Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2013 Mar;5(2):102-105. 10.4168/aair.2013.5.2.102.
Preparation and Characterization of an Extract of German Cockroach From a Korean Source
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine and Institute of Allergy, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. parkjw@yuhs.ac
- 2Center for Immunology and Pathology, Korea National Institute of Health, Cheongwon, Korea.
- 3Department of Environmental Medical Biology and Institute of Tropical Medicine, Arthropod of Medical Importance Resource Bank, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2260345
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2013.5.2.102
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The cockroach (CR) is an important cause of respiratory allergic disorders. We prepared a German CR extract in a standardized way and analyzed its allergenic properties.
METHODS
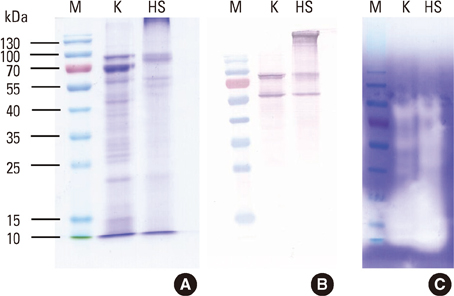
The extract was prepared from German CR (Blattella germanica) obtained from a Korean colony, and its allergenic activity was compared with that of the commercial Hollister-Stier (HS) extract. The concentrations of Bla g 1 and Bla g 2 were measured, and an in vitro specific IgE binding inhibition assay was performed to assess IgE reactivity. Proteolytic activity was examined by gelatin zymography.
RESULTS
Bla g 1 and Bla g 2 were detected at 405 U/mg and 273 ng/mg, respectively, in the Korean extract, and at 187 U/mg and 56 ng/mg, respectively, in the HS extract. The Korean extract showed 94.2% inhibition of IgE reactivity, as compared with the HS extract. A similar pattern of IgE-reactive bands was detected for the two extracts, indicating that their allergenic components are similar. The proteolytic activities of the Korean and HS extracts were found to be similar in gelatin zymography. The endotoxin levels in the Korean and HS extracts were 3,440 EU/mL and 6,580 EU/mL, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
The German CR extract was prepared in a standardized way. The extract produced in this study will be useful for the development of allergy diagnostics and immunotherapeutic agents.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Allergen standardization
Jung-Won Park, Kyoung Yong Jeong
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2018;6(4):191-196. doi: 10.4168/aard.2018.6.4.191.
Reference
-
1. Rosenstreich DL, Eggleston P, Kattan M, Baker D, Slavin RG, Gergen P, Mitchell H, McNiff-Mortimer K, Lynn H, Ownby D, Malveaux F. The role of cockroach allergy and exposure to cockroach allergen in causing morbidity among inner-city children with asthma. N Engl J Med. 1997. 336:1356–1363.2. Ahluwalia SK, Matsui EC. The indoor environment and its effects on childhood asthma. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011. 11:137–143.3. Jeong KY, Hong CS, Lee JS, Park JW. Optimization of allergen standardization. Yonsei Med J. 2011. 52:393–400.4. Kwon SW, Oh SG, Yoon UK, Kim SW, Lee YS, Kim KH, Kim WJ, Kim JK, Kim DS, Kim HS, Ryu IS, Ree SY, Jeaung BJ, Kim KE, Kim DS, Lee KY, Lee HI. Distribution of cockroaches in Korea. Allergy. 1993. 13:334–341.5. Jeong KY, Lee IY, Lee J, Ree HI, Hong CS, Yong TS. Effectiveness of education for control of house dust mites and cockroaches in Seoul, Korea. Korean J Parasitol. 2006. 44:73–79.6. Patterson ML, Slater JE. Characterization and comparison of commercially available German and American cockroach allergen extracts. Clin Exp Allergy. 2002. 32:721–727.7. Slater JE, James R, Pongracic JA, Liu AH, Sarpong S, Sampson HA, Satinover SM, Woodfolk JA, Mitchell HE, Gergen PJ, Eggleston PA. Biological potency of German cockroach allergen extracts determined in an inner city population. Clin Exp Allergy. 2007. 37:1033–1039.8. Wada K, Matsuwaki Y, Moriyama H, Kita H. Cockroach induces inflammatory responses through protease-dependent pathways. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2011. 155:Suppl 1. 135–141.9. Jeong KY, Kim C, Yong TS. Enzymatic activities of allergen extracts from three species of dust mites and cockroaches commonly found in Korean home. Korean J Parasitol. 2010. 48:151–155.10. Jeong KY, Choi SY, Lee JH, Lee IY, Yong TS, Lee JS, Hong CS, Park JW. Standardization of house dust mite extracts in Korea. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2012. 4:346–350.11. Jeong KY, Lee H, Shin KH, Yi MH, Jeong KJ, Hong CS, Yong TS. Sequence polymorphisms of major German cockroach allergens Bla g 1, Bla g 2, Bla g 4, and Bla g 5. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2008. 145:1–8.12. Lee SY, Kim DS, Kim KE, Jeaung BJ, Lee KY. IgE binding patterns to German cockroach whole body extract in Korean atopic asthmatic children. Yonsei Med J. 1998. 39:409–416.13. Yi MH, Jeong KY, Kim CR, Yong TS. IgE-binding reactivity of peptide fragments of Bla g 1.02, a major German cockroach allergen. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2009. 27:121–129.14. Lee H, Jeong KY, Shin KH, Yi MH, Gantulaga D, Hong CS, Yong TS. Reactivity of German cockroach allergen, Bla g 2, peptide fragments to IgE antibodies in patients' sera. Korean J Parasitol. 2008. 46:243–246.15. Page K. Role of cockroach proteases in allergic disease. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2012. 12:448–455.16. Grier TJ, LeFevre DM, Duncan EA, Esch RE, Coyne TC. Allergen stabilities and compatibilities in mixtures of high-protease fungal and insect extracts. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2012. 108:439–447.17. Trivedi B, Valerio C, Slater JE. Endotoxin content of standardized allergen vaccines. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003. 111:777–783.18. Baumholtz MA, Parish LC, Witkowski JA, Nutting WB. The medical importance of cockroaches. Int J Dermatol. 1997. 36:90–96.19. Tatfeng YM, Usuanlele MU, Orukpe A, Digban AK, Okodua M, Oviasogie F, Turay AA. Mechanical transmission of pathogenic organisms: the role of cockroaches. J Vector Borne Dis. 2005. 42:129–134.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Allergenic Characterization of a Novel Allergen, Homologous to Chymotrypsin, from German Cockroach
- IgE binding patterns to German cockroach whole body extract in Korean atopic asthmatic children
- Identification and Characterization of German Cockroach Allergen
- Ampicillin treated German cockroach extract leads to reduced inflammation in human lung cells and a mouse model of Asthma
- A Study on Prick Test Using Cockroach Crude Extract and Environment in Atopy Patients