
Reference
-
1. De Hoog GS, Guarro J, Gene J, Figueras MJ. Atlas of clinical fungi. 2000. 2nd ed. Virgili: Centraalbureau voor Schimmelcultures;645–668.2. Ellis D, Davis S, Alexiou H, Handke R, Bartley R. Descriptions of medical fungi. 2007. 2nd ed. Adelaide: Nexus Print Solutions;62–65.3. Li DM, Li RY, De Hoog GS, Wang YX, Wang DL. Exophiala asiatica, a new species from a fatal case in China. Med Mycol. 2009. 47:101–109.
Article4. Aoyama Y, Nomura M, Yamanaka S, Ogawa Y, Kitajima Y. Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis caused by Exophiala xenobiotica in a non-Hodgkin lymphoma patient. Med Mycol. 2009. 47:95–99.
Article5. Zeng JS, De Hoog GS. Exophiala spinifera and its allies: diagnostics from morphology to DNA barcoding. Med Mycol. 2008. 46:193–208.
Article6. Zeng JS, Sutton DA, Fothergill AW, Rinaldi MG, Harrak MJ, de Hoog GS. Spectrum of clinically relevant Exophiala species in the United States. J Clin Microbiol. 2007. 45:3713–3720.
Article7. De Hoog GS, Zeng JS, Harrak MJ, Sutton DA. Exophiala xenobiotica sp. nov., an opportunistic black yeast inhabiting environments rich in hydrocarbons. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2006. 90:257–268.
Article8. Kawasaki M, Anzawa K, Tanabe H, Mochizuki T, Ishizaki H, Nishimura K. Intra-species variation of genotypes of Exophiala jeanselmei isolated from patients in Japan. Nihon Ishinkin Gakkai Zasshi. 2005. 46:261–265.
Article9. Kawasaki M, Ishizaki H, Nishimura K, Miyaji M. Mitochondrial DNA analysis of Exophiala jeanselmei and Exophiala dermatitidis. Mycopathologia. 1990. 110:107–112.
Article10. de Hoog GS, Vicente V, Caligiorne RB, Kantarcioglu S, Tintelnot K, Gerrits van den Ende AH, et al. Species diversity and polymorphism in the Exophiala spinifera clade containing opportunistic black yeast-like fungi. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. 41:4767–4778.
Article11. Matos T, Haase G, Gerrits van den Ende AH, de Hoog GS. Molecular diversity of oligotrophic and neurotropic members of the black yeast genus Exophiala, with accent on E. dermatitidis. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2003. 83:293–303.12. Vitale RG, de Hoog GS. Molecular diversity, new species and antifungal susceptibilities in the Exophiala spinifera clade. Med Mycol. 2002. 40:545–556.
Article13. Wang L, Yokoyama K, Miyaji M, Nishimura K. Identification, classification, and phylogeny of the pathogenic species Exophiala jeanselmei and related species by mitochondrial cytochrome b gene analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 2001. 39:4462–4467.
Article14. Kawasaki M, Ishizaki H, Matsumoto T, Matsuda T, Nishimura K, Miyaji M. Mitochondrial DNA analysis of Exophiala jeanselmei var. lecanii-corni and Exophiala castellanii. Mycopathologia. 1999. 146:75–77.15. Uijthof JM, Van Belkum A, De Hoog GS, Haase G. Exophiala dermatitidis and Sarcinomyces phaeomuriformis: ITS1-sequencing and nutritional physiology. Med Mycol. 1998. 36:143–151.
Article16. White TJ, Burns T, Lee S, Taylor J. Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ, editors. Amplication and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. 1990. San Diego: Academic Press;315–322.
Article17. Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG. The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997. 25:4876–4882.
Article18. Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S. MEGA4: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2007. 24:1596–1599.
Article19. Nei M, Kumar S. Molecular evolution and phylogenetics. 2000. New York: Oxford University Press.20. Queiroz-Telles F, Esterre P, Perez-Blanco M, Vitale RG, Salgado CG, Bonifaz A. Chromoblastomycosis: an overview of clinical manifestations, diagnosis and treatment. Med Mycol. 2009. 47:3–15.
Article21. Al-Tawfiq JA, Amr SS. Madura leg due to Exophiala jeanselmei successfully treated with surgery and itraconazole therapy. Med Mycol. 2009. 47:648–652.
Article22. Revankar SG. Dematiaceous fungi. Mycoses. 2007. 50:91–101.
Article23. Suh MK. Phaeohyphomycosis in Korea. Nihon Ishinkin Gakkai Zasshi. 2005. 46:67–70.
Article24. Suh MK, Lee YH. Infectious caused by dematiaceous fungi. Korean J Med Mycol. 2005. 10:77–82.25. Suh MK, Kwon SW, Kim TH, Sun YW, Lim JW, Ha GY, et al. A case of subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis caused by exophiala jeanselmei. Korean J Dermatol. 2005. 43:124–127.26. Suh MK, Suh JC, Seo SK, Na GY, Kim YJ, Bang JS, et al. A case of subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis caused by exophiala jeanselmei. Korean J Dermatol. 1999. 37:395–399.27. Kim HU, Kang SH, Matsumoto T. Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis caused by Exophiala jeanselmei in a patient with advanced tuberculosis. Br J Dermatol. 1998. 138:351–353.
Article28. Kim DS, Yoon YM, Kim SW. Phaeohyphomycosis due to. Exophiala dermatitidis successfully treated with itraconazole. Korean J Med Mycol. 1999. 4:79–83.29. Lee SC, Chun IK, Kim YP. A case of phaeomycotic subcutaneous abscess caused by Wangiella Dermatitidis. Korean J Dermatol. 1986. 24:692–696.30. Chang CL, Kim DS, Park DJ, Kim HJ, Lee CH, Shin JH. Acute cerebral phaeohyphomycosis due to Wangiella dermatitidis accompanied by cerebrospinal fluid eosinophilia. J Clin Microbiol. 2000. 38:1965–1966.
Article31. De Hoog GS. Rhinocladiella and allied genera. Stud Mycol. 1977. 15:141–144.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Molecular Analysis of Exophiala Species Using Molecular Markers
- A Case of Subcutaneous Phaeohyphomycosis Caused by Exophiala oligosperma Showing Multiple Cysts
- A Case of Phaeohyphomycosis from Exophiala Species Mimicking Facial Cutaneous Tumor
- Phaeohyphomycosis Due to Exophiala dermatitidis Successfully Treated with Itraconazole
- Fungemia due to Exophiala dermatitidis