Korean Circ J.
2014 Sep;44(5):301-306. 10.4070/kcj.2014.44.5.301.
Effect of High Dose Rosuvastatin Loading before Percutaneous Coronary Intervention on Contrast-Induced Nephropathy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, Regional Cardiocerebrovascular Center, Wonkwang University Hospital, Iksan, Korea. dryunkh@gmail.com
- KMID: 2223868
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2014.44.5.301
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES
Contrast-induced nephropathy (CIN) is associated with increased morbidity and mortality. This observational, non-randomized study evaluated the effect of rosuvastatin loading before percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) on the incidence of CIN in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS).
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
A total of 824 patients who underwent PCI for ACS were studied (408 patients in the statin group=40 mg rosuvastatin loading before PCI; 416 patients of control group=no statin pretreatment). Serum creatinine concentrations were measured before and 24 and 48 hours after PCI. The primary endpoint was development of CIN defined as an increase in serum creatinine concentration of > or =0.5 mg/dL or > or =25% above baseline within 72 hours after PCI.
RESULTS
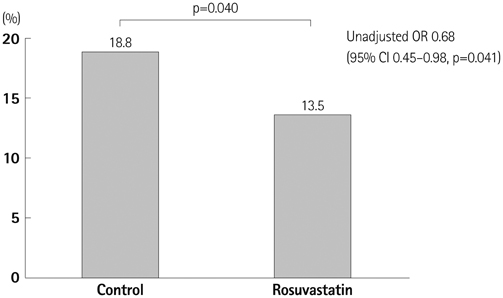
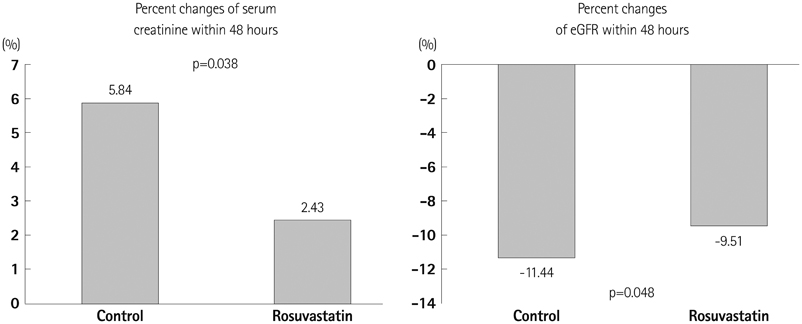
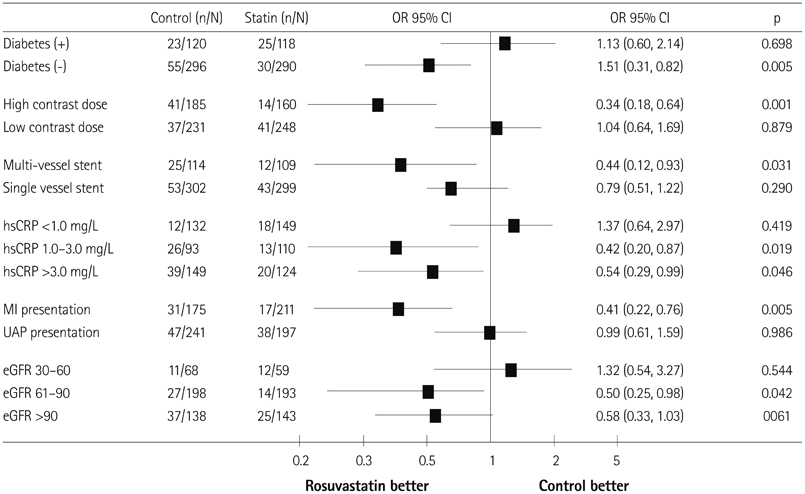
The incidence of CIN was significantly lower in the statin group than that in the control group (18.8% vs. 13.5%, p=0.040). The maximum percent changes in serum creatinine and estimated glomerular filtration rate in the statin group within 48 hours were significantly lower than those in the control group (5.84+/-22.59% vs. 2.43+/-24.49%, p=0.038; -11.44+/-14.00 vs. -9.51+/-13.89, p=0.048, respectively). The effect of rosuvastatin on preventing CIN was greater in the subgroups of patients with diabetes, high-dose contrast medium, multivessel stents, high baseline C-reactive protein, and myocardial infarction. A multivariate analysis revealed that rosuvastatin loading was independently associated with a decreased risk for CIN (odds ratio, 0.64; 95% confidence interval, 0.43-0.95, p=0.026).
CONCLUSION
High-dose rosuvastatin loading before PCI was associated with a significantly lower incidence of CIN in patients with ACS.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Acute Coronary Syndrome
C-Reactive Protein
Contrast Media
Creatinine
Glomerular Filtration Rate
Humans
Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA Reductase Inhibitors
Incidence
Kidney
Mortality
Multivariate Analysis
Myocardial Infarction
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention*
Stents
Rosuvastatin Calcium
C-Reactive Protein
Contrast Media
Creatinine
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Iso-osmolar Iodixanol Is Better than Low-osmolar Contrast for CIN Prevention. And Then?
Sang-Ho Jo
Korean Circ J. 2021;51(2):182-184. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2021.0003.Contrast-induced Acute Kidney Injury and Inflammation
Kyeong Ho Yun
Korean Circ J. 2018;48(1):84-85. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2017.0357.
Reference
-
1. McCullough PA. Contrast-induced acute kidney injury. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008; 51:1419–1428.2. Giusti-Paiva A, Martinez MR, Felix JV, et al. Simvastatin decreases nitric oxide overproduction and reverts the impaired vascular responsiveness induced by endotoxic shock in rats. Shock. 2004; 21:271–275.3. Wong PC, Li Z, Guo J, Zhang A. Pathophysiology of contrast-induced nephropathy. Int J Cardiol. 2012; 158:186–192.4. Jo SH, Koo BK, Park JS, et al. Prevention of radiocontrast medium-induced nephropathy using short-term high-dose simvastatin in patients with renal insufficiency undergoing coronary angiography (PROMISS) trial--a randomized controlled study. Am Heart J. 2008; 155:499.e1–499.e8.5. Levey AS, Coresh J, Balk E, et al. National Kidney Foundation practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Ann Intern Med. 2003; 139:137–147.6. Budano C, Levis M, D'Amico M, et al. Impact of contrast-induced acute kidney injury definition on clinical outcomes. Am Heart J. 2011; 161:963–971.7. Dangas G, Iakovou I, Nikolsky E, et al. Contrast-induced nephropathy after percutaneous coronary interventions in relation to chronic kidney disease and hemodynamic variables. Am J Cardiol. 2005; 95:13–19.8. Takemoto M, Liao JK. Pleiotropic effects of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme a reductase inhibitors. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2001; 21:1712–1719.9. Sposito AC, Chapman MJ. Statin therapy in acute coronary syndromes: mechanistic insight into clinical benefit. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2002; 22:1524–1534.10. Pappy R, Stavrakis S, Hennebry TA, Abu-Fadel MS. Effect of statin therapy on contrast-induced nephropathy after coronary angiography: a meta-analysis. Int J Cardiol. 2011; 151:348–353.11. Toso A, Maioli M, Leoncini M, et al. Usefulness of atorvastatin (80 mg) in prevention of contrast-induced nephropathy in patients with chronic renal disease. Am J Cardiol. 2010; 105:288–292.12. Xinwei J, Xianghua F, Jing Z, et al. Comparison of usefulness of simvastatin 20 mg versus 80 mg in preventing contrast-induced nephropathy in patients with acute coronary syndrome undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. Am J Cardiol. 2009; 104:519–524.13. Quintavalle C, Fiore D, De Micco F, et al. Impact of a high loading dose of atorvastatin on contrast-induced acute kidney injury. Circulation. 2012; 126:3008–3016.14. Leoncini M, Toso A, Maioli M, Tropeano F, Villani S, Bellandi F. Early high-dose rosuvastatin for contrast-induced nephropathy prevention in acute coronary syndrome: results from the PRATO-ACS Study (Protective Effect of Rosuvastatin and Antiplatelet Therapy On contrast-induced acute kidney injury and myocardial damage in patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014; 63:71–79.15. Han Y, Zhu G, Han L, et al. Short-term rosuvastatin therapy for prevention of contrast-induced acute kidney injury in patients with diabetes and chronic kidney disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014; 63:62–70.16. Liuni A, Luca MC, Gori T, Parker JD. Rosuvastatin prevents conduit artery endothelial dysfunction induced by ischemia and reperfusion by a cyclooxygenase-2-dependent mechanism. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010; 55:1002–1006.17. Yun KH, Jeong MH, Oh SK, et al. The beneficial effect of high loading dose of rosuvastatin before percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Int J Cardiol. 2009; 137:246–251.18. Yun KH, Oh SK, Rhee SJ, Yoo NJ, Kim NH, Jeong JW. 12-month follow-up results of high dose rosuvastatin loading before percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Int J Cardiol. 2011; 146:68–72.19. Kim JW, Yun KH, Kim EK, et al. Effect of high dose rosuvastatin loading before primary percutaneous coronary intervention on infarct size in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Korean Circ J. 2014; 44:76–81.20. Ridker PM, MacFadyen J, Cressman M, Glynn RJ. Efficacy of rosuvastatin among men and women with moderate chronic kidney disease and elevated high-sensitivity C-reactive protein: a secondary analysis from the JUPITER (Justification for the Use of Statins in Prevention-an Intervention Trial Evaluating Rosuvastatin) trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010; 55:1266–1273.21. Vidt DG, Harris S, McTaggart F, Ditmarsch M, Sager PT, Sorof JM. Effect of short-term rosuvastatin treatment on estimated glomerular filtration rate. Am J Cardiol. 2006; 97:1602–1606.22. Agarwal R. Statin induced proteinuria: renal injury or renoprotection? J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004; 15:2502–2503.23. Gotoh K, Masaki T, Chiba S, et al. Effects of hydrophilic statins on renal tubular lipid accumulation in diet-induced obese mice. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2013; 7:e342–e352.24. Yun KH, Shin IS, Shin SN, et al. Effect of previous statin therapy in patients with acute coronary syndrome and percutaneous coronary intervention. Korean Circ J. 2011; 41:458–463.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of High Dose Rosuvastatin Loading before Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention on Infarct Size in Patients with ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction
- Determination of Safe Contrast Media Dosage to Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate Ratios to Avoid Contrast-Induced Nephropathy After Elective Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
- Multiple Markers of Contrast Induced Nephropathy after the Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
- Successful Treatment of Unprotected Left Main Coronary Bifurcation Lesion Using Minimum Contrast Volume with Intravascular Ultrasound Guidance
- Erratum to: Effect of High Dose Rosuvastatin Loading before Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention on Infarct Size in Patients with ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction