J Rhinol.
2015 Nov;22(2):69-74. 10.18787/jr.2015.22.2.69.
Sublingual Immunotherapy in Asian Children: 2-Year Follow-Up Results
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. lhman@korea.ac.kr
- 2Department of Biomedical Science, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Institute for Medical Devices Clinical Trial Center, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2223200
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.18787/jr.2015.22.2.69
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
S: House-dust mites are the main cause of allergic rhinitis in Asia, for which immunotherapy (SLIT) is a currently accepted treatment. However, few studies have evaluated the efficiency of SLIT on Asian children with allergic rhinitis for a period longer than one year. The aim of this study was to investigate the efficacy and safety of SLIT for Asian children with allergic rhinitis due to house-dust mites over a 2-year period.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This study included 65 patients who had allergic rhinitis due to Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus and Dermatophagoides farinae. All patients were treated with SLIT (Staloral(R)). Symptom scores and quality of life were evaluated by using questionnaires over two years. The medication score was assessed monthly by a diary medication card and serologic tests were evaluated before and two years after the start of treatment. Adverse effects and dropout rates were also investigated.
RESULTS
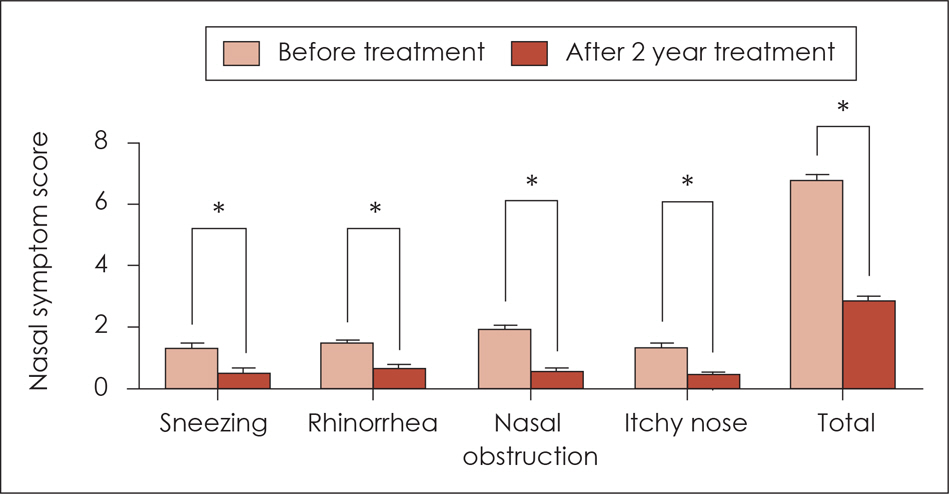
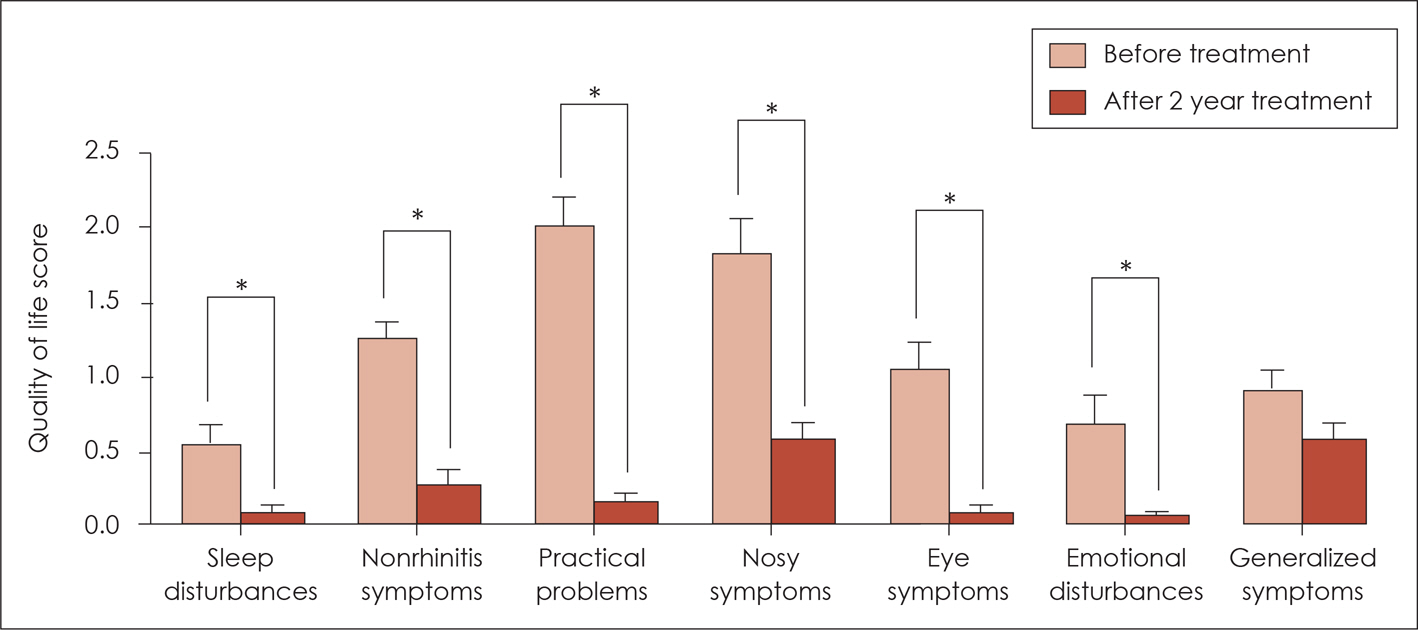
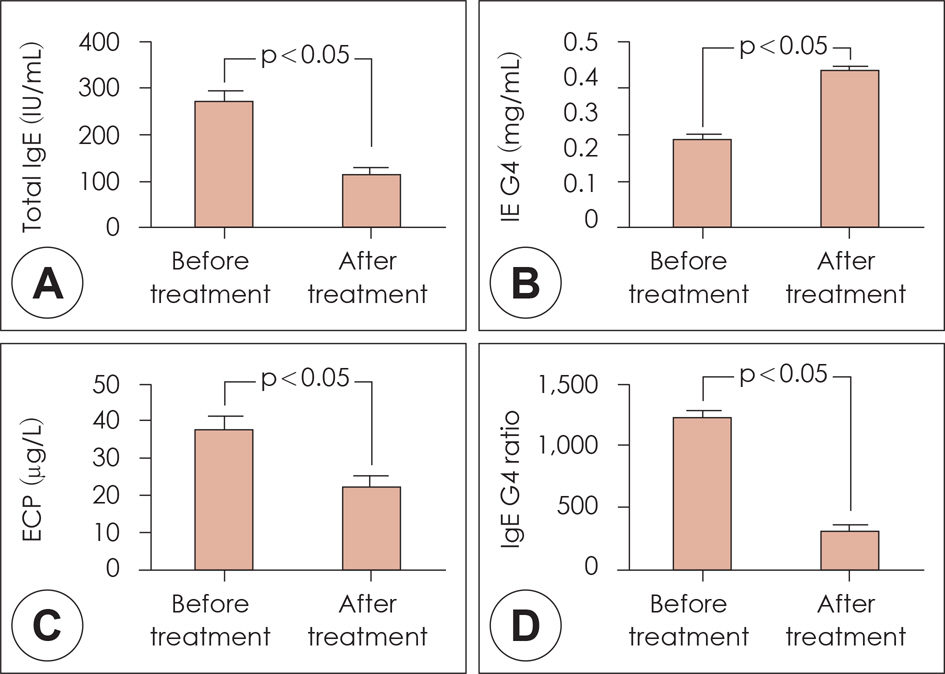
All nasal and non-nasal symptoms and quality of life were significantly improved after two years of treatment. Furthermore, the total medication score decreased significantly and the serologic tests showed a significant change two years after the start of SLIT. Although minor adverse effects were reported, no systemic reactions were observed. The dropout rate was 40%.
CONCLUSION
SLIT is an efficient and safe therapeutic tool for a period of two years in Asian children with allergic rhinitis to house-dust mites.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1). Cho YS, Choi SH, Park KH, Park HJ, Kim JW, Moon IJ, et al. Prevalence of otolaryngologic diseases in South Korea: data from the Korea national health and nutrition examination survey 2008. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2010; 3(4):183–93.
Article2). Zhang YM, Zhang J, Liu SL, Zhang X, Yang SN, Gao J, et al. Prevalence and Associated Risk Factors of Allergic Rhinitis in Preschool Children in Beijing. Laryngoscope. 2013; 123:28–35.
Article3). Pawankar R, Bunnag C, Khaltaev N, Bousquet J. Allergic Rhinitis and Its Impact on Asthma in Asia Pacific and the ARIA Update 2008. The WAO Journal. 2012; 5(Suppl 3):s212–7.
Article4). Kim SY, Yoon SJ, Jo MW, Kim EJ, Kim HJ, Oh IH. Economic burden of allergic rhinitis in Korea. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2010; 24(5):e110–3.
Article5). Piconi S, Trabattoni D, Rainone V, Borgonovo L, Passerini S, Rizzardini G, et al. Immunological effects of sublingual immunotherapy: clinical efficacy is associated with modulation of programmed cell death ligand 1, IL-10, and IgG4. J Immunol. 2010; 185(12):7723–30.
Article6). Park IH, Hong SM, Lee HM. Efficacy and safety of sublingual immunotherapy in Asian children. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2012; 76:1761–6.
Article7). Gidaro GB, Marcucci F, Sensi L, Incorvaia C, Frati F, Ciprandi G. The safety of sublingual-swallow immunotherapy: an analysis of published studies. Clin Exp Allergy. 2005; 35:565–71.8). Baba K, Konno A, Takenaka H. Practical Guideline for the Management of Allergic Rhinitis in Japan Perennial Rhinitis and Pollinosis. Life Science 2009 (6th).9). Novembre E, Galli E, Landi F, Caffarelli C, Pifferi M, De Marco E, et al. Coseasonal sublingual immunotherapy reduces the development of asthma in children with allergic rhinoconjunctivitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 114(4):851–7.
Article10). Ott H, Sieber J, Brehler R, Folster-Holst R, Kapp A, Klimek L, et al. Efficacy of grass pollen sublingual immunotherapy for three consecutive seasons and after cessation of treatment: the ECRIT study. Allergy. 2009; 64(1):179–86.
Article11). Wilson DR, Lima MT, Durham SR. Sublingual immunotherapy for allergic rhinitis: systematic review and metaanalysis. Allergy. 2005; 60(1):4–12.
Article12). Bousquet J, Van Cauwenberge P, Khaltaev N. Allergic rhinitis and its impact on asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001; 108(5 Suppl):s147–334.
Article13). Novak N, Bieber T, Allam JP. Immunological mechanisms of sublingual allergen-specific immunotherapy. Allergy. 2011; 66(6):733–9.
Article14). Passalacqua G, Compalati E, Canonica GW. Sublingual immunotherapy for allergic rhinitis: an update. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2011; 19(1):43–7.
Article15). Toskala E. A contemporary review of sublingual immunotherapy. Laryngoscope. 2009; 119(11):2178–81.
Article16). Warner JO. Low dose sublingual therapy in patients with allergic rhinitis due to house dust mite. Clin Allergy. 1986; 16(5):387–8.
Article17). Incorvaia C, Masieri S, Berto P, Scurati S, Frati F. Specific immunotherapy by the sublingual route for respiratory allergy. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2010; 6(1):29.
Article18). Ciprandi G, Cadario G, Valle C, Ridolo E, Verini M, Di Gioacchi-no M, et al. Sublingual immunotherapy in polysensitized patients: effect on quality of life. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2010; 20(4):274–9.19). Vita D, Caminiti L, Ruggeri P, Pajno GB. Sublingual immunotherapy: adherence based on timing and monitoring control visits. Allergy. 2010; 65:668–9.
Article20). Pajno GB, Vita D, Caminiti L, Arrigo T, Lombardo F, Incorvaia C, et al. Children's compliance with allergen immunotherapy according to administration routes. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005; 116:1380–1.
Article21). Giannarini L, Maggi E. Decrease of allergen-specific T-cell response induced by local nasal immunotherapy. Clin Exp Allergy. 1998; 28:404–12.
Article22). Alberse R.C. Van der Gaag R, Van Leeuwen J. Serologic aspects of IgG4 antibodies. I. Prolonged immunization results in an IgG4-re-stricted response. J Immunol. 1983; 130:722–6.23). Kim ST, Han DH, Moon IJ, Lee CH, Min YG, Rhee CS. Clinical and immunologic effects of sublingual immunotherapy on patients with allergic rhinitis to house-dust mites: 1-year follow-up results. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2010; 24:271–5.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Gum pigmentation: an unusual adverse effect of sublingual immunotherapy
- A practical view of immunotherapy for food allergy
- Nondaily dosing schedule of allergen-specific sublingual immunotherapy: efficacy and safety
- Sublingual immunotherapy for allergic rhinitis
- Outcome of Sublingual Immunotherapy in Patients With Allergic Rhinitis Sensitive to House Dust Mites