Korean Circ J.
2015 Jan;45(1):77-80. 10.4070/kcj.2015.45.1.77.
Aggravation of Hepatopulmonary Syndrome after Sildenafil Treatment in a Patient with Coexisting Portopulmonary Hypertension
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Heart, Vascular and Stroke Institute, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. dukkyung.kim@samsung.com
- 2Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2223850
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2015.45.1.77
Abstract
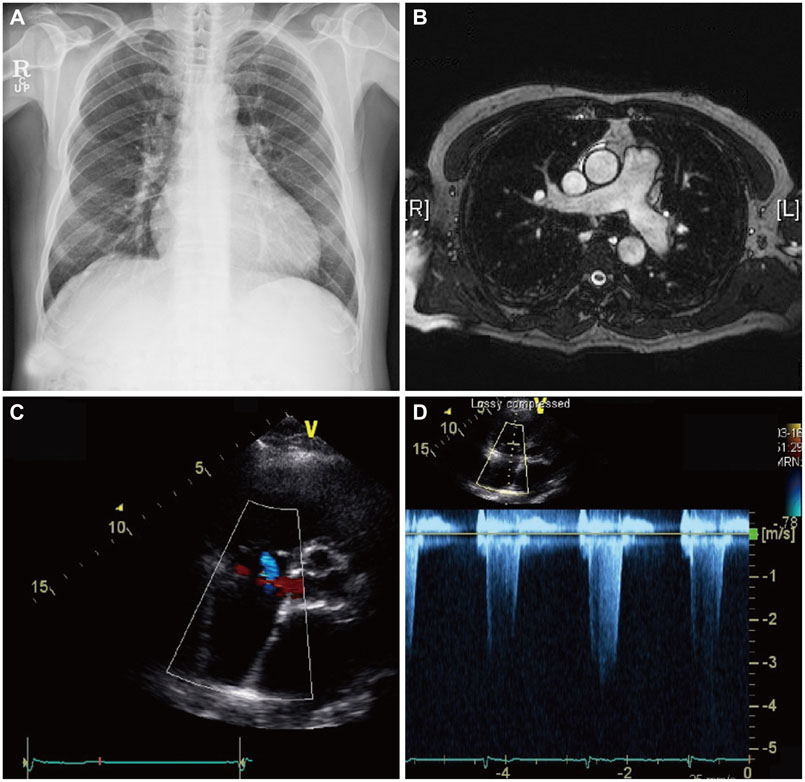
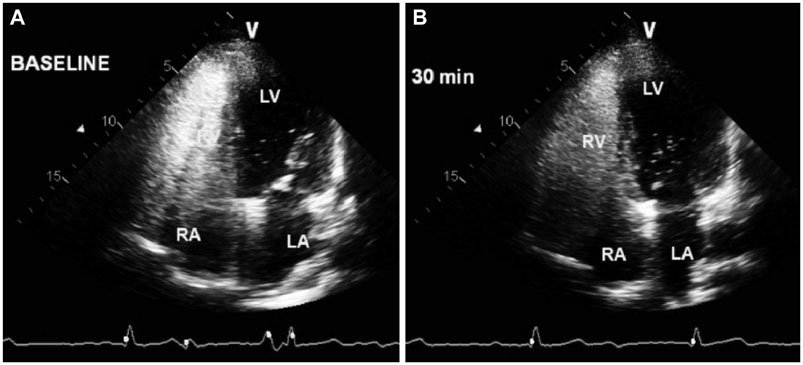
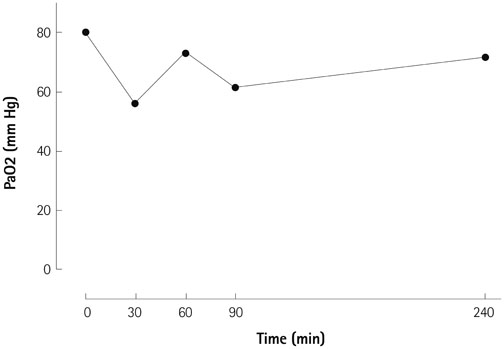
- Hepatopulmonary syndrome (HPS) and portopulmonary hypertension (PPHTN) are complications of portal hypertension and cirrhosis. Their pathophysiological mechanisms clearly differ. HPS is characterized by a defect in arterial oxygenation induced by pulmonary vascular dilatation. In contrast, PPHTN is predominantly due to excessive pulmonary vasoconstriction and vascular remodeling, but is rarely associated with hypoxia. We report a case of a patient who had both HPS and PPHTN at the time of presentation. HPS was aggravated after sildenafil administration for the treatment of PPHTN. We demonstrated increased amount of intrapulmonay shunt after sildenafil challenge by using agitated saline contrast transthoracic echocardiography.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hoeper MM, Krowka MJ, Strassburg CP. Portopulmonary hypertension and hepatopulmonary syndrome. Lancet. 2004; 363:1461–1468.2. Rodríguez-Roisin R, Krowka MJ. Hepatopulmonary syndrome--a liver-induced lung vascular disorder. N Engl J Med. 2008; 358:2378–2387.3. Rodríguez-Roisin R, Krowka MJ, Hervé P, et al. Pulmonary-Hepatic vascular Disorders (PHD). Eur Respir J. 2004; 24:861–880.4. Pham DM, Subramanian R, Parekh S. Coexisting hepatopulmonary syndrome and portopulmonary hypertension: implications for liver transplantation. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2010; 44:e136–e140.5. Zopey R, Susanto I, Barjaktarevic I, Wang T. Transition from hepatopulmonary syndrome to portopulmonary hypertension: a case series of 3 patients. Case Rep Pulmonol. 2013; 2013:561870.6. Schwartz BG, Levine LA, Comstock G, Stecher VJ, Kloner RA. Cardiac uses of phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012; 59:9–15.7. Reichenberger F, Voswinckel R, Steveling E, et al. Sildenafil treatment for portopulmonary hypertension. Eur Respir J. 2006; 28:563–567.8. Gough MS, White RJ. Sildenafil therapy is associated with improved hemodynamics in liver transplantation candidates with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Liver Transpl. 2009; 15:30–36.9. Kleinsasser A, Loeckinger A, Hoermann C, et al. Sildenafil modulates hemodynamics and pulmonary gas exchange. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001; 163:339–343.10. Castro PF, Greig D, Verdejo HE, et al. Intrapulmonary shunting associated with sildenafil treatment in a patient with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Thorax. 2011; 66:1097–1098.11. Olschewski H, Rose F, Schermuly R, et al. Prostacyclin and its analogues in the treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Pharmacol Ther. 2004; 102:139–153.12. Shao D, Park JE, Wort SJ. The role of endothelin-1 in the pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Pharmacol Res. 2011; 63:504–511.13. Ling Y, Zhang J, Luo B, et al. The role of endothelin-1 and the endothelin B receptor in the pathogenesis of hepatopulmonary syndrome in the rat. Hepatology. 2004; 39:1593–1602.14. Zhang J, Ling Y, Tang L, Luo B, Pollock DM, Fallon MB. Attenuation of experimental hepatopulmonary syndrome in endothelin B receptor-deficient rats. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009; 296:G704–G708.15. Fallon MB. Mechanisms of pulmonary vascular complications of liver disease: hepatopulmonary syndrome. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2005; 39(4):Suppl 2. S138–S142.16. Gudavalli A, Kalaria VG, Chen X, Schwarz KQ. Intrapulmonary arteriovenous shunt: diagnosis by saline contrast bubbles in the pulmonary veins. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2002; 15:1012–1014.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Portopulmonary hypertension in pregnancy: Treatment with sildenafil
- Pulmonary Complications in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis
- What do we take consideration in the patient who has an unpredicted severe portopulmonary hypertension in liver transplantation?: a case report
- The Hepatopulmonary Syndrome
- Perioperative Combined Use of Sildenafil and Inhaled Iloprost for Moderate Portopulmonary Hypertension in a Patient Undergoing Liver Transplantation: A case report