Korean Circ J.
2014 Mar;44(2):76-81. 10.4070/kcj.2014.44.2.76.
Effect of High Dose Rosuvastatin Loading before Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention on Infarct Size in Patients with ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, Regional Cardiocerebrovascular Center, Wonkwang University Hospital, Iksan, Korea. dryunkh@gmail.com
- KMID: 2223895
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2014.44.2.76
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES
High dose rosuvastatin loading before percutaneous coronary interventions (PCI) reduces the myocardial damage and the incidence of adverse cardiac events in patients with stable angina and acute coronary syndrome. However, no studies are present yet about rosuvastatin loading in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) in a primary PCI setting.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
A total of 475 patients who underwent primary PCI for STEMI were studied. The study population was divided into two groups with 208 patients in the statin group=40 mg rosuvastatin loading before primary PCI and 267 patients in the control group=no statin pretreatment. At median 3 days after PCI a single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) was performed with technetium 99m tetrofosmin For this study were compared infarct size, corrected Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) frame count and the myocardial blush grade (MBG) between the both groups.
RESULTS
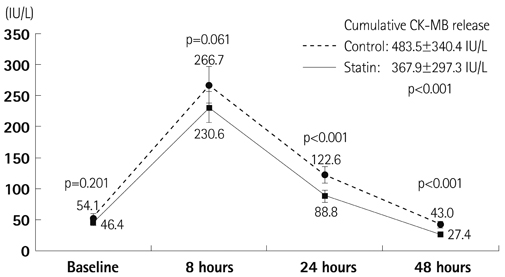
Baseline clinical and procedural characteristics were similar between the groups. Infarct size, as assessed by SPECT, was significantly smaller (19.0+/-15.9% vs. 22.9+/-16.5%, p=0.009) in the statin group than in the control group. Patients of the statin group showed a lower corrected TIMI frame count (28.2+/-19.3 vs. 32.6+/-21.4, p=0.020), and higher MBG (2.49+/-0.76 vs. 2.23+/-0.96, p=0.001) than the patients of the control group. The multivariate analysis revealed that rosuvastatin loading {odds ratio (OR) 0.61}, pain to balloon time (OR 2.05), anterior myocardial infarction (OR 3.89) and final the MBG (OR 2.93) were independent predictors of a large infarct size.
CONCLUSION
A high dose rosuvastatin loading before the primary PCI reduced the infarct size by microvascular myocardial perfusion improvement.
MeSH Terms
-
Acute Coronary Syndrome
Angina, Stable
Angioplasty
Humans
Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA Reductase Inhibitors
Incidence
Multivariate Analysis
Myocardial Infarction*
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention*
Perfusion
Stents
Technetium
Tomography, Emission-Computed, Single-Photon
Rosuvastatin Calcium
Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA Reductase Inhibitors
Technetium
Figure
Reference
-
1. Randomised trial of cholesterol lowering in 4444 patients with coronary heart disease: the Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study (4S). Lancet. 1994; 344:1383–1389.2. Shepherd J, Cobbe SM, Ford I, et al. Prevention of coronary heart disease with pravastatin in men with hypercholesterolemia. West of Scotland Coronary Prevention Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1995; 333:1301–1307.3. Sacks FM, Pfeffer MA, Moye LA, et al. The effect of pravastatin on coronary events after myocardial infarction in patients with average cholesterol levels. Cholesterol and Recurrent Events Trial investigators. N Engl J Med. 1996; 335:1001–1009.4. Hong YJ, Jeong MH, Lim JH, et al. The prognostic significance of statin therapy according to the level of C-reactive protein in acute myocardial infarction patients who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention. Korean Circ J. 2003; 33:891–900.5. Ridker PM, Danielson E, Fonseca FA, et al. Reduction in C-reactive protein and LDL cholesterol and cardiovascular event rates after initiation of rosuvastatin: a prospective study of the JUPITER trial. Lancet. 2009; 373:1175–1182.6. Patti G, Pasceri V, Colonna G, et al. Atorvastatin pretreatment improves outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndromes undergoing early percutaneous coronary intervention: results of the ARMYDA-ACS randomized trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007; 49:1272–1278.7. Yun KH, Jeong MH, Oh SK, et al. The beneficial effect of high loading dose of rosuvastatin before percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Int J Cardiol. 2009; 137:246–251.8. Briguori C, Visconti G, Focaccio A, et al. Novel approaches for preventing or limiting events (Naples) II trial: impact of a single high loading dose of atorvastatin on periprocedural myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009; 54:2157–2163.9. Yun KH, Oh SK, Rhee SJ, Yoo NJ, Kim NH, Jeong JW. 12-month follow-up results of high dose rosuvastatin loading before percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Int J Cardiol. 2011; 146:68–72.10. Di Sciascio G, Patti G, Pasceri V, Gaspardone A, Colonna G, Montinaro A. Efficacy of atorvastatin reload in patients on chronic statin therapy undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: results of the ARMYDA-RECAPTURE (Atorvastatin for Reduction of Myocardial Damage During Angioplasty) Randomized Trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009; 54:558–565.11. Kim JS, Kim J, Choi D, et al. Efficacy of high-dose atorvastatin loading before primary percutaneous coronary intervention in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: the STATIN STEMI trial. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2010; 3:332–339.12. van 't Hof AW, Liem A, Suryapranata H, Hoorntje JC, de Boer MJ, Zijlstra F. Zwolle Myocardial Infarction Study Group. Angiographic assessment of myocardial reperfusion in patients treated with primary angioplasty for acute myocardial infarction: myocardial blush grade. Circulation. 1998; 97:2302–2306.13. Gibson CM, Cannon CP, Daley WL, et al. TIMI frame count: a quantitative method of assessing coronary artery flow. Circulation. 1996; 93:879–888.14. Lev EI, Kornowski R, Vaknin-Assa H, et al. Effect of previous treatment with statins on outcome of patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction treated with primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Am J Cardiol. 2009; 103:165–169.15. Yun KH, Shin IS, Shin SN, et al. Effect of previous statin therapy in patients with acute coronary syndrome and percutaneous coronary intervention. Korean Circ J. 2011; 41:458–463.16. Hahn JY, Kim HJ, Choi YJ, et al. Effects of atorvastatin pretreatment on infarct size in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Am Heart J. 2011; 162:1026–1033.17. Liu HL, Yang Y, Yang SL, et al. Administration of a loading dose of atorvastatin before percutaneous coronary intervention prevents inflammation and reduces myocardial injury in STEMI patients: a randomized clinical study. Clin Ther. 2013; 35:261–272.18. Sposito AC, Chapman MJ. Statin therapy in acute coronary syndromes: mechanistic insight into clinical benefit. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2002; 22:1524–1534.19. Lee CW, Park CS, Hwang I, et al. Expression of HMG-CoA reductase in human coronary atherosclerotic plaques and relationship to plaque destabilisation. Heart. 2011; 97:715–720.20. McTaggart F. Comparative pharmacology of rosuvastatin. Atheroscler Suppl. 2003; 4:9–14.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Erratum to: Effect of High Dose Rosuvastatin Loading before Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention on Infarct Size in Patients with ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction
- Current Status of Coronary Intervention in Patients with ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction and Multivessel Coronary Artery Disease
- Comparison of the Infarct Size between the Loading of Ticagrelor and Clopidogrel in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction Undergoing Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
- Effects of Remote Ischemic Conditioning on Late Infarct Size and Left Ventricular Function in Patients with ST-segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction
- Effects of High-dose Atorvastatin Pretreatment in Patients with ST-segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction Undergoing Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: A Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Study