J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2014 May;55(5):640-645. 10.3341/jkos.2014.55.5.640.
Reconstruction of Orbital Medial Wall Fracture with Absorbable and Non-Absorbable Orbital Implant: Comparative Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Kim's Eye Hospital, Konyang University College of Medicine, Myung-Gok Eye Research Institute, Seoul, Korea. hs0903@kimeye.com
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2218083
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2014.55.5.640
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To compare the surgical results and complications of medial wall fracture reconstruction using non-absorbable porous polyethylene implants (Medpor(R), Stryker Instruments, Kalamazoo, Michigan, USA) and an absorbable polymer of polyglycolic acid (PGA) and polylactic acid (PLA) (Mesh plate(R), Inion Ltd, Tampere, Finland).
METHODS
We retrospectively reviewed the data of patients who underwent reconstruction of medial wall fracture between January 2007 and June 2012 and divided them into 2 groups according to orbital implant type (Medpor(R), Mesh plate(R)).
RESULTS
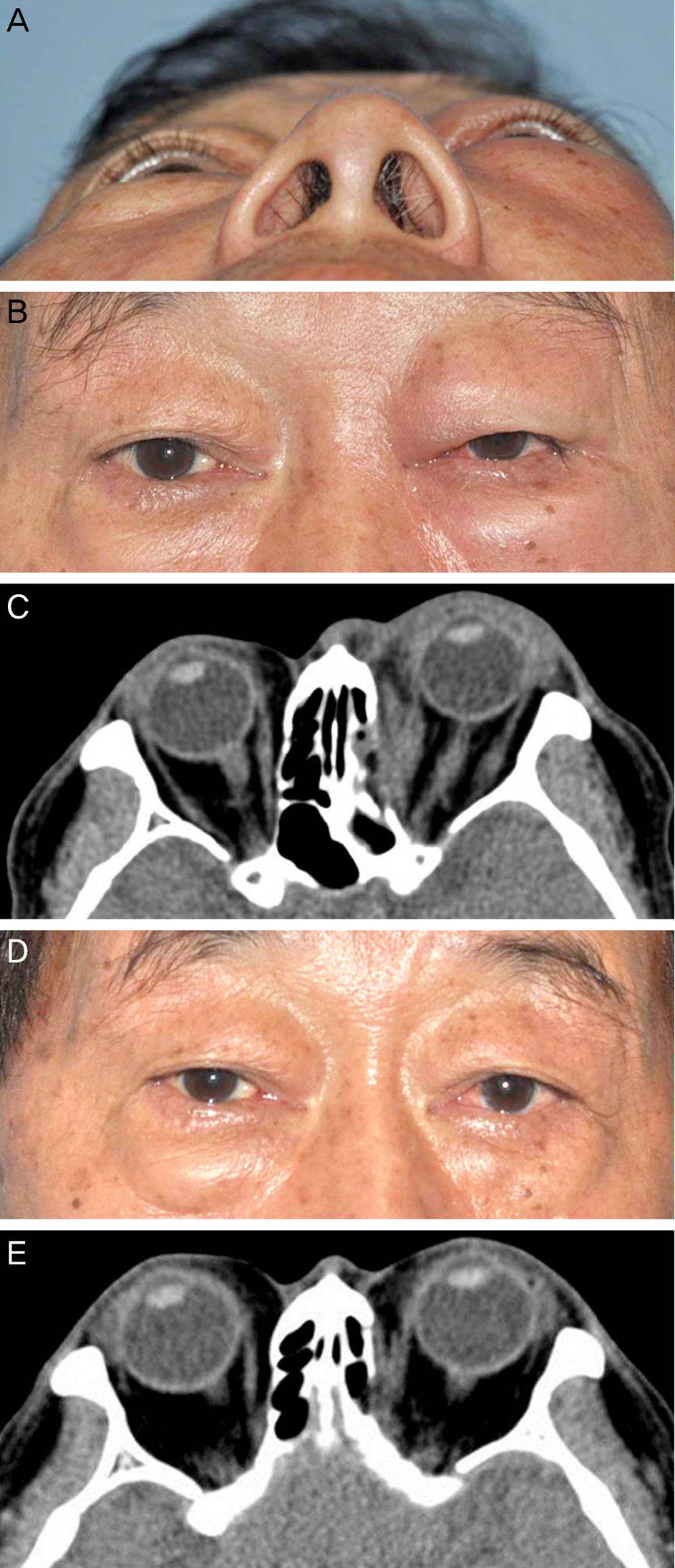
Among the 86 patients, 37 were treated with Medpor(R) and 49 with Mesh plate(R). There was no statistically significant difference in limitation of motion or diplopia score between the 2 groups at postoperative 6 months (Fisher's exact test, p = 0.192, p = 0.128, respectively). Mean postoperative exophthalmometry differences between the eyes were 0.49 +/- 1.04 mm and 0.37 +/- 0.62 mm in Medpor(R) and Mesh plate(R) groups, respectively, showing no statistically significant difference (independent t-test, p = 0.512). Postoperative complications such as inflammation or implant malposition were observed only in 3 patients in the Medpor(R) group.
CONCLUSIONS
No difference was observed between Medpor(R) and Mesh plate(R) in terms of surgical results during the postoperative 6 month period after reconstruction of orbital medial wall fracture. However, postoperative complications were observed in 3 patients in the Medpor(R) group.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Lim HS, Kook KH. Results of reconstruction of orbital wall fracture with bioresorbable plate. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:1761–7.
Article2. Jeon C, Shin JH, Woo KI, Kim YD. Porous polyethylene/titanium implants in the treatment of large orbital fractures. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:1133–40.
Article3. Chi MJ, Jeung JW, Lee JH. Reconstruction of orbital wall fracture with resorbable copolymer mesh. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006; 47:1021–30.4. Avashia YJ, Sastry A, Fan KL, et al. Materials used for reconstruction after orbital floor fracture. The Journal of Craniofacial Surgery. 2012; 23:1991–7.
Article5. Han DH, Chi M. Comparison of the outcomes of blowout fracture repair according to the orbital implant. The Journal of Craniofacial Surgery. 2011; 22:1422–5.
Article6. Dietz A, Ziegler CM, Dacho A, et al. Effectiveness of a new perforated 0.15 mm poly-p-dioxanon-foil versus titanium-dynamic mesh in reconstruction of the orbital floor. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2001; 29:82–8.
Article7. Al-Sukhun J, Lindqvist C. A comparative study of 2 implants used to repair inferior orbital wall bony defects: autogenous bone graft versus bioresorbable poly-L/DL-Lactide [P(L/DL)LA 70/30] plate. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006; 64:1038–48.
Article8. Kim YJ, Choi SH, Jun YJ, Seo BC. Open reduction in trapdoor-type blowout fractures using absorbable mesh plates. The Journal of Craniofacial Surgery. 2011; 22:2264–7.
Article9. Hwang K, Kim DH. Comparison of the supporting strength of a poly-L-Lactic acid sheet and porous polyethylene (Medpor) for the reconstruction of orbital floor fractures. The Journal of Craniofacial Surgery. 2010; 21:847–53.
Article10. Kontio RK, Laine P, Salo A, et al. Reconstruction of internal orbital wall fracture with iliac crest free bone graft: clinical, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging follow-up study. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006; 118:1365–74.
Article11. Kraus M, Gatot A, Fliss DM. Repair of traumatic inferior orbital wall defects with nasoseptal cartilage. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2001; 59:1397–400.
Article12. Krishnan V, Johnson JV. Orbital floor reconstruction with autogenous mandibular symphyseal bone grafts. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1997; 55:327–30.
Article13. Mauriello JA Jr, Wasserman B, Kraut R. Use of Vicryl (polyglactin- 910) mesh implant for repair of orbital floor fracture causing diplopia: a study of 28 patients over 5 years. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 1993; 9:191–5.14. Burres SA, Cohn AM, Mathog RH. Repair of orbital blowout fracture with Marlex mesh and Gelfilm. Layngoscope. 1981; 91:1881–6.15. Iizuka T, Mikkonen P, Paukku P, Lindqvist C. Reconstruction of orbital floor with polydioxanone plate. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1991; 20:83–7.16. Wellisz T. Clinical experience with the Medpor porous polyethylene implant. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 1993; 17:339–44.
Article17. Kim BJ, Kim YD. Porous polyethylene (Medpor®) channel implants in orbital fracture repairs. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2002; 43:1238–49.18. Choi JC, Bstandig S, Iwamoto MA, et al. Porous polyethylene sheet implant with barrier surface: a rabbit study. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 1998; 14:32–6.19. Rubin PA, Popham JK, Bilyk JR, Shore JW. Comparison of fibrovascular ingrowth into hydroxyapatite and porous polyethylene orbital implants. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 1994; 10:96–103.
Article20. Uygur S, Cukurluoglu O, Ozmen S, et al. Resorbable mesh plate in the treatment of blow-out fracture might cause gaze restriction. The Journal of Craniofacial Surgery. 2009; 20:71–2.
Article21. Tuncer S, Yavuzer R, Kandal S, et al. Reconstruction of traumatic orbital floor fractures with resorbable mesh plate. The Journal of Craniofacial Surgery. 2007; 18:598–605.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Two-Year Follow-up on the Use of Absorbable Mesh Plates in the Treatment of Medial Orbital Wall Fractures
- Reduction of Trapdoor Type Orbital Floor Fracture with Absorbable Mesh
- Comparison of Absorbable Mesh Plate versus Titanium-Dynamic Mesh Plate in Reconstruction of Blow-Out Fracture: An Analysis of Long-Term Outcomes
- A Case of Delayed Orbital Cellulitis after Orbital Wall Fracture Repair Using Absorbable Implant
- Orbital Wall Reconstruction with Osteoconductive Unsintered Hydroxyapatite/Poly L-Lactide