Korean Circ J.
2008 Aug;38(8):411-418. 10.4070/kcj.2008.38.8.411.
Effect of Early Statin Therapy on Circulating Endothelial Progenitor Cells During the Acute Phase in Patients With Acute Myocardial Infarction
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Iksan, Korea. oskcar@wonkwang.ac.kr
- KMID: 2225761
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2008.38.8.411
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: The mobilization of circulating endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) might represent a useful strategy for the clinical therapy of ischemic heart disease. We examined the effect of early statin therapy before reperfusion therapy on the circulating EPCs during the acute phase in patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI).
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
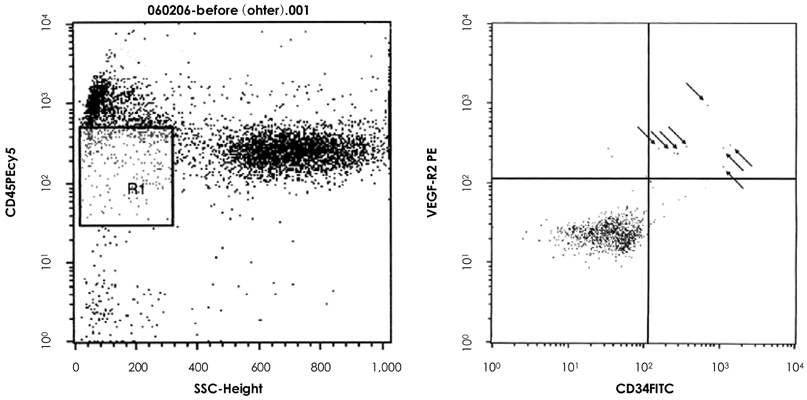
A total of 84 consecutive AMI patients undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) within 24 hours of pain onset were included in this study. We randomly divided the patients into 3 groups according to rosuvastatin therapy before PCI: the control group (n:27, 19 males and 8 females, 58+/-2 years of age), the rosuvastatin 10 mg group (n: 28, 21 males and 7 females, 58+/-3 years of age) and the 40 mg group (n: 29, 23 males and 6 females, 59+/-2 years of age). The circulating EPCs and high sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) levels were analyzed on admission and at 1, 3, 5, 7 and 30 days after PCI. The circulating EPCs were measured by flow cytometry as the CD45(low)CD34+VEGFR2+ cells.
RESULTS
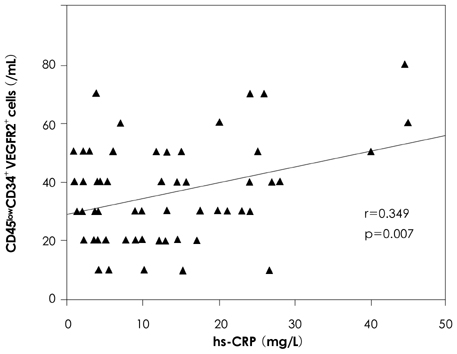
The circulating EPCs peaked on day 3 after PCI, whereas the increment of circulating EPCs was significantly suppressed in the rosuvastatin 10 mg and 40 mg groups compared with the control group on day 3 (control vs rosuvastatin 10 mg vs rosuvastatin 40 mg: 0.072% vs 0.067% vs 0.061%, respectively, p=0.002) and day 5 (0.068% vs 0.060% vs 0.058%, respectively, p=0.029). The level of hs-CRP markedly increased from day 1 and this peaked on day 3 after PCI. Early statin therapy significantly suppressed the elevation of hs-CRP compared with the control group on day 1 (24.36 mg/L vs 17.88 mg/L vs 13.08 mg/L, respectively, p=0.035) and on day 3 (30.15 mg/L vs 22.78 mg/L vs 17.16 mg/L, respectively, p=0.034). There was a statistically significant correlation between the circulating EPCs and the hs-CRP (r=0.349, p=0.007).
CONCLUSION
In the AMI patients, the early stain therapy before reperfusion therapy didn't increase the mobilization of circulating EPCs, but it suppressed the elevation of hs-CRP. This data suggests that the mobilization of circulating EPCs may be related to systemic inflammation during the acute phase in patients with AMI.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
C-Reactive Protein
Female
Flow Cytometry
Fluorobenzenes
Humans
Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA Reductase Inhibitors
Inflammation
Male
Myocardial Infarction
Myocardial Ischemia
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
Pyrimidines
Reperfusion
Stem Cells
Sulfonamides
Rosuvastatin Calcium
C-Reactive Protein
Fluorobenzenes
Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA Reductase Inhibitors
Pyrimidines
Sulfonamides
Figure
Reference
-
1. Asahara T, Murohara T, Sullivan A, et al. Isolation of putative progenitor endothelial cells for angiogenesis. Science. 1997. 275:964–967.2. Kondo T, Hayashi M, Takeshita K, et al. Smoking cessation rapidly increases circulating progenitor cell in peripheral blood in chronic smokers. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004. 24:1442–1447.3. Kim W, Jeong MH, Cho SH, et al. Effect of green tea consumption on endothelial function and circulating endothelial progenitor cells in chronic smokers. Circ J. 2006. 70:1052–1057.4. Shintani S, Murohara T, Ikeda H, et al. Mobilization of endothelial progenitor cells in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2001. 103:2776–2779.5. Lim DS. Stem cells for cardiovascular disease. Korean Circ J. 2004. 34:435–440.6. Choi JH, Kim DK. Therapeutic angiogenesis for cardiovascular diseases: the present and future. Korean Circ J. 2003. 33:739–745.7. Leonel AM, Rutella S, Bonanno G, et al. Mobilization of bone marrow-derived stem cells after myocardial infarction and left ventricular function. Eur Heart J. 2005. 26:1196–1204.8. Libby P, Aikawa M. Effects of statins in reducing thrombotic risk and modulating plaque vulnerability. Clin Cardiol. 2003. 26(1 Suppl 1):I11–I14.9. Ray KK, Cannon CP. Intensive statin therapy in acute coronary syndromes: clinical benefits and vascular biology. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2004. 15:637–643.10. Ray KK, Cannon CP. Early time to benefit with intensive statin treatment: could it be the pleiotropic effects? Am J Cardiol. 2005. 96:54F–60F.11. Dupuis J, Tardif JC, Cernacek P, Theroux P. Cholesterol reduction rapidly improves endothelial function after acute coronary syndromes. Circulation. 1999. 99:3227–3233.12. Strandberg TE, Vanhanen H, Tikkanen MJ. Effect of statins on C-reactive protein in patients with coronary artery disease. Lancet. 1999. 353:118–119.13. Vasa M, Fichtlscherer S, Adler K, et al. Increase in circulating endothelial progenitor cells by statin therapy in patients with stable coronary artery disease. Circulation. 2001. 103:2885–2890.14. George J, Shmilovich H, Deutsch V, Miller H, Keren G, Roth A. Comparative analysis of methods for assessment of circulating endothelial progenitor cells. Tissue Eng. 2006. 12:331–335.15. Massa M, Rosti V, Ferrario M, et al. Increased circulating hematopoietic and endothelial progenitor cells in the early phase of acute myocardial infarction. Blood. 2005. 105:199–206.16. George J, Goldstein E, Abashidze S, et al. Circulating endothelial progenitor cells in patients with unstable angina: association with systemic inflammation. Eur Heart J. 2004. 25:1003–1008.17. Dimmeler S, Aicher A, Vasa M, et al. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statin) increase endothelial progenitor cells via the PI 3-kinase/Akt pathway. J Clin Invest. 2001. 108:391–397.18. Landmesser U, Engberding N, Bahlmann FH, et al. Statin-induced improvement of endothelial progenitor cell mobilization, myocardial neovascularization, left ventricular function, and survival after experimental myocardial infarction requires endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Circulation. 2004. 110:1933–1939.19. Rupp S, Badorff C, Koyanagi M, et al. Statin therapy in patients with coronary artery disease improves the impaired endothelial progenitor cell differentiation into cardiomyogenic cells. Basic Res Cardiol. 2004. 99:61–68.20. Suh W, Kim KL, Choi JH, et al. C-reactive protein impairs angiogenic functions and decreases the secretion of arteriogenic chemo-cytokines in human endothelial progenitor cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004. 321:65–71.21. Laufs U, Werner N, Link A, et al. Physical training increases endothelial progenitor cells, inhibits neointima formation, and enhances angiogenesis. Circulation. 2004. 109:220–226.22. Guven H, Shepherd RM, Bach RG, Capoccia BJ, Link DC. The number of endothelial progenitor cell colonies in the blood is increased in patients with angiographically significant coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006. 48:1579–1587.23. Aicher A, Zeiher AM, Dimmer S. Mobilizing endothelial progenitor cells. Hypertension. 2005. 45:321–325.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Serum Myoglobin in the Early Phase of Acute Myocardial Infarction
- Clinical Benefit of Statins in Korean Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction: Experience of the Korea Acute Myocardial Infarction Registry
- Benefit of Early Statin Therapy in Acute Myocardial Infarction in Korea
- Primary Coronary Stenting as a Successful Treatment of Acute Myocardial
- Effects of Endothelial Progenitor Cells Used for Autograft Transplantation in Acute Myocardial Infarction Pig Model