Korean Circ J.
2014 Jul;44(4):250-254. 10.4070/kcj.2014.44.4.250.
Evaluation of the Temporal Association between Kawasaki Disease and Viral Infections in South Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Children's Hospital, Seoul, Korea. cielcel0@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Biostatistics, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Uijeongbu St. Mary's Hospital, Uijeongbu, Korea.
- 4Department of Pediatrics, Inje University Seoul Paik Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Pediatrics, Ewha Womans University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2223886
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2014.44.4.250
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES
This study is aimed at elucidating potential temporal associations between the occurrence of Kawasaki disease (KD) and various viral infections.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
We obtained monthly patterns of KD from the seventh nationwide survey and viral detection data from the Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention from 2009 to 2011 and evaluated temporal correlations between them for each month. The respiratory viruses detected using a multiplex real-time-polymerase chain reaction kit were influenza virus (A/H1N1, A/H3N2, A/H5N1, and B), adenovirus, parainfluenza virus (type 1, 2, 3), respiratory syncytial virus (type A, B), human rhinovirus, human coronavirus (OC43/229E, NL63), human bocavirus, and enterovirus.
RESULTS
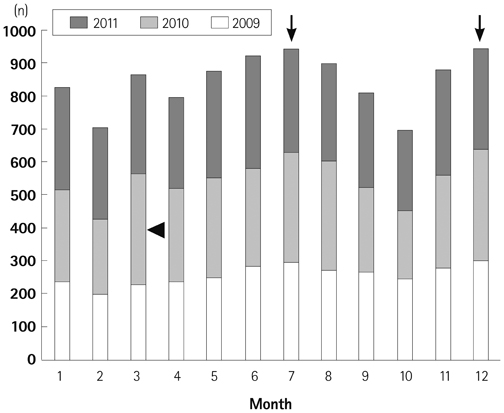
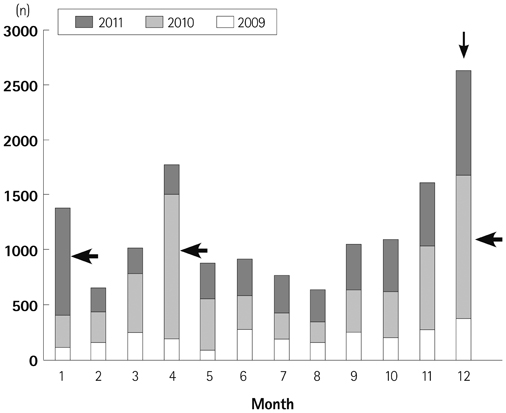
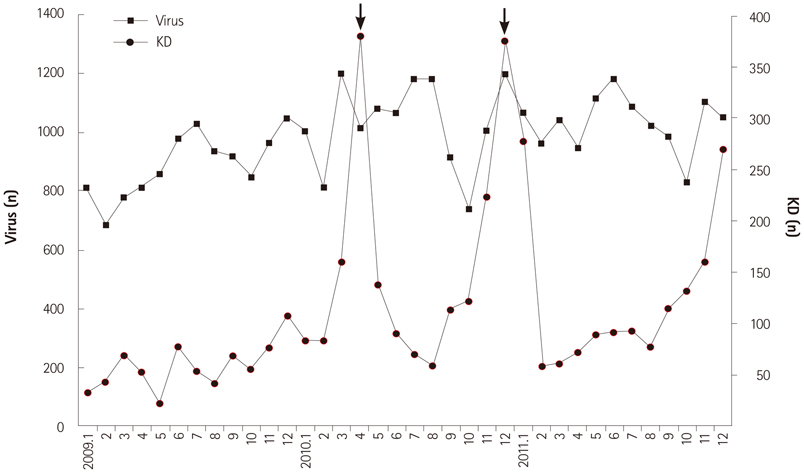
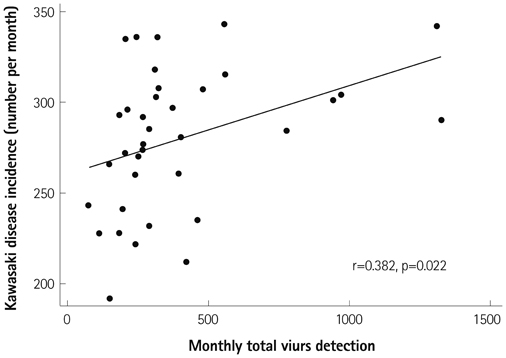
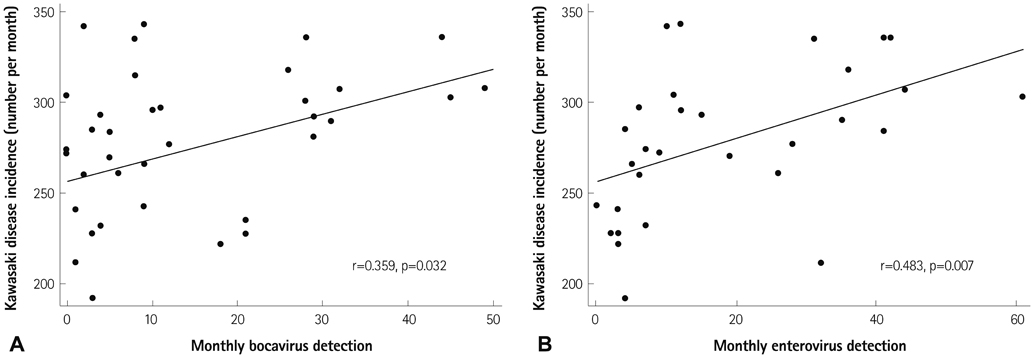
We obtained data from a total of 13031 patients who were treated for acute KD from 87 hospitals with pediatric residence programs. During this survey, KD showed highest overall incidence in summer and winter seasons and lowest incidence in February and October. We received viral detection data for a total of 14267 patients. Viral detection was highest during winter and spring seasons. The most commonly detected virus was human rhinovirus (32.6%), followed by influenza virus (26.8%). The monthly incidence of KD showed significant correlation with the monthly overall viral detection (p=0.022, r=0.382). In particular, human bocavirus and enterovirus have significant correlations with monthly patterns of KD occurrence (p=0.032 and p=0.007, respectively) and influenza virus correlated with KD occurrence with borderline significance (p=0.063).
CONCLUSION
The temporal association between monthly occurrence of KD and viral detection suggests the etiologic importance of precedent infection in the development of KD.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kawasaki T. [Acute febrile mucocutaneous syndrome with lymphoid involvement with specific desquamation of the fingers and toes in children]. Arerugi. 1967; 16:178–222.2. Wood LE, Tulloh RM. Kawasaki disease in children. Heart. 2009; 95:787–792.3. Newburger JW, Takahashi M, Gerber MA, et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: a statement for health professionals from the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, American Heart Association. Pediatrics. 2004; 114:1708–1733.4. Luca NJ, Yeung RS. Epidemiology and management of Kawasaki disease. Drugs. 2012; 72:1029–1038.5. Nakamura Y, Yashiro M, Uehara R, Oki I, Watanabe M, Yanagawa H. Monthly observation of the number of patients with Kawasaki disease and its incidence rates in Japan: chronological and geographical observation from nationwide surveys. J Epidemiol. 2008; 18:273–279.6. Park YW, Han JW, Hong YM, et al. Epidemiological features of Kawasaki disease in Korea, 2006-2008. Pediatr Int. 2011; 53:36–39.7. Burgner D, Harnden A. Kawasaki disease: what is the epidemiology telling us about the etiology? Int J Infect Dis. 2005; 9:185–194.8. Principi N, Rigante D, Esposito S. The role of infection in Kawasaki syndrome. J Infect. 2013; 67:1–10.9. Esper F, Shapiro ED, Weibel C, Ferguson D, Landry ML, Kahn JS. Association between a novel human coronavirus and Kawasaki disease. J Infect Dis. 2005; 191:499–502.10. Catalano-Pons C, Giraud C, Rozenberg F, Meritet JF, Lebon P, Gendrel D. Detection of human bocavirus in children with Kawasaki disease. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2007; 13:1220–1222.11. Rigante D, Cantarini L, Piastra M, et al. Kawasaki syndrome and concurrent Coxsackie virus B3 infection. Rheumatol Int. 2012; 32:4037–4040.12. Cheong HM. The prevalence of the respiratory viruses in the patients with acute respiratory infections, 2012. Public Health Weekly Report. Cheongju: KCDC;2013. Vol 6:p. 589–594.13. Kim GB, Han JW, Park YW, et al. Epidemiologic features of Kawasaki disease in South Korea: data from nationwide survey, 2009-2011. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2014; 33:24–27.14. Takahashi K, Oharaseki T, Yokouchi Y. Pathogenesis of Kawasaki disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 2011; 164:Suppl 1. 20–22.15. Santos RA, Nogueira CS, Granja S, Baptista JB, Ribeiro ML, Rocha MG. Kawasaki disease and human bocavirus--potential association? J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2011; 44:235–237.16. Chang LY, Lu CY, Shao PL, et al. Viral infections associated with Kawasaki disease. J Formos Med Assoc. 2014; 113:148–154.17. Jordan-Villegas A, Chang ML, Ramilo O, Mejías A. Concomitant respiratory viral infections in children with Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2010; 29:770–772.18. Cho EY, Eun BW, Kim NH, et al. Association between Kawasaki disease and acute respiratory viral infections. Korean J Pediatr. 2009; 52:1241–1248.19. Kim JH, Yu JJ, Lee J, et al. Detection rate and clinical impact of respiratory viruses in children with Kawasaki disease. Korean J Pediatr. 2012; 55:470–473.20. Nakamura Y, Yashiro M, Uehara R, et al. Epidemiologic features of Kawasaki disease in Japan: results of the 2009-2010 nationwide survey. J Epidemiol. 2012; 22:216–221.21. Rodó X, Ballester J, Cayan D, et al. Association of Kawasaki disease with tropospheric wind patterns. Sci Rep. 2011; 1:152.22. Frazer J. Infectious disease: Blowing in the wind. Nature. 2012; 484:21–23.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Research trends on causes of Kawasaki disease in the COVID-19 era: focus on viral infections
- Study of Epstein Barr Virus Antibodies in Patients with Kawasaki Disease
- Kawasaki Disease
- Clinical usefulness of serum procalcitonin level in distinguishing between Kawasaki disease and other infections in febrile children
- Viral Hepatitis in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease