Korean J Health Promot.
2015 Dec;15(4):244-253. 10.15384/kjhp.2015.15.4.244.
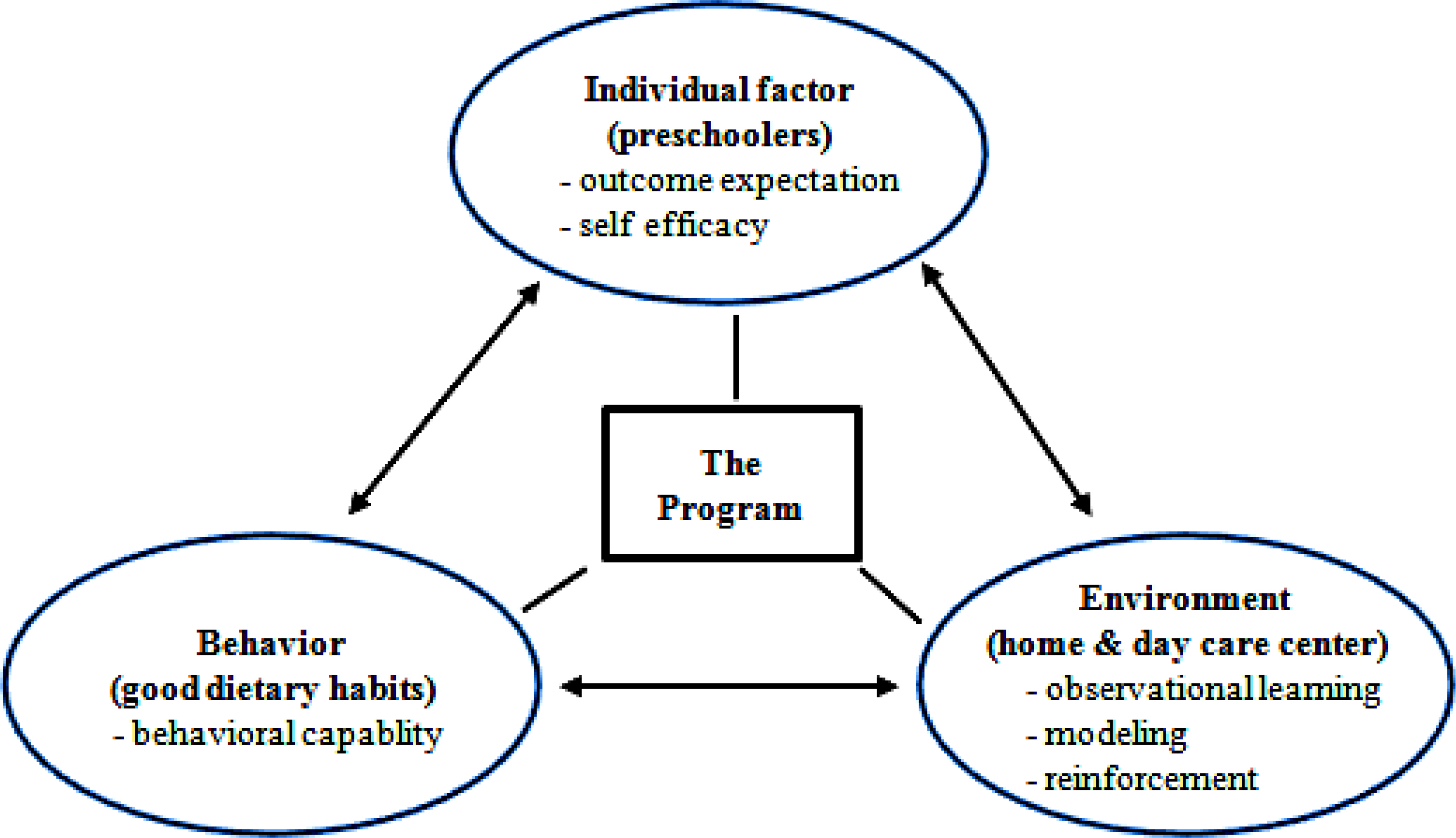
A Program to Build Preschooler's Eating Habit Based on Social Cognitive Theory
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nursing, Wonju College of Medicine, Yonsei University, Wonju, Korea. yhshin@yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Institute of Lifestyle Medicine, Wonju College of Medicine, Yonsei University, Wonju, Korea.
- KMID: 2247051
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.15384/kjhp.2015.15.4.244
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Human diet and eating habits are formed in childhood so that eating habits in this period have a great impact on the nutritional status of children. Eating behaviors of children are formed by those of family members at home or their diet at preschool and mass media. The purpose of this study was to develop a program to build healthy dietary habits in preschoolers based on Social Cognitive Theory, which emphasizes the dynamic interaction among an action, an individual and its environment, and to explore the effects of the program.
METHODS
A non-equivalent control group, pretest-posttest design was be used in this study. All participants were dyads of preschoolers and one of their parents collected from two day care centers, 18 for the experimental group and 16 for the control group. The program was evaluated by their Knowledge about Nutrition and Dietary Habits among Preschoolers and Parents Perception of Preschoolers' Dietary Habits. The program was conducted between March and June, 2015.
RESULTS
At follow-up, knowledge related to nutrition (t=-2.74, p=0.010) and dietary habits (t=-3.67, p<0.001) among the preschoolers were significantly higher in the experimental group than in the control group. However, the perception of parents on the change of their children's eating habit didn't show significant difference (t=1.13, p=0.265).
CONCLUSIONS
The results of this study is able to be used in dietary education of preschool children as one of the evidence, and be applied as an example of children's health promotion to help them have ideal eating habits, through cooperation with a university in community and day care centers.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.Yu KH. A study on the dietary behaviors, physical development and nutrient intakes in preschool children. J Nutr Health. 2009. 42(1):23–37.2.Shiu LK., Loke WM., Vijaya K., Sandhu NK. Nurturing healthy dietary habits among children and youth in Singapore. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2012. 21(1):144–50.3.Brown JE. Nutrition through the Life Cycle. 3rd ed.Belmont: Thomson Wadsworth;2008. p.38.4.Kudlová E., Schneidrová D. Dietary patterns and their changes in early childhood. Cent Eur J Public Health. 2012. 20(2):126–34.
Article5.Jeon SE. Development and Evaluation of Nutrition Education Program based on the Social Cognitive Theory for Preschool Children[dissertation]. Jeju: Jeju National University;2013. Korean.6.Jeong MS., Kim NH. A survey on nutrition education realities and needs in early childhood education centers. J Eco Early Childhood Education. 2011. 10(2):131–54.7.Kim MY., Ahn HS. Effect of the nutrition education for infant feeding on mother's knowledge, attitude, practice of weaning. Korean J Food Culture. 2003. 18(4):320–32.8.Horodynski MA., Stommel M., Brophy-Herb H., Xie Y., Weatherspoon L. Low-income African American and non-Hispanic white mothers' self efficacy, “picky eater” perception, and toddler fruit and vegetable consumption. Public Health Nurs. 2010. 27(5):408–17.9.Huh BY., Park YS., Bang KS. The structural model for the health related factors of preschoolers. J Korean Soc Matern Child Health. 2012. 16(1):1–13.10.Park YM. A study on development and effect of group nutrition education program of day-care center children [dissertation]. Daegu: The Catholic University of Daegu;2007. Korean.11.Min IJ. A study on dietary life habits, food preference of the infants, and knowledges and attitudes of teachers and parents about nutrition, and growth and problem behavior of the infants [dissertation]. Seoul: Kyung Hee University;2009. Korean.12.Kim YS. Effects of nutrition education through social cognitive theory for elementary school students: focusing on the nutrition education of sugar intake [dissertation]. Seoul: Yonsei University;2010. Korean.13.Bandura A. Self-efficacy: The exercise of control. New York: W.H. Freeman and Company;1997. p. 5–8.14.Kim JA. The effects of the home connected nutrient educational program on the knowledge in nutrients and the eating habits of children [dissertation]. Gwangju: Chonnam National University;2010. Korean.15.Shin YH. Health Promotion. 3rd ed.Seoul: Gyechuk Munwhasa;2015. p. 110–7.16.Glanz K., Rimer BK., Lewis FM. Health Behavior and Health Education. 3rd ed.SanFrancisco: Jossey-Bass;2002. p. 168–76.17.Nicki LP., Barbara LM. Pediatric Nursing: Caring for Children and their Families. 3rd ed. New York: Delmar; 2012. p.157–90.18.Park KM. A survey of teachers' recognition of nutrition knowledge and nutrition education at day-care centers. Korean J Community Nutrition. 2005. 10(6):920–9.19.Dewar DL., Lubans DR., Plotnikoff RC., Morgan PJ. Development and evaluation of social cognitive measures related to adolescent dietary behaviors. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2012. 9:36.
Article20.Sin EY., Lee YK. Development and application of health belief model based nutrition education program for day care center children. Korean J Community Nutrition. 2006. 11(4):488–501.21.Lee JI. A comparative study of eating habit and nutritional knowledge for the effectiveness of nutrition education of pre-schoolers in child care centers [dissertation]. Seoul: Hanyang University;2008. Korean.22.Hong ME. Effect of a nutrition education program developed by a public health center on preschool children's nutritional knowledge and dietary habits and the parent's dietary attitudes [dissertation]. Daejeon: Chungbuk National University;2009. Korean.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of a Physical Activity Program based on Social Cognitive Theory for Old-Old Women with Knee Osteoarthritis
- Factors influencing on intention to intake fruit: moderating effect of fruit intake habit
- A Qualitative Study of the Awareness and Influencing Factors of the Dietary Habits of the Male and Female Workers' at a Manufacturing Facility in Gwangju
- Development of Nutrition Education Program for Consumers to Reduce Sodium Intake Applying the Social Cognitive Theory: Based on Focus Group Interviews
- Effects of a Moderate Drinking Program based on Social Cognitive Theory on College Students with Drinking Problems